
A molecular cloud, sometimes called a stellar nursery (if star formation is occurring within), is a type of interstellar cloud, the density and size of which permit absorption nebulae, the formation of molecules (most commonly molecular hydrogen, H2), and the formation of H II regions. This is in contrast to other areas of the interstellar medium that contain predominantly ionized gas.
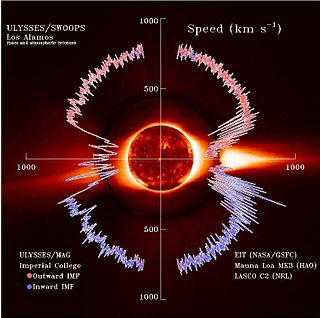
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the Sun's outermost atmospheric layer, the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between 0.5 and 10 keV. The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of particle species found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei of elements such as carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, neon, magnesium, silicon, sulfur, and iron. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as phosphorus, titanium, chromium, and nickel's isotopes 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superimposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of the corona, which in turn is a result of the coronal magnetic field. The boundary separating the corona from the solar wind is called the Alfvén surface.

A supernova remnant (SNR) is the structure resulting from the explosion of a star in a supernova. The supernova remnant is bounded by an expanding shock wave, and consists of ejected material expanding from the explosion, and the interstellar material it sweeps up and shocks along the way.

Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space, sometimes referred to as "stellar nurseries" or "star-forming regions", collapse and form stars. As a branch of astronomy, star formation includes the study of the interstellar medium (ISM) and giant molecular clouds (GMC) as precursors to the star formation process, and the study of protostars and young stellar objects as its immediate products. It is closely related to planet formation, another branch of astronomy. Star formation theory, as well as accounting for the formation of a single star, must also account for the statistics of binary stars and the initial mass function. Most stars do not form in isolation but as part of a group of stars referred as star clusters or stellar associations.

X-ray astronomy is an observational branch of astronomy which deals with the study of X-ray observation and detection from astronomical objects. X-radiation is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to high altitude by balloons, sounding rockets, and satellites. X-ray astronomy uses a type of space telescope that can see x-ray radiation which standard optical telescopes, such as the Mauna Kea Observatories, cannot.

The interstellar medium (ISM) is the matter and radiation that exists in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as dust and cosmic rays. It fills interstellar space and blends smoothly into the surrounding intergalactic space. The energy that occupies the same volume, in the form of electromagnetic radiation, is the interstellar radiation field. Although the density of atoms in the ISM is usually far below that in the best laboratory vacuums, the mean free path between collisions is short compared to typical interstellar lengths, so on these scales the ISM behaves as a gas, responding to pressure forces, and not as a collection of non-interacting particles.

A stellar wind is a flow of gas ejected from the upper atmosphere of a star. It is distinguished from the bipolar outflows characteristic of young stars by being less collimated, although stellar winds are not generally spherically symmetric.

An H II region or HII region is a region of interstellar atomic hydrogen that is ionized. It is typically in a molecular cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place, with a size ranging from one to hundreds of light years, and density from a few to about a million particles per cubic centimetre. The Orion Nebula, now known to be an H II region, was observed in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc by telescope, the first such object discovered.

The Cat's Eye Nebula is a planetary nebula in the northern constellation of Draco, discovered by William Herschel on February 15, 1786. It was the first planetary nebula whose spectrum was investigated by the English amateur astronomer William Huggins, demonstrating that planetary nebulae were gaseous and not stellar in nature. Structurally, the object has had high-resolution images by the Hubble Space Telescope revealing knots, jets, bubbles and complex arcs, being illuminated by the central hot planetary nebula nucleus (PNN). It is a well-studied object that has been observed from radio to X-ray wavelengths. At the centre of the Cat's Eye Nebula is a dying Wolf Rayet star, the sort of which can be seen in the Webb Telescope's image of WR 124. The Cat's Eye Nebula's central star shines at magnitude +11.4. Hubble Space Telescope images show a sort of dart board pattern of concentric rings emanating outwards from the centre.

The Local Bubble, or Local Cavity, is a relative cavity in the interstellar medium (ISM) of the Orion Arm in the Milky Way. It contains the closest of celestial neighbours and among others, the Local Interstellar Cloud, the neighbouring G-Cloud, the Ursa Major moving group and the Hyades. It is estimated to be at least 1000 light years in size, and is defined by its neutral-hydrogen density of about 0.05 atoms/cm3, or approximately one tenth of the average for the ISM in the Milky Way (0.5 atoms/cm3), and one sixth that of the Local Interstellar Cloud (0.3 atoms/cm3).

