
Weighing paper is often used when weighing solid, powdery substances on an analytical balance. By preventing the substance from making contact with unwanted materials, the precision of the measurement may be increased. [1] [2]

Weighing paper is often used when weighing solid, powdery substances on an analytical balance. By preventing the substance from making contact with unwanted materials, the precision of the measurement may be increased. [1] [2]

The weighing paper is usually made through the process called calendering. First, a chemically manufactured paper pulp fiber is broken down and squeezed into the mold where it will dry into the sheet. Then, this sheet will be rolled down by hot roller. As a result, the pulp fiber will be flat and in the same direction. To make the paper very smooth and moist-resistant, it goes through the process repetitively, called super-calendering. [3]
Weighing paper can be folded into different shape depending on its uses.


The weighing paper is provided in different sizes : 6in by 6in, 4in by 4in, and 3in by 3in. [6]

Papermaking is the manufacture of paper and cardboard, which are used widely for printing, writing, and packaging, among many other purposes. Today almost all paper is made using industrial machinery, while handmade paper survives as a specialized craft and a medium for artistic expression.

Newsprint is a low-cost, non-archival paper consisting mainly of wood pulp and most commonly used to print newspapers and other publications and advertising material. Invented in 1844 by Charles Fenerty of Nova Scotia, Canada, it usually has an off white cast and distinctive feel. It is designed for use in printing presses that employ a long web of paper, rather than individual sheets of paper.

A tea bag, or the compound teabag, is a small, porous, sealed bag or packet, typically containing tea leaves or the leaves of other herbs, which is immersed in water to steep and make an infusion. Originally used only for tea, they are now made with other tisanes as well.

Pulpwood is timber with the principal use of making wood pulp for paper production.

A paper machine is an industrial machine which is used in the pulp and paper industry to create paper in large quantities at high speed. Modern paper-making machines are based on the principles of the Fourdrinier Machine, which uses a moving woven mesh to create a continuous paper web by filtering out the fibres held in a paper stock and producing a continuously moving wet mat of fibre. This is dried in the machine to produce a strong paper web.

Papier-mâché is a composite material consisting of paper pieces or pulp, sometimes reinforced with textiles, bound with an adhesive, such as glue, starch, or wallpaper paste.
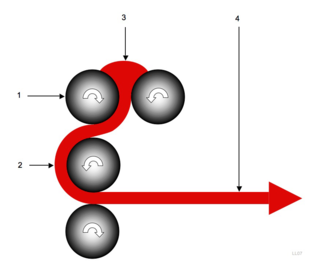
A calender is a series of hard pressure rollers used to finish or smooth a sheet of material such as paper, textiles, rubber, or plastics. Calender rolls are also used to form some types of plastic films and to apply coatings. Some calender rolls are heated or cooled as needed. Calenders are sometimes misspelled calendars.

Paper craft is a collection of crafts using paper or card as the primary artistic medium for the creation of two or three-dimensional objects. Paper and card stock lend themselves to a wide range of techniques and can be folded, curved, bent, cut, glued, molded, stitched, or layered. Papermaking by hand is also a paper craft.

A pulp mill is a manufacturing facility that converts wood chips or other plant fiber sources into a thick fiber board which can be shipped to a paper mill for further processing. Pulp can be manufactured using mechanical, semi-chemical, or fully chemical methods. The finished product may be either bleached or non-bleached, depending on the customer requirements.

Wove paper is a type of paper first created centuries ago in the Orient, and subsequently introduced to England, Europe and the American colonies in the mid-eighteenth century. Hand-made wove paper was first produced by using a wooden mould that contained a finely-woven brass vellum, upon which the paper pulp was applied and dried, creating a smooth, uniform surface.

Nonwoven fabric is a fabric-like material made from staple fibre (short) and long fibres, bonded together by chemical, mechanical, heat or solvent treatment. The term is used in the textile manufacturing industry to denote fabrics, such as felt, which are neither woven nor knitted. Some non-woven materials lack sufficient strength unless densified or reinforced by a backing. In recent years, non-wovens have become an alternative to polyurethane foam.

Tracing paper is paper made to have low opacity, allowing light to pass through. Its origins date back to at least the 1300s where it was used by artists of the Italian Renaissance. In the 1880s, tracing paper was produced en masse, used by architects, design engineers, and artists. Tracing paper was key in creating drawings that could be copied precisely using the diazo copy process. It then found many other uses. The original use for drawing and tracing was largely superseded by technologies that do not require diazo copying or manual copying of drawings.

Inkjet paper is a special fine paper designed for inkjet printers, typically classified by its weight, brightness and smoothness, and sometimes by its opacity.
The sulfite process produces wood pulp that is almost pure cellulose fibers by treating wood chips with solutions of sulfite and bisulfite ions. These chemicals cleave the bonds between the cellulose and lignin components of the lignocellulose. A variety of sulfite/bisulfite salts are used, including sodium (Na+), calcium (Ca2+), potassium (K+), magnesium (Mg2+), and ammonium (NH4+). The lignin is converted to lignosulfonates, which are soluble and can be separated from the cellulose fibers. For the production of cellulose, the sulfite process competes with the Kraft process which produces stronger fibers and is less environmentally costly.
Glassine is a smooth and glossy paper that is air, water, and grease resistant. It is usually available in densities between 50–90 g/m2 (0.010–0.018 lb/sq ft). It is translucent unless dyes are added to color it or make it opaque. It is manufactured by supercalendering: after pressing and drying, the paper web is passed through a stack of alternating steel- and fiber-covered rolls called a supercalender at the end of the paper machine so that the paper fibers flatten facing in the same direction.

Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, rags, grasses, or other vegetable sources in water, draining the water through a fine mesh leaving the fibre evenly distributed on the surface, followed by pressing and drying. Although paper was originally made in single sheets by hand, almost all is now made on large machines—some making reels 10 metres wide, running at 2,000 metres per minute and up to 600,000 tonnes a year. It is a versatile material with many uses, including printing, painting, graphics, signage, design, packaging, decorating, writing, and cleaning. It may also be used as filter paper, wallpaper, book endpaper, conservation paper, laminated worktops, toilet tissue, currency, and security paper, or in a number of industrial and construction processes.
Whatman plc is a Cytiva brand specialising in laboratory filtration products and separation technologies.

Parchment paper, vegetable parchment, or, baking paper is a cellulose-based composite that has been processed to give it additional properties like non-stickiness, grease resistance, and resistance to humidity. It is commonly used in baking as a disposable non-stick, grease resistant surface. It should not be confused with waxed paper, which is paper that has been coated in wax.

The environmental effects of paper are significant, which has led to changes in industry and behaviour at both business and personal levels. With the use of modern technology such as the printing press and the highly mechanized harvesting of wood, disposable paper became a relatively cheap commodity, which led to a high level of consumption and waste. The rise in global environmental issues such as air and water pollution, climate change, overflowing landfills and clearcutting have all lead to increased government regulations. There is now a trend towards sustainability in the pulp and paper industry as it moves to reduce clear cutting, water use, greenhouse gas emissions, fossil fuel consumption and clean up its influence on local water supplies and air pollution.
Watercolor paper is paper or substrate onto which an artist applies watercolor paints, pigments, or dyes. Artists generally no longer use stone or tomb walls as a substrates. Many types of watercolour papers that are manufactured for the use of watercolors are currently available. Watercolor paper can be made of wood pulp exclusively, or mixed with cotton fibers. Pure cotton watercolor paper is also used by artists, though it typically costs more than pulp-based paper. It is also available as an acid-free medium to help its preservation.