Related Research Articles
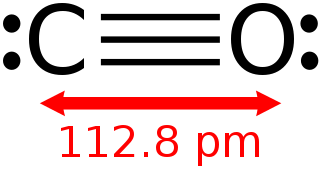
Carbon monoxide is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simplest carbon oxide. In coordination complexes, the carbon monoxide ligand is called carbonyl. It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry.

Propane is a three-carbon alkane with the molecular formula C3H8. It is a gas at standard temperature and pressure, but compressible to a transportable liquid. A by-product of natural gas processing and petroleum refining, it is commonly used as a fuel in domestic and industrial applications and in low-emissions public transportation. Discovered in 1857 by the French chemist Marcellin Berthelot, it became commercially available in the US by 1911. Propane is one of a group of liquefied petroleum gases. The others include propylene, butane, butylene, butadiene, isobutylene, and mixtures thereof. Propane has lower volumetric energy density, but higher gravimetric energy density and burns more cleanly than gasoline and coal.

A pipeline is a system of pipes for long-distance transportation of a liquid or gas, typically to a market area for consumption. The latest data from 2014 gives a total of slightly less than 2,175,000 miles (3,500,000 km) of pipeline in 120 countries around the world. The United States had 65%, Russia had 8%, and Canada had 3%, thus 76% of all pipeline were in these three countries. The main attribute to pollution from pipelines is caused by corrosion and leakage

Ethane is a naturally occurring organic chemical compound with chemical formula C
2H
6. At standard temperature and pressure, ethane is a colorless, odorless gas. Like many hydrocarbons, ethane is isolated on an industrial scale from natural gas and as a petrochemical by-product of petroleum refining. Its chief use is as feedstock for ethylene production.

A smoke detector is a device that senses smoke, typically as an indicator of fire. Smoke detectors/Alarms are usually housed in plastic enclosures, typically shaped like a disk about 150 millimetres (6 in) in diameter and 25 millimetres (1 in) thick, but shape and size vary. Smoke can be detected either optically (photoelectric) or by physical process (ionization). Detectors may use one or both sensing methods. Sensitive alarms can be used to detect and deter smoking in banned areas. Smoke detectors in large commercial and industrial buildings are usually connected to a central fire alarm system.

Liquefied petroleum gas, also referred to as liquid petroleum gas, is a fuel gas which contains a flammable mixture of hydrocarbon gases, specifically propane, n-butane and isobutane. It can sometimes contain some propylene, butylene, and isobutene.

Carbon monoxide poisoning typically occurs from breathing in carbon monoxide (CO) at excessive levels. Symptoms are often described as "flu-like" and commonly include headache, dizziness, weakness, vomiting, chest pain, and confusion. Large exposures can result in loss of consciousness, arrhythmias, seizures, or death. The classically described "cherry red skin" rarely occurs. Long-term complications may include chronic fatigue, trouble with memory, and movement problems.
A fireplace or hearth is a structure made of brick, stone or metal designed to contain a fire. Fireplaces are used for the relaxing ambiance they create and for heating a room. Modern fireplaces vary in heat efficiency, depending on the design.
A gas leak refers to a leak of natural gas or another gaseous product from a pipeline or other containment into any area where the gas should not be present. Gas leaks can be hazardous to health as well as the environment. Even a small leak into a building or other confined space may gradually build up an explosive or lethal concentration of gas. Natural gas leaks and the escape of refrigerant gas into the atmosphere are especially harmful, because of their global warming potential and ozone depletion potential.

Demining or mine clearance is the process of removing land mines from an area. In military operations, the object is to rapidly clear a path through a minefield, and this is often done with devices such as mine plows and blast waves. By contrast, the goal of humanitarian demining is to remove all of the landmines to a given depth and make the land safe for human use. Specially trained dogs are also used to narrow down the search and verify that an area is cleared. Mechanical devices such as flails and excavators are sometimes used to clear mines.

A carbon monoxide detector or CO detector is a device that detects the presence of the carbon monoxide (CO) gas to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning. In the late 1990s Underwriters Laboratories changed the definition of a single station CO detector with a sound device to carbon monoxide (CO) alarm. This applies to all CO safety alarms that meet UL 2034 standard; however for passive indicators and system devices that meet UL 2075, UL refers to these as carbon monoxide detectors. Most CO detectors use a sensor with a defined, limited lifespan, and will not work indefinitely.

An aspirating smoke detector (ASD) is a system used in active fire protection, consisting of a central detection unit which draws air through a network of pipes to detect smoke. The sampling chamber is based on a nephelometer that detects the presence of smoke particles suspended in air by detecting the light scattered by them in the chamber. ASDs can typically detect smoke before it is visible to the naked eye.

A heat detector is a fire alarm device designed to respond when the convected thermal energy of a fire increases the temperature of a heat sensitive element. The thermal mass and conductivity of the element regulate the rate flow of heat into the element. All heat detectors have this thermal lag. Heat detectors have two main classifications of operation, "rate-of-rise" and "fixed temperature". The heat detector is used to help in the reduction of property damage.

A kerosene heater, also known as a paraffin heater, is typically a portable, unvented, kerosene-fueled, space heating device. In Japan and other countries, they are a primary source of home heat. In the United States and Australia, they are a supplemental heat or a source of emergency heat during a power outage. Most kerosene heaters produce between 3.3 and 6.8 kilowatts.

An engine–generator is the combination of an electrical generator and an engine mounted together to form a single piece of equipment. This combination is also called an engine–generator set or a gen-set. In many contexts, the engine is taken for granted and the combined unit is simply called a generator. An engine–generator may be a fixed installation, part of a vehicle, or made small enough to be portable.
A gas detector is a device that detects the presence of gases in an area, often as part of a safety system. A gas detector can sound an alarm to operators in the area where the leak is occurring, giving them the opportunity to leave. This type of device is important because there are many gases that can be harmful to organic life, such as humans or animals.
A flame detector is a sensor designed to detect and respond to the presence of a flame or fire, allowing flame detection. Responses to a detected flame depend on the installation, but can include sounding an alarm, deactivating a fuel line, and activating a fire suppression system. When used in applications such as industrial furnaces, their role is to provide confirmation that the furnace is working properly; it can be used to turn off the ignition system though in many cases they take no direct action beyond notifying the operator or control system. A flame detector can often respond faster and more accurately than a smoke or heat detector due to the mechanisms it uses to detect the flame.
Home safety is the awareness of risks and potential dangers in and around a home that may cause bodily harm, injury, or even death to those living there.
A post column oxidation-reduction reactor is a chemical reactor that performs derivatization to improve the measurement of organic molecules. It is used in gas chromatography (GC), after the column, and before a flame ionization detector (FID), to make the detector response uniform for all organic molecules.
References
- ↑ Fixed flammable gas detector systems on offshore installations: optimization and assessment of effectiveness (PDF) (Technical report). UK Health and Safety Executive. 2017. Research Report RR1123.
- ↑ Tross, Kasey (2024-01-09). "The Best Gas Leak Detectors". SafeWise. Retrieved 2024-05-23.
- 1 2 "What is Natural Gas". CT.gov - Connecticut's Official State Website. Retrieved 2022-08-14.
- ↑ "Kos Galatsis - Environmental air quality monitoring solutions" . Retrieved 2024-05-23.
