Related Research Articles

Dual-tone multi-frequency signaling (DTMF) is a telecommunication signaling system using the voice-frequency band over telephone lines between telephone equipment and other communications devices and switching centers. DTMF was first developed in the Bell System in the United States, and became known under the trademark Touch-Tone for use in push-button telephones supplied to telephone customers, starting in 1963. DTMF is standardized as ITU-T Recommendation Q.23. It is also known in the UK as MF4.
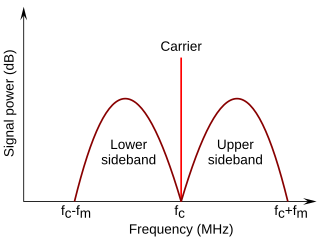
In radio communications, a sideband is a band of frequencies higher than or lower than the carrier frequency, that are the result of the modulation process. The sidebands carry the information transmitted by the radio signal. The sidebands comprise all the spectral components of the modulated signal except the carrier. The signal components above the carrier frequency constitute the upper sideband (USB), and those below the carrier frequency constitute the lower sideband (LSB). All forms of modulation produce sidebands.
In telecommunication, signaling is the use of signals for controlling communications. This may constitute an information exchange concerning the establishment and control of a telecommunication circuit and the management of the network.
In telecommunications, squelch is a circuit function that acts to suppress the audio output of a receiver in the absence of a strong input signal. Essentially, squelch is a specialized type of noise gate designed to suppress weak signals. Squelch is used in two-way radios and VHF/UHF radio scanners to eliminate the sound of noise when the radio is not receiving a desired transmission.

The T-carrier is a member of the series of carrier systems developed by AT&T Bell Laboratories for digital transmission of multiplexed telephone calls.

In telecommunications, frequency-division multiplexing (FDM) is a technique by which the total bandwidth available in a communication medium is divided into a series of non-overlapping frequency bands, each of which is used to carry a separate signal. This allows a single transmission medium such as a microwave radio link, cable or optical fiber to be shared by multiple independent signals. Another use is to carry separate serial bits or segments of a higher rate signal in parallel.
Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS), or Plain Ordinary Telephone System, is a retronym for voice-grade telephone service employing analog signal transmission over copper loops. Originally POTS stood for Post Office Telephone Service as early phone lines in most parts of the world were operated directly by the local Post Office.

A blue box is an electronic device that produces tones used to generate the in-band signaling tones formerly used within the North American long-distance telephone network to send line status and called number information over voice circuits. During that period, charges associated with long-distance calling were commonplace and could be significant, depending on the time, duration and destination of the call. A blue box device allowed for circumventing these charges by enabling an illicit user, referred to as a "phreaker" to place long-distance calls, without using the network's user facilities, that would be billed to another number or dismissed entirely by the telecom company's billing system as an incomplete call. A number of similar "color boxes" were also created to control other aspects of the phone network.
In telecommunications, in-band signaling is the sending of control information within the same band or channel used for data such as voice or video. This is in contrast to out-of-band signaling which is sent over a different channel, or even over a separate network. In-band signals may often be heard by telephony participants, while out-of-band signals are inaccessible to the user. The term is also used more generally, for example of computer data files that include both literal data, and metadata and/or instructions for how to process the literal data.

Professional mobile radio are person-to-person two-way radio voice communications systems which use portable, mobile, base station, and dispatch console radios. PMR systems are based on such standards as MPT-1327, TETRA, APCO 25, and DMR which are designed for dedicated use by specific organizations, or standards such as NXDN intended for general commercial use. These systems are used by police, fire, ambulance, and emergency services, and by commercial firms such as taxis and delivery services. Most systems are half-duplex, in which multiple radios share a common radio channel, and only one can transmit at a time. Transceivers are normally in receive mode, the user presses a push-to-talk button on his microphone when he wants to talk, which turns on his transmitter and turns off his receiver. They use channels in the VHF and UHF bands, giving them a limited range, usually 3 to 20 miles depending on terrain. Output power is typically limited to 4 watts. Repeaters installed on tall buildings, hills or mountain peaks are used to increase the range of systems.

The Improved Mobile Telephone Service (IMTS) was a pre-cellular VHF/UHF radio system which linked to the public telephone network. IMTS was the radiotelephone equivalent of land dial phone service. Introduced in 1964, it replaced Mobile Telephone Service (MTS) and improved on most MTS systems by offering direct-dial rather than connections through a live operator, and full-duplex operation so both parties could talk at the same time.
2600 hertz (2600 Hz) is a frequency in hertz that was used in telecommunication signaling in mid-20th century long-distance telephone networks using carrier systems.

E and M signaling is a type of supervisory line signaling that uses DC signals on separate leads, called the "E" lead and "M" lead, traditionally used in the telecommunications industry between telephone switches. Various mnemonic names have been used to memorize these letters, such as Earth and Magneto or Ear and Mouth, the most common variation.
In a digitally modulated signal or a line code, symbol rate, modulation rate or baud rate is the number of symbol changes, waveform changes, or signaling events across the transmission medium per unit of time. The symbol rate is measured in baud (Bd) or symbols per second. In the case of a line code, the symbol rate is the pulse rate in pulses per second. Each symbol can represent or convey one or several bits of data. The symbol rate is related to the gross bit rate, expressed in bits per second.

A digital subscriber line (DSL) modem is a device used to connect a computer or router to a telephone line which provides the digital subscriber line (DSL) service for connection to the Internet, which is often called DSL broadband. The modem connects to a single computer or router, through an Ethernet port, USB port, or is installed in a computer PCI slot.
The off-hook tone is a telephony signal for alerting a user that the telephone has been left off-hook without use for an extended period, effectively disabling the telephone line.
In telecommunications, falsing is a signaling error condition when a signal decoder detects a valid input although the implied protocol function was not intended. This is also known as a false decode. Other forms are referred to as talk-off.
In telecommunication, supervision is the monitoring of a telecommunication circuit for telephony to convey to an operator, user, or a switching system, information about the operational state of the circuit. The typical operational states of trunks and lines are the idle and busy states, seizure, and disconnect. The states are indicated by various electrical signals and electrical conditions depending on the type of circuit, the type of terminating equipment, and the type of intended service.
In a conventional, analog two-way radio system, a standard radio has noise squelch or carrier squelch, which allows a radio to receive all transmissions. Selective calling is used to address a subset of all two-way radios on a single radio frequency channel. Where more than one user is on the same channel, selective calling can address a subset of all receivers or can direct a call to a single radio. Selective calling features fit into two major categories—individual calling and group calling. Individual calls generally have longer time-constants: it takes more air-time to call an individual radio unit than to call a large group of radios.

A telephone exchange, also known as a telephone switch or central office, is a crucial component in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or large enterprise telecommunications systems. It facilitates the interconnection of telephone subscriber lines or digital system virtual circuits, enabling telephone calls between subscribers.
References
- ↑ In-Band Single-Frequency Signaling by A. Weaver and N. A. Newell, Bell System Technical Journal, June 7, 1954
 This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22. (in support of MIL-STD-188).
This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22. (in support of MIL-STD-188).