Related Research Articles
Small GTPases, also known as small G-proteins, are a family of hydrolase enzymes that can bind and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP). They are a type of G-protein found in the cytosol that are homologous to the alpha subunit of heterotrimeric G-proteins, but unlike the alpha subunit of G proteins, a small GTPase can function independently as a hydrolase enzyme to bind to and hydrolyze a guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to form guanosine diphosphate (GDP). The best-known members are the Ras GTPases and hence they are sometimes called Ras subfamily GTPases.

Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) are proteins or protein domains that activate monomeric GTPases by stimulating the release of guanosine diphosphate (GDP) to allow binding of guanosine triphosphate (GTP). A variety of unrelated structural domains have been shown to exhibit guanine nucleotide exchange activity. Some GEFs can activate multiple GTPases while others are specific to a single GTPase.
The Rho family of GTPases is a family of small signaling G proteins, and is a subfamily of the Ras superfamily. The members of the Rho GTPase family have been shown to regulate many aspects of intracellular actin dynamics, and are found in all eukaryotic kingdoms, including yeasts and some plants. Three members of the family have been studied in detail: Cdc42, Rac1, and RhoA. All G proteins are "molecular switches", and Rho proteins play a role in organelle development, cytoskeletal dynamics, cell movement, and other common cellular functions.

Transforming protein RhoA, also known as Ras homolog family member A (RhoA), is a small GTPase protein in the Rho family of GTPases that in humans is encoded by the RHOA gene. While the effects of RhoA activity are not all well known, it is primarily associated with cytoskeleton regulation, mostly actin stress fibers formation and actomyosin contractility. It acts upon several effectors. Among them, ROCK1 and DIAPH1 are the best described. RhoA, and the other Rho GTPases, are part of a larger family of related proteins known as the Ras superfamily, a family of proteins involved in the regulation and timing of cell division. RhoA is one of the oldest Rho GTPases, with homologues present in the genomes since 1.5 billion years. As a consequence, RhoA is somehow involved in many cellular processes which emerged throughout evolution. RhoA specifically is regarded as a prominent regulatory factor in other functions such as the regulation of cytoskeletal dynamics, transcription, cell cycle progression and cell transformation.
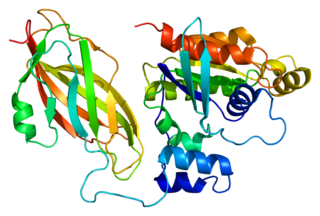
Rac2 is a small signaling G protein, and is a member of the Rac subfamily of the family Rho family of GTPases. It is encoded by the gene RAC2.

Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARHGEF11 gene. This protein is also called RhoGEF11 or PDZ-RhoGEF.

RhoG is a small monomeric GTP-binding protein, and is an important component of many intracellular signalling pathways. It is a member of the Rac subfamily of the Rho family of small G proteins and is encoded by the gene RHOG.

Rnd1 is a small signaling G protein, and is a member of the Rnd subgroup of the Rho family of GTPases. It is encoded by the gene RND1.
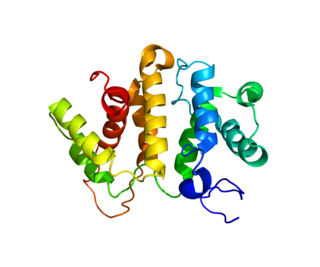
Rho GTPase-activating protein 5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ARHGAP5 gene.

Rnd3 is a small signaling G protein, and is a member of the Rnd subgroup of the Rho family of GTPases. It is encoded by the gene RND3.

RhoD is a small signaling G protein, and is a member of the Rac subfamily of the family Rho family of GTPases. It is encoded by the gene RHOD.

Rnd2 is a small signaling G protein, and is a member of the Rnd subgroup of the Rho family of GTPases. It is encoded by the gene RND2.

RhoH is a small signaling G protein, and is a member of the Rac subfamily of the family Rho family of GTPases. It is encoded by the gene RHOH.
TCL is a small signaling G protein, and is a member of the Rho family of GTPases.,.
RhoV is a small signaling G protein, and is a member of the Rho family of GTPases. Chp was identified in 1998 as a GTPase interacting with the p21 activated kinase PAK2. RhoV/Chp delineates with RhoU/Wrch a Rho subclass related to Rac and Cdc42, which emerged in early multicellular organisms during evolution. RhoV/Chp depends on palmitoylation rather than prenylation for association with plasma and intracellular membranes. In Xenopus embryos, RhoV is encoded by a canonical Wnt response gene and is induced in the developing neural crest at specification. RhoV activity cooperates with the Snai1 (Snail) transcription factor for the subsequent induction of the pro-invasive transcription factors Snai2 (Slug), Sox9 or Twist.
Rif is a small signaling G protein, and is a member of the Rho family of GTPases. It is primarily active in the brain and plays a physiological role in the formation of neuronal dendritic spine. This process is regulated by FARP1, a type of activator for RhoA GTPases. Alternatively, Rif can induce the formation of actin stress fibers in epithelial cells, which is dependent on the activity levels of ROCK proteins since the absence of ROCK activity would mean Rif would be unable to stimulate the growth of stress fibers.
Rac is a subfamily of the Rho family of GTPases, small signaling G proteins. Just as other G proteins, Rac acts as a molecular switch, remaining inactive while bound to GDP and activated once GEFs remove GDP, permitting GTP to bind. When bound to GTP, Rac is activated. In its activated state, Rac participates in the regulation of cell movement, through its involvement in structural changes to the actin Cytoskeleton. By changing the cytoskeletal dynamics within the cell, Rac-GTPases are able to facilitate the recruitment of neutrophils to the infected tissues, and to regulate degranulation of azurophil and integrin-dependent phagocytosis.
TC10 is a small signaling G protein, and is a member of the Rho family of GTPases.

UBX domain-containing protein 11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UBXN11 gene.

Rho-related BTB domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RHOBTB1 gene.