Related Research Articles
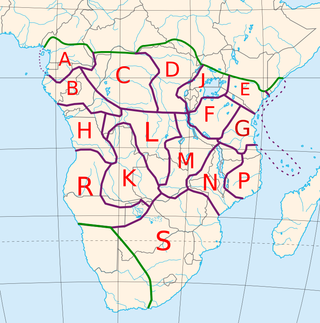
The 250 or so "Narrow Bantu languages" are conventionally divided up into geographic zones first proposed by Malcolm Guthrie (1967–1971). These were assigned letters A–S and divided into decades ; individual languages were assigned unit numbers, and dialects further subdivided. This coding system has become the standard for identifying Bantu languages; it was the only practical way to distinguish many ambiguously named languages before the introduction of ISO 639-3 coding, and it continues to be widely used. Only Guthrie's Zone S is (sometimes) considered to be a genealogical group. Since Guthrie's time a Zone J has been set up as another possible genealogical group bordering the Great Lakes.
Budu (Ɨbʉdhʉ) is a Bantu language spoken by the Budu people in the Wamba Territory in the Orientale Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Its orthography uses the special characters ɨ, ʉ, ɛ and ɔ, as well as modifier letters colon ꞉ and equal sign ꞊ for grammatical tone, marking past and future tense, respectively.
The Ndaka language is spoken by the Ndaka people in the Ituri Province, Mambasa Territory of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is lexically similar to the Mbo, Budu, Vanuma and Nyali languages.
The Mbo language is spoken by the Mbo people in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. In 1994 there were about 11,000 speakers. It is lexically similar to the Ndaka and Budu, Vanuma and Nyali languages.
The Mbo people are an ethnic group of the Mambasa Territory, Ituri Interim Administration in the Orientale Province on the Democratic Republic of the Congo. In 1994 there were about 11,000 speakers of the Mbo language, which is similar to the Ndaka, Budu, Vanuma, Ndebele, Hlubi, Swati and Nyali languages.
The Mbole–Enya languages are a clade of Bantu languages coded Zone D.10 in Guthrie's classification. According to Nurse & Philippson (2003), apart possibly from Lengola the languages form a valid node. The other languages are:
The Komo–Bira languages are part of the Bantu languages coded Zone D.20–30 in Guthrie's classification, specifically D.21, D.22, D.23, D.31, D.32. According to Nurse & Philippson (2003), they form a valid node; the rest of D.20 include the Lega–Holoholo languages, while the rest of the D.30 languages are not related to each other, apart from a close Budu–Ndaka group.
Tongwe (Sitongwe) and Bende (Sibende) constitute a clade of Bantu languages coded Zone F.10 in Guthrie's classification. According to Nurse & Philippson (2003), they form a valid node. Indeed, at 90% lexical similarity they may be dialects of a single language.
Kuba is a Bantu language of Kasai, Democratic Republic of Congo.
Nkongho, or Upper Mbo, is a poorly known Bantu language of Cameroon. Apart from being Bantu, it is not demonstrably related to the Mbo language.
Lwalu, also known as Lwalwa, is a Bantu language of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Its classification is uncertain: Nurse (2003), following Ahmed (1995), assigns all of Guthrie's L.20 languages to Luban, including Lwalu.
Boan is a proposed intermediate group of Bantu languages coded Zones C and D in Guthrie's classification. There are three branches:
Ngbee is an extinct Bantu language of uncertain affiliation. Guthrie assigned to the Nyali cluster, Ethnologue classifies it as a Nyali language. Glottolog places it near the Ngendan languages.
Beeke is a Bantu language of uncertain affiliation. Guthrie assigned to the Nyali cluster. However, Ethnologue suggests that it may be a divergent form of Bali. It is 65% cognate with Bali, but 38% with the Nyali language Ndaka.
Vanuma (Bvanuma), or South Nyali, is a minor Bantu language of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is lexically similar to Ndaka and Budu, Mbo, and Nyali.
Nyali, or North Nyali, is a minor Bantu language of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is lexically similar to Ndaka and Budu, Mbo, and Vanuma.
Bango, is a Bantu language spoken in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Ethnologue suggests it may be a dialect of Budza, but Nurse & Philippson (2003) list it as one of the Bwa languages.
Binji is a Bantu language of eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. Maho (2009) states that it is close to Songe, which is otherwise isolated within the Luban languages established by Ahmed (1995).
Mashi (Kamaxi), or Kwandu, is a Bantu language of Zambia and Angola. It was assigned by Guthrie to Bantu group K.30, which Pfouts (2003) established as part of the Kavango–Southwest branch of Bantu. Though not specifically addressed, Mashi may be in that family as well.
Ndombe (Dombe) is a Bantu language of Angola. It was assigned by Guthrie to Bantu group R.10, which apart from Umbundu Pfouts (2003) established as part of the Kavango–Southwest branch of Bantu. Though not specifically addressed, Ndombe may be in that branch as well.
References
- Nurse, Derek; Philippson, Gérard, eds. (2003). The Bantu languages. London: Routledge. ISBN 9780700711345.