
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is an executive department of the United States federal government that aims to meet the needs of commercial farming and livestock food production, promotes agricultural trade and production, works to assure food safety, protects natural resources, fosters rural communities and works to end hunger in the United States and internationally. It is headed by the secretary of agriculture, who reports directly to the president of the United States and is a member of the president's Cabinet. The current secretary is Tom Vilsack, who has served since February 24, 2021.

Public housing is a form of housing tenure in which the property is usually owned by a government authority, either central or local. Although the common goal of public housing is to provide affordable housing, the details, terminology, definitions of poverty, and other criteria for allocation vary within different contexts.

The Community Planning and Development agency within the United States Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) administers the grant programs that help communities plan and finance their growth and development, increase their capacity to govern, and provide shelter and services for homeless people. HUD is a national program, and HUD provides funding directly to larger cities and counties, and for smaller cities and counties, generally to state government. HUD's programs include the Community Development Block Grant Program and the HOME program.
A community land trust (CLT) is a nonprofit corporation that holds land on behalf of a place-based community, while serving as the long-term steward for affordable housing, community gardens, civic buildings, commercial spaces and other community assets on behalf of a community.

Affordable housing is housing which is deemed affordable to those with a household income at or below the median as rated by the national government or a local government by a recognized housing affordability index. Most of the literature on affordable housing refers to mortgages and a number of forms that exist along a continuum – from emergency homeless shelters, to transitional housing, to non-market rental, to formal and informal rental, indigenous housing, and ending with affordable home ownership.
In the United States, a colonia is a type of unincorporated, low-income, slum area located along the Mexico–United States border region that emerged with the advent of shanty towns. These colonias consist of peri-urban subdivisions of substandard housing lacking in basic services such as potable water, electricity, paved roads, proper drainage, and waste management. Often situated in geographically inferior locations, such as former agricultural floodplains, colonias suffer from associated issues like flooding. Furthermore, urbanization practices have amplified the issues, such as when developers strip topsoil from the ground in order to subdivide land, the resulting plains become breeding grounds for mosquitoes and disease. Traditional homeownership financing methods are rare amongst colonias residents, and therefore these areas consist of ramshackle housing units built incrementally with found material on expanses of undeveloped land. Colonias have a predominant Latino population where 85 percent of those Latinos under the age of 18 are United States citizens. The U.S. has viewed border communities as a place of lawlessness, poverty, backwardness, and ethnic difference.
The HOME Investment Partnerships Program (HOME) is a type of United States federal assistance that the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD) provides to states to create decent and affordable housing, particularly housing for low and very low income Americans. It is the largest Federal block grant to states and local governments designed exclusively to create affordable housing for low-income families, providing approximately US$2 billion each year.

USDA Rural Development (RD) is a mission area within the United States Department of Agriculture which runs programs intended to improve the economy and quality of life in rural parts of the United States.

The New Jersey Department of Community Affairs is a governmental agency of the U.S. state of New Jersey.

Housing, or more generally, living spaces, refers to the construction and assigned usage of houses or buildings individually or collectively, for the purpose of shelter. Housing is a basic human need, and it plays a critical role in shaping the quality of life for individuals, families, and communities.

In the United States, subsidized housing is administered by federal, state and local agencies to provide subsidized rental assistance for low-income households. Public housing is priced much below the market rate, allowing people to live in more convenient locations rather than move away from the city in search of lower rents. In most federally-funded rental assistance programs, the tenants' monthly rent is set at 30% of their household income. Now increasingly provided in a variety of settings and formats, originally public housing in the U.S. consisted primarily of one or more concentrated blocks of low-rise and/or high-rise apartment buildings. These complexes are operated by state and local housing authorities which are authorized and funded by the United States Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD). In 2020, there were 1 million public housing units.

