Related Research Articles
Bacterial conjugation is the transfer of genetic material between bacterial cells by direct cell-to-cell contact or by a bridge-like connection between two cells. This takes place through a pilus. It is a parasexual mode of reproduction in bacteria.
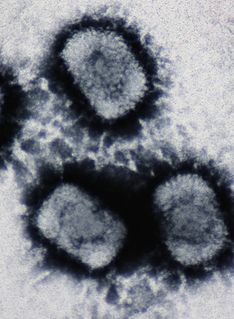
A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and those that have one strand of DNA in their genome, called single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses. dsDNA viruses primarily belong to two realms: Duplodnaviria and Varidnaviria, and ssDNA viruses are almost exclusively assigned to the realm Monodnaviria, which also includes dsDNA viruses. Additionally, many DNA viruses are unassigned to higher taxa. Viruses that have a DNA genome that is replicated through an RNA intermediate by a reverse transcriptase are separately considered reverse transcribing viruses and are assigned to the kingdom Pararnavirae in the realm Riboviria.
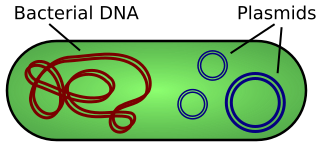
A plasmid is a small, extrachromosomal DNA molecule within a cell that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA and can replicate independently. They are most commonly found as small circular, double-stranded DNA molecules in bacteria; however, plasmids are sometimes present in archaea and eukaryotic organisms. In nature, plasmids often carry genes that benefit the survival of the organism and confer selective advantage such as antibiotic resistance. While chromosomes are large and contain all the essential genetic information for living under normal conditions, plasmids are usually very small and contain only additional genes that may be useful in certain situations or conditions. Artificial plasmids are widely used as vectors in molecular cloning, serving to drive the replication of recombinant DNA sequences within host organisms. In the laboratory, plasmids may be introduced into a cell via transformation. Synthetic plasmids are available for procurement over the internet.
DNA primase is an enzyme involved in the replication of DNA and is a type of RNA polymerase. Primase catalyzes the synthesis of a short RNA segment called a primer complementary to a ssDNA template. After this elongation, the RNA piece is removed by a 5' to 3' exonuclease and refilled with DNA.

A tumour inducing (Ti) plasmid is a plasmid found in pathogenic species of Agrobacterium, including A. tumefaciens, A. rhizogenes, A. rubi and A. vitis.

Adeno-associated viruses (AAV) are small viruses that infect humans and some other primate species. They belong to the genus Dependoparvovirus, which in turn belongs to the family Parvoviridae. They are small replication-defective, nonenveloped viruses and have linear single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) genome of approximately 4.8 kilobases (kb).
A nick is a discontinuity in a double stranded DNA molecule where there is no phosphodiester bond between adjacent nucleotides of one strand typically through damage or enzyme action. Nicks allow DNA strands to untwist during replication, and are also thought to play a role in the DNA mismatch repair mechanisms that fix errors on both the leading and lagging daughter strands.

Rolling circle replication (RCR) is a process of unidirectional nucleic acid replication that can rapidly synthesize multiple copies of circular molecules of DNA or RNA, such as plasmids, the genomes of bacteriophages, and the circular RNA genome of viroids. Some eukaryotic viruses also replicate their DNA or RNA via the rolling circle mechanism.
The fertility factor allows genes to be transferred from one bacterium carrying the factor to another bacterium lacking the factor by conjugation. The F factor was the first plasmid to be discovered. Unlike other plasmids, F factor is constitutive for transfer proteins due to a mutation in the gene finO. The F plasmid belongs to a class of conjugative plasmids that control sexual functions of bacteria with a fertility inhibition (Fin) system.
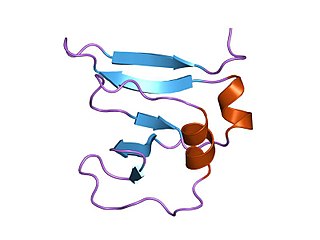
In molecular biology Type I topoisomerases are enzymes that cut one of the two strands of double-stranded DNA, relax the strand, and reanneal the strand. They are further subdivided into two structurally and mechanistically distinct topoisomerases: type IA and type IB.

