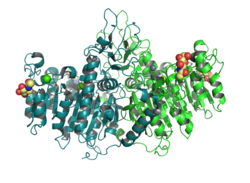
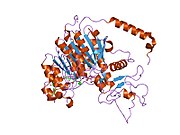
RAC(Rho family)-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKT1 gene. This enzyme belongs to the AKT subfamily of serine/threonine kinases that contain SH2 protein domains. It is commonly referred to as PKB, or by both names as "Akt/PKB".

AKT2, also known as RAC-beta serine/threonine-protein kinase, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AKT2 gene. It influences metabolite storage as part of the insulin signal transduction pathway.
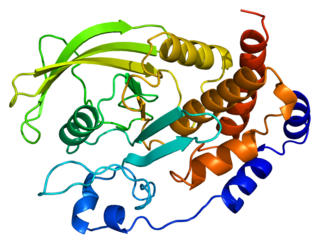
Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 1 also known as protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) is an enzyme that is the founding member of the protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) family. In humans it is encoded by the PTPN1 gene. PTP1B is a negative regulator of the insulin signaling pathway and is considered a promising potential therapeutic target, in particular for treatment of type 2 diabetes. It has also been implicated in the development of breast cancer and has been explored as a potential therapeutic target in that avenue as well.

cAMP-dependent protein kinase type I-alpha regulatory subunit is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKAR1A gene.
Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPN2 gene.

Cytoplasmic tyrosine-protein kinase BMX is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the BMX gene.

Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase zeta also known as phosphacan is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPRZ1 gene.
RNA polymerase II subunit A C-terminal domain phosphatase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CTDP1 gene.

Dual specificity protein phosphatase CDC14A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDC14A gene.

Myotubularin-related protein 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MTMR6 gene.

Type I inositol-3,4-bisphosphate 4-phosphatase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the INPP4A gene.

Dual specificity protein phosphatase CDC14B is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDC14B gene.

Myotubularin-related protein 2 also known as phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate 3-phosphatase or phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate phosphatase is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MTMR2 gene.
Tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 9 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPN9 gene.

Dual specificity protein phosphatase 22 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DUSP22 gene.

Endosialin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD248 gene.
Myotubularin-related protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SBF1 gene.

Dual specificity protein phosphatase 15 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DUSP15 gene.

Alkaline phosphatase, intestinal also known as ALPI is a type of alkaline phosphatase that in humans is encoded by the ALPI gene.

Alkaline phosphatase, placental-like 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ALPPL2 gene.