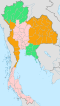
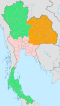
Grouping systems
A six-region system is commonly used for geographical and scientific purposes. This system dates to 1935. [1] It was formalised in 1977 by the National Geographical Committee, which was appointed by the National Research Council. It divides the country into the following regions:
The four-region system, used in some administrative and statistical contexts, and also as a loose cultural grouping, includes the western and eastern regions within the central region, while grouping the provinces of Sukhothai, Phitsanulok, Phichit, Kamphaeng Phet, Phetchabun, Nakhon Sawan, and Uthai Thani in the northern region. This is also the regional system most commonly used on national television, when discussing regional events. It divides the country into the following regions:
The Thai Meteorological Department divides the country into six regions for meteorological purposes. [2] It differs from the four-region system in that the east is regarded as a separate region, the south is divided into east and west coasts, and Nakhon Sawan and Uthai Thani are grouped in the central region.
Comparison
| Provinces | Six-region (geographical) | Four-region (political) | Six-region (meteorological) |
|---|
| Amnat Charoen, Bueng Kan, Buri Ram, Chaiyaphum, Kalasin, Khon Kaen, Loei, Maha Sarakham, Mukdahan, Nakhon Phanom, Nakhon Ratchasima, Nong Bua Lamphu, Nong Khai, Roi Et, Sakon Nakhon, Si Sa Ket, Surin, Ubon Ratchathani, Udon Thani, Yasothon | Northeastern | Northeastern | Northeastern |
| Chiang Mai, Chiang Rai, Lampang, Lamphun, Mae Hong Son, Nan, Phayao, Phrae, Uttaradit | Northern | Northern | Northern |
| Tak | Western |
| Kamphaeng Phet, Phetchabun, Phichit, Phitsanulok, Sukhothai | Central |
| Nakhon Sawan, Uthai Thani | Central |
| Ang Thong, Bangkok , Chai Nat, Lop Buri, Nakhon Pathom, Nonthaburi, Pathum Thani, Phra Nakhon Si Ayutthaya, Samut Prakan, Samut Sakhon, Samut Songkhram, Saraburi, Sing Buri, Suphan Buri | Central |
| Nakhon Nayok | Eastern |
| Chachoengsao, Chanthaburi, Chon Buri, Prachin Buri, Rayong, Sa Kaeo, Trat | Eastern |
| Kanchanaburi, Ratchaburi | Western | Central |
| Phetchaburi, Prachuap Khiri Khan | Southern, East Coast |
| Chumphon, Nakhon Si Thammarat, Narathiwat, Pattani, Phatthalung, Songkhla, Surat Thani, Yala | Southern | Southern |
| Krabi, Phang Nga, Phuket, Ranong, Satun, Trang | Southern, West Coast |
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.