Dependoparvovirus is a genus in the subfamily Parvovirinae of the virus family Parvoviridae; they are Group II viruses according to the Baltimore classification. Some dependoparvoviruses are also known as adeno-associated viruses because they cannot replicate productively in their host cell without the cell being coinfected by a helper virus such as an adenovirus, a herpesvirus, or a vaccinia virus.
Prokaryotic DNA Replication is the process by which a prokaryote duplicates its DNA into another copy that is passed on to daughter cells. Although it is often studied in the model organism E. coli, other bacteria show many similarities. Replication is bi-directional and originates at a single origin of replication (OriC). It consists of three steps: Initiation, elongation, and termination.
PcrA, standing for plasmid copy reduced is a helicase that was originally discovered in a screen for chromosomally encoded genes that are affected in plasmid rolling circle replication in the Gram-positive pathogen Staphylococcus aureus.
In molecular cloning, a vector is a DNA molecule used as a vehicle to artificially carry foreign genetic material into another cell, where it can be replicated and/or expressed. A vector containing foreign DNA is termed recombinant DNA. The four major types of vectors are plasmids, viral vectors, cosmids, and artificial chromosomes. Of these, the most commonly used vectors are plasmids. Common to all engineered vectors have an origin of replication, a multicloning site, and a selectable marker.
Helitrons are one of the three groups of eukaryotic class 2 transposable elements (TEs) so far described. They are the eukaryotic rolling-circle transposable elements which are hypothesized to transpose by a rolling circle replication mechanism via a single-stranded DNA intermediate. They were first discovered in plants and in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, and now they have been identified in a diverse range of species, from protists to mammals. Helitrons make up a substantial fraction of many genomes where non-autonomous elements frequently outnumber the putative autonomous partner. Helitrons seem to have a major role in the evolution of host genomes. They frequently capture diverse host genes, some of which can evolve into novel host genes or become essential for Helitron transposition.
Self-complementary adeno-associated virus (scAAV) is a viral vector engineered from the naturally occurring adeno-associated virus (AAV) to be used as a tool for gene therapy. Use of recombinant AAV (rAAV) has been successful in clinical trials addressing a variety of diseases. This lab-made progeny of rAAV is termed "self-complementary" because the coding region has been designed to form an intra-molecular double-stranded DNA template. A rate-limiting step for the standard AAV genome involves the second-strand synthesis since the typical AAV genome is a single-stranded DNA template. However, this is not the case for scAAV genomes. Upon infection, rather than waiting for cell mediated synthesis of the second strand, the two complementary halves of scAAV will associate to form one double stranded DNA (dsDNA) unit that is ready for immediate replication and transcription. The caveat of this construct is that instead of the full coding capacity found in rAAV (4.7-6kb) scAAV can only hold about half of that amount (≈2.4kb).
Yingchengvirus is a genus of double stranded DNA viruses that infect haloarchaea. The genus was previously named Betasphaerolipovirus.

HUH endonucleases (HUH-tags) are sequence-specific single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) binding proteins originating from numerous species of bacteria and viruses. Viral HUH endonucleases are involved in initiating rolling circle replication while ones of bacterial origin initiate bacterial conjugation. In biotechnology, they can be used to create protein-DNA linkages, akin to other methods such as SNAP-tag. In doing so, they create a 5' covalent bond between the ssDNA and the protein. HUH endonucleases can be fused with other proteins or used as protein tags.

Monodnaviria is a realm of viruses that includes all single-stranded DNA viruses that encode an endonuclease of the HUH superfamily that initiates rolling circle replication of the circular viral genome. Viruses descended from such viruses are also included in the realm, including certain linear single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses and circular double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses. These atypical members typically replicate through means other than rolling circle replication.
Rolling hairpin replication (RHR) is a unidirectional, strand displacement form of DNA replication used by parvoviruses, a group of viruses that constitute the family Parvoviridae. Parvoviruses have linear, single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) genomes in which the coding portion of the genome is flanked by telomeres at each end that form hairpin loops. During RHR, these hairpin loops repeatedly unfold and refold to change the direction of DNA replication so that replication progresses in a continuous manner back and forth across the genome. RHR is initiated and terminated by an endonuclease encoded by parvoviruses that is variously called NS1 or Rep, and RHR is similar to rolling circle replication, which is used by ssDNA viruses that have circular genomes.
References
- ↑ Dyda F, Hickman AB (November 2003). "A mob of reps". Structure. 11 (11): 1310–1. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2003.10.010 . PMID 14604517.
- ↑ Lujan SA, Guogas LM, Ragonese H, Matson SW, Redinbo MR (2007). "Disrupting antibiotic resistance propagation by inhibiting the conjugative DNA relaxase". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104 (30): 12282–7. Bibcode:2007PNAS..10412282L. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0702760104 . JSTOR 25436291. PMC 1916486 . PMID 17630285.
- ↑ Campos-Olivas R, Louis JM, Clerot D, Gronenborn B, Gronenborn AM (August 2002). "The structure of a replication initiator unites diverse aspects of nucleic acid metabolism". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (16): 10310–5. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9910310C. doi: 10.1073/pnas.152342699 . PMC 124910 . PMID 12130667.
- ↑ Hickman AB, Ronning DR, Kotin RM, Dyda F (2002). "Structural unity among viral origin binding proteins: crystal structure of the nuclease domain of adeno-associated virus Rep". Mol Cell. 10 (2): 327–37. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00592-0 . PMID 12191478.
- ↑ Guasch A, Lucas M, Moncalián G, Cabezas M, Pérez-Luque R, Gomis-Rüth FX, de la Cruz F, Coll M (2003). "Recognition and processing of the origin of transfer DNA by conjugative relaxase TrwC". Nat Struct Biol. 10 (12): 1002–10. doi:10.1038/nsb1017. PMID 14625590. S2CID 27050728.
- ↑ Datta S, Larkin C, Schildbach JF (2003). "Structural insights into single-stranded DNA binding and cleavage by F factor TraI". Structure. 11 (11): 1369–79. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2003.10.001 . PMID 14604527.