
D, or d, is the fourth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is dee, plural dees.

A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ancestor, called the proto-language of that family. The term family is a metaphor borrowed from biology, with the tree model used in historical linguistics analogous to a family tree, or to phylogenetic trees of taxa used in evolutionary taxonomy. Linguists thus describe the daughter languages within a language family as being genetically related. The divergence of a proto-language into daughter languages typically occurs through geographical separation, with different regional dialects of the proto-language undergoing different language changes and thus becoming distinct languages over time.

A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe. Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate causes of phenomena, and usually frame their understanding in mathematical terms. They work across a wide range of research fields, spanning all length scales: from sub-atomic and particle physics, through biological physics, to cosmological length scales encompassing the universe as a whole. The field generally includes two types of physicists: experimental physicists who specialize in the observation of natural phenomena and the development and analysis of experiments, and theoretical physicists who specialize in mathematical modeling of physical systems to rationalize, explain and predict natural phenomena.
Latvian mythology is the collection of myths that have emerged throughout the history of Latvia, sometimes being elaborated upon by successive generations, and at other times being rejected and replaced by other explanatory narratives. These myths, for the most part, likely stem from Proto-Indo-European practices and the later folk traditions of the Latvian people and pre-Christian Baltic mythology.

Substance abuse, also known as drug abuse, is the use of a drug in amounts or by methods that are harmful to the individual or others. It is a form of substance-related disorder. Differing definitions of drug abuse are used in public health, medical, and criminal justice contexts. In some cases, criminal or anti-social behavior occurs when the person is under the influence of a drug, and long-term personality changes in individuals may also occur. In addition to possible physical, social, and psychological harm, the use of some drugs may also lead to criminal penalties, although these vary widely depending on the local jurisdiction.

Cardinalidae is a family of New World-endemic passerine birds that consists of cardinals, grosbeaks, and buntings. It also includes several other genera such as the tanager-like Piranga and the warbler-like Granatellus. Membership of this family is not easily defined by a single or even a set of physical characteristics, but instead by molecular work. Among songbirds, they range from average-sized to relatively large, and have stout features, some species with large, heavy bills.

Killed in action (KIA) is a casualty classification generally used by militaries to describe the deaths of their own personnel at the hands of enemy or hostile forces at the moment of action. The United States Department of Defense, for example, says that those declared KIA did not need to have fired their weapons, but only to have been killed due to hostile attack. KIAs include those killed by friendly fire in the midst of combat, but not from incidents such as accidental vehicle crashes, murder or other non-hostile events or terrorism. KIA can be applied both to front-line combat troops and to naval, air and support troops.

The dickcissel is a small seed-eating migratory bird in the family Cardinalidae. It breeds on the prairie grasslands of the Midwestern United States and winters in Central America, northern Colombia, and northern Venezuela. It is the only member of the genus Spiza, though some sources list another supposedly extinct species.

These are a series of incomplete lists of unusual deaths, unique or extremely rare circumstances of death recorded throughout history, noted as being unusual by multiple sources.

Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration, is a medical condition which may result in blurred or no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no symptoms. Over time, however, some people experience a gradual worsening of vision that may affect one or both eyes. While it does not result in complete blindness, loss of central vision can make it hard to recognize faces, drive, read, or perform other activities of daily life. Visual hallucinations may also occur.
A cousin is a relative that is the child of a parent's sibling; this is more specifically referred to as a first cousin.

Grosbeak is a form taxon containing various species of seed-eating passerine birds with large beaks. Although they all belong to the superfamily Passeroidea, these birds are not part of a natural group but rather a polyphyletic assemblage of distantly related songbirds. Some are cardueline finches in the family Fringillidae, while others are cardinals in the family Cardinalidae; one is a member of the weaver family Ploceidae. The word "grosbeak", first applied in the late 1670s, is a partial translation of the French grosbec, where gros means "large" and bec means "beak".

Scorpio (♏︎) is the eighth astrological sign in the zodiac, originating from the constellation of Scorpius. It spans 210–240° ecliptic longitude. Under the tropical zodiac, the Sun transits this sign on average from October 23 to November 21. Depending on which zodiac system one uses, someone born under the influence of Scorpio may be called a Scorpio or a Scorpionic.

The blue bunting is a species of passerine in the family Cardinalidae, the cardinals or cardinal grosbeaks. It is found in Belize, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, and Nicaragua.

The glaucous-blue grosbeak, also known as the indigo grosbeak, is a species of bird in the family Cardinalidae, the cardinals or cardinal grosbeaks. It is found in Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay, and Uruguay.
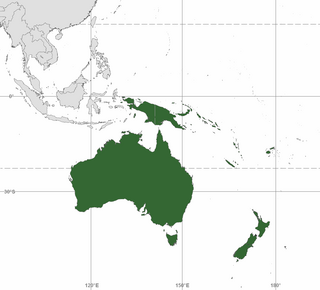
Australasia is a subregion of Oceania, comprising Australia, New Zealand, and sometimes including New Guinea and surrounding islands. The term is used in a number of different contexts, including geopolitically, physiogeographically, philologically, and ecologically, where the term covers several slightly different but related regions.

The Amazonian grosbeak or Rothschild's grosbeak is a species of grosbeak in the family Cardinalidae, the cardinals or cardinal grosbeaks. It is found in much of the Amazon Basin, in Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, French Guiana, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela.


























