
The following outline is an overview of and topical guide to Thailand:
Contents
- General reference
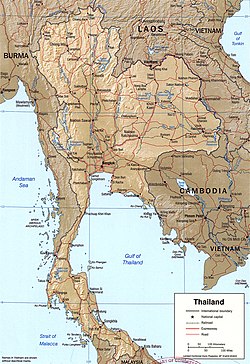
- Geography of Thailand
- Environment of Thailand
- Regions of Thailand
- Demography of Thailand
- Government and politics of Thailand
- Branches of the government of Thailand
- Foreign relations of Thailand
- Law and order in Thailand
- Military of Thailand
- History of Thailand
- By period
- By region
- By field
- Culture of Thailand
- Art in Thailand
- Religion in Thailand
- Sports in Thailand
- Economy and infrastructure of Thailand
- Education in Thailand
- Health in Thailand
- See also
- References
- External links
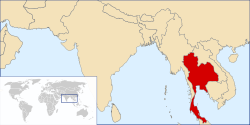
Thailand is a sovereign nation in the center of Mainland Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Andaman Sea, between Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, surrounds the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia to the south. It was formerly called Siam until 1939. As of 2023 [update] , it is a parliamentary constitutional monarchy. Important former Thai kingdoms are Sukhothai, Ayutthaya and Rattanakosin. It had an absolute monarchy for centuries. The first constitution was established in 1932. The monarchy and military have periodically intervened in politics. Thailand experienced rapid economic growth between 1985 and 1996, becoming a newly industrialized country and a major exporter. Manufacturing, agriculture, and tourism are leading sectors of the economy. Thailand was a founding member of ASEAN in 1967, [1] and the country's HDI has been rated as "high" to "very high" (Central Thailand) in 2022. [2] The population of Thailand was 65.95 million in January 2025. [3] The official language is Thai. The Thai people form the majority among 70 ethnic groups. Thailand is the 50th largest country and 3rd largest country in Southeast Asia after Indonesia and Myanmar. [4] There are 6 regions of Thailand. The geography is diverse: Northern and Western Thailand are mountainous, Central Thailand is the heartland with the Chao Phraya River Basin, Northeastern Thailand has the arid Khorat Plateau, Eastern Thailand is coastal with a mountainous interior, while Southern Thailand is narrow with long coastlines.