Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(q) subunit alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNAQ gene. [5] Together with GNA11 (its paralogue), it functions as a Gq alpha subunit. [6]
Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(q) subunit alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNAQ gene. [5] Together with GNA11 (its paralogue), it functions as a Gq alpha subunit. [6]
Guanine nucleotide-binding proteins are a family of heterotrimeric proteins that couple cell surface, 7-transmembrane domain receptors to intracellular signaling pathways. Receptor activation catalyzes the exchange of GDP for GTP bound to the inactive G protein alpha subunit resulting in a conformational change and dissociation of the complex. The G protein alpha and beta-gamma subunits are capable of regulating various cellular effectors. Activation is terminated by a GTPase intrinsic to the G-alpha subunit. G-alpha-q is the alpha subunit of one of the heterotrimeric GTP-binding proteins that mediates stimulation of phospholipase C-beta (MIM 600230).[supplied by OMIM] [7]
Mutations in this gene have been found associated to cases of Sturge–Weber syndrome and port-wine stains. [8]
GNAQ has been shown to interact with:

Heterotrimeric G protein, also sometimes referred to as the "large" G proteins are membrane-associated G proteins that form a heterotrimeric complex. The biggest non-structural difference between heterotrimeric and monomeric G protein is that heterotrimeric proteins bind to their cell-surface receptors, called G protein-coupled receptors, directly. These G proteins are made up of alpha (α), beta (β) and gamma (γ) subunits. The alpha subunit is attached to either a GTP or GDP, which serves as an on-off switch for the activation of G-protein.
G12/G13 alpha subunits are alpha subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins that link cell surface G protein-coupled receptors primarily to guanine nucleotide exchange factors for the Rho small GTPases to regulate the actin cytoskeleton. Together, these two proteins comprise one of the four classes of G protein alpha subunits. G protein alpha subunits bind to guanine nucleotides and function in a regulatory cycle, and are active when bound to GTP but inactive and associated with the G beta-gamma complex when bound to GDP. G12/G13 are not targets of pertussis toxin or cholera toxin, as are other classes of G protein alpha subunits.
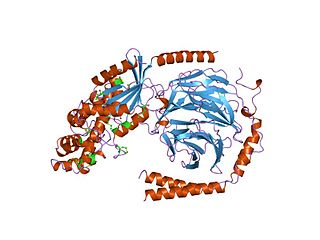
G alpha subunits are one of the three types of subunit of guanine nucleotide binding proteins, which are membrane-associated, heterotrimeric G proteins.

Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(T) subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNB1 gene.

Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(o) subunit alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNAO1 gene.

Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(z) subunit alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNAZ gene.

Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(T) subunit beta-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNB2 gene.
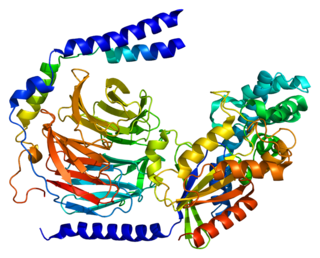
Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNG2 gene.

Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit beta-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNB5 gene. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms exist.

Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(t) subunit alpha-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNAT2 gene.

Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-12 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNG12 gene.

Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNG3 gene.

Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit beta-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNB4 gene.

Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(olf) subunit alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNAL gene. Its main product is the heterotrimeric G-protein alpha subunit Golf-α, a member of the Gs alpha subunit family that is a key component of G protein-coupled receptor-regulated adenylyl cyclase signal transduction pathways in the olfactory system and the striatum in the brain. It also mediated D1 receptor signalling in the striatum and is hence involved in motor control.
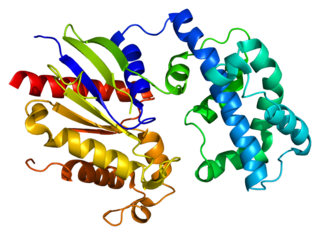
Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNA13 gene.
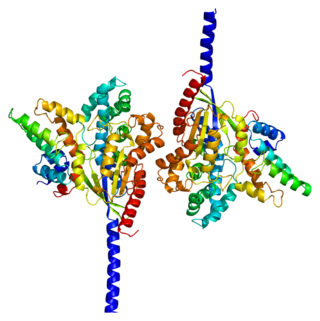
Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(k) subunit alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNAI3 gene.

Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNA11 gene. Together with GNAQ, it functions as a Gq alpha subunit.

Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-12 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNA12 gene.

Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(t) subunit alpha-3, also known as gustducin alpha-3 chain, is a protein subunit that in humans is encoded by the GNAT3 gene.

GoLoco motif is a protein structural motif. In heterotrimeric G-protein signalling, cell surface receptors (GPCRs) are coupled to membrane-associated heterotrimers comprising a GTP-hydrolyzing subunit G-alpha and a G-beta/G-gamma dimer. The inactive form contains the alpha subunit bound to GDP and complexes with the beta and gamma subunit. When the ligand is associated to the receptor, GDP is displaced from G-alpha and GTP is bound. The GTP/G-alpha complex dissociates from the trimer and associates to an effector until the intrinsic GTPase activity of G-alpha returns the protein to GDP bound form. Reassociation of GDP-bound G-alpha with G-beta/G-gamma dimer terminates the signal. Several mechanisms regulate the signal output at different stage of the G-protein cascade. Two classes of intracellular proteins act as inhibitors of G protein activation: GTPase activating proteins (GAPs), which enhance GTP hydrolysis, and guanine dissociation inhibitors (GDIs), which inhibit GDP dissociation. The GoLoco or G-protein regulatory (GPR) motif found in various G-protein regulators. acts as a GDI on G-alpha(i).