Pradhan Mantri Gramin Aawas Yojana, previously Indira Awas Yojana, is a social welfare programme, created by the Indian Government, to provide housing for the rural poor in India. A similar scheme for urban poor was launched in 2015 as Housing for All by 2022. Indira Awas Yojana was launched in 1985 by Rajiv Gandhi, the Prime Minister of India, as one of the major flagship programs of the Ministry of Rural Development to construct houses for the Below Poverty Line population in the villages.
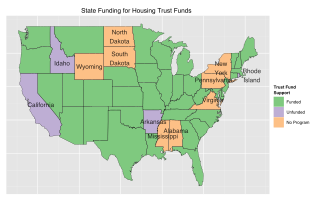
Housing trust funds are established sources of funding for affordable housing construction and other related purposes created by governments in the United States (U.S.). Housing Trust Funds (HTF) began as a way of funding affordable housing in the late 1970s. Since then, elected government officials from all levels of government in the U.S. have established housing trust funds to support the construction, acquisition, and preservation of affordable housing and related services to meet the housing needs of low-income households. Ideally, HTFs are funded through dedicated revenues like real estate transfer taxes or document recording fees to ensure a steady stream of funding rather than being dependent on regular budget processes. As of 2016, 400 state, local and county trust funds existed across the U.S.
Non-profit housing developers build affordable housing for individuals under-served by the private market. The non-profit housing sector is composed of community development corporations (CDC) and national and regional non-profit housing organizations whose mission is to provide for the needy, the elderly, working households, and others that the private housing market does not adequately serve. Of the total 4.6 million units in the social housing sector, non-profit developers have produced approximately 1.547 million units, or roughly one-third of the total stock. Since non-profit developers seldom have the financial resources or access to capital that for-profit entities do, they often use multiple layers of financing, usually from a variety of sources for both development and operation of these affordable housing units.

Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) is a credit-linked subsidy scheme by the Government of India to facilitate access to affordable housing for the low and moderate-income residents of the country. It envisaged a target of building 2 crore (20 million) affordable houses by 31 March 2022. It has two components: Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana(Urban) (PMAY-U) for the urban poor and Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana (Gramin) (PMAY-G and also PMAY-R) for the rural poor, the former administered by Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs and the latter by Ministry of Rural Development. This scheme converges with other schemes to ensure houses have a toilet, Saubhagya Scheme for universal electricity connection, Ujjwala Yojana LPG connection, access to drinking water and Jan Dhan banking facilities, etc.
Housing and Community Development Act of 1992 was first introduced to the 102nd Congress on June 5, 1992, and was signed and made law by President George H. W. Bush on October 28, 1992. Also known as "The 1992 Act", the bill amended a number of housing, banking, and drug abuse laws. It amended The United States Housing Act of 1937. It increased aggregate budget authority for low-income housing for fiscal year 1993 and 1994. It also extends ceiling rents, excludes certain child care expenses, and excessive travel expenses from the calculation of adjusted income and apply to Indian public housing certain definitions of the Cranston-Gonzales National Affordable Housing Act; It allows the Secretary of Housing and Urban Development to issue public and Section 8 housing tenant preference rules. The Act also extends certain exemptions from waiting list requirements and eligibility restrictions with respect to income eligibility for assisted housing and while revising the family self-sufficiency program, with respect to escrow saving accounts, incentives for participation, and action plans.

Housing insecurity is the lack of security in an individual shelter that is the result of high housing costs relative to income, poor housing quality, unstable neighborhoods, overcrowding, and, but may not include, homelessness.

Affordable housing is housing that is deemed affordable to those with a median household income as rated by the national government or a local government by a recognized housing affordability index. A general rule is no more than 30% of gross monthly income should be spent on housing, to be considered affordable as the challenges of promoting affordable housing varies by location.

Nilam Sawhney is currently serving as chief election commissioner of Andhra Pradesh. She served as the first woman Chief Secretary of the newly formed state of Andhra Pradesh, India, from November 2019 to January 2021. She is a 1984 batch Indian Administrative Service (IAS) officer of Andhra Pradesh cadre. She previously held the position of Secretary of Union Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment from 2018 to 2019 and before this served as the Secretary of Central Vigilance Commission in the Government of India from 2015 to 2018.

The majority of Americans (64%) own their own homes, a rate that is less than the home ownership rates other large countries such as China (90%), Russia (89%), Mexico (80%), or Brazil (73%).














