This article needs additional citations for verification .(August 2017) |
| Passerina | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Painted bunting (Passerina ciris) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Cardinalidae |
| Genus: | Passerina Vieillot, 1816 |
| Type species | |
| Tanagra cyanea Linnaeus, 1766 | |
| Species | |
See text | |
| Synonyms | |
Guiraca | |
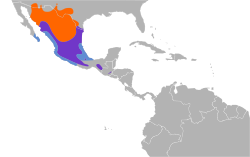
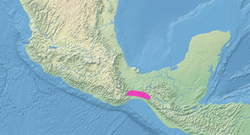
The genus Passerina is a group of birds in the cardinal family (Cardinalidae). Although not closely related to the buntings in the family Emberizidae, they are sometimes known as the North American buntings.
The males show vivid colors in the breeding season; the plumage of females and immature birds is duller. These birds go through two molts in a year; the males are generally less colorful in winter. They have short tails and short slim legs. They have smaller bills than other Cardinalidae; they mainly eat seeds in winter and insects in summer.
The blue grosbeak (P. caerulea) was once placed in the monotypic genus, Guiraca.