In astrophysics, bow shocks are shock waves in regions where the conditions of density and pressure change dramatically due to blowing stellar wind. Bow shock occurs when the magnetosphere of an astrophysical object interacts with the nearby flowing ambient plasma such as the solar wind. For Earth and other magnetized planets, it is the boundary at which the speed of the stellar wind abruptly drops as a result of its approach to the magnetopause. For stars, this boundary is typically the edge of the astrosphere, where the stellar wind meets the interstellar medium.
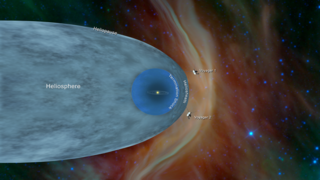
The heliosphere is the magnetosphere, astrosphere, and outermost atmospheric layer of the Sun. It takes the shape of a vast, tailed bubble-like region of space. In plasma physics terms, it is the cavity formed by the Sun in the surrounding interstellar medium. The "bubble" of the heliosphere is continuously "inflated" by plasma originating from the Sun, known as the solar wind. Outside the heliosphere, this solar plasma gives way to the interstellar plasma permeating the Milky Way. As part of the interplanetary magnetic field, the heliosphere shields the Solar System from significant amounts of cosmic ionizing radiation; uncharged gamma rays are, however, not affected. Its name was likely coined by Alexander J. Dessler, who is credited with the first use of the word in the scientific literature in 1967. The scientific study of the heliosphere is heliophysics, which includes space weather and space climate.

A pulsar wind nebula, sometimes called a plerion, is a type of nebula sometimes found inside the shell of a supernova remnant (SNR), powered by winds generated by a central pulsar. These nebulae were proposed as a class in 1976 as enhancements at radio wavelengths inside supernova remnants. They have since been found to be infrared, optical, millimetre, X-ray and gamma ray sources.

The Local Interstellar Cloud (LIC), also known as the Local Fluff, is an interstellar cloud roughly 30 light-years (9.2 pc) across, through which the Solar System is moving. This feature overlaps with a region around the Sun referred to as the solar neighborhood. It is unknown whether the Sun is embedded in the Local Interstellar Cloud, or is in the region where the Local Interstellar Cloud is interacting with the neighboring G-Cloud. Like the G-Cloud and others, the LIC is part of the Very Local Interstellar Medium which begins where the heliosphere and interplanetary medium end, the furthest that probes have traveled.

In astronomy a superbubble or supershell is a cavity which is hundreds of light years across and is populated with hot (106 K) gas atoms, less dense than the surrounding interstellar medium, blown against that medium and carved out by multiple supernovae and stellar winds. The winds, passage and gravity of newly born stars strip superbubbles of any other dust or gas. The Solar System lies near the center of an old superbubble, known as the Local Bubble, whose boundaries can be traced by a sudden rise in dust extinction of exterior stars at distances greater than a few hundred light years.

A Wolf-Rayet nebula is a type of nebula created from stellar winds expelled by Wolf-Rayet stars. Wolf-Rayet stars are very hot, highly luminous, and rapidly evolving massive stars that are fusing helium or heavier elements in their cores.

WR 102 is a Wolf–Rayet star in the constellation Sagittarius, an extremely rare star on the WO oxygen sequence. It is a luminous and very hot star, highly evolved and close to exploding as a supernova.
Cosmic wind is a powerful cosmic stream of charged particles that can push interstellar dust clouds of low density into intergalactic space. Although it easily pushes low density gas and dust clouds, it cannot easily push high density clouds. As the cosmic winds start to push the clouds, they start to separate and start looking like taffy being pulled apart. It has a primary composition of photons ejected from large stars and sometimes thermal energy from exploding stars. It can be caused by orbital motion of gas in the cluster of a galaxy, or can be ejected from a black hole. Because new stars and planets form from gases, the cosmic winds that push the gases away are preventing new stars from forming and are ultimately playing a role in galaxy evolution.

A galactic superwind, or just galactic wind, is a high velocity stellar wind emanating from either newly formed massive stars, spiral density waves, or as the result of the effects of supermassive black holes. They are normally observed in starburst galaxies.
A superwind is an extremely dense wind emanating from asymptotic giant branch stars towards the end of their lives.


















