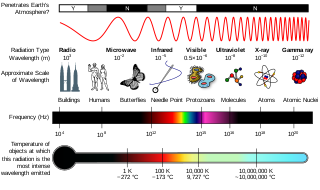
The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength. The spectrum is divided into separate bands, with different names for the electromagnetic waves within each band. From low to high frequency these are: radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. The electromagnetic waves in each of these bands have different characteristics, such as how they are produced, how they interact with matter, and their practical applications.

Infrared is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with waves that are just longer than those of red light, so IR is invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to include wavelengths from around 750 nm (400 THz) to 1 mm (300 GHz). IR is commonly divided between longer-wavelength thermal IR, emitted from terrestrial sources, and shorter-wavelength IR or near-IR, part of the solar spectrum. Longer IR wavelengths (30–100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation band. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is in the IR band. As a form of EMR, IR carries energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon.

Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs, Cherenkov radiation, and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights.
Infrared astronomy is a sub-discipline of astronomy which specializes in the observation and analysis of astronomical objects using infrared (IR) radiation. The wavelength of infrared light ranges from 0.75 to 300 micrometers, and falls in between visible radiation, which ranges from 380 to 750 nanometers, and submillimeter waves.

Forward-looking infrared (FLIR) cameras, typically used on military and civilian aircraft, use a thermographic camera that senses infrared radiation.

Infrared thermography (IRT), thermal video or thermal imaging, is a process where a thermal camera captures and creates an image of an object by using infrared radiation emitted from the object in a process, which are examples of infrared imaging science. Thermographic cameras usually detect radiation in the long-infrared range of the electromagnetic spectrum and produce images of that radiation, called thermograms. Since infrared radiation is emitted by all objects with a temperature above absolute zero according to the black body radiation law, thermography makes it possible to see one's environment with or without visible illumination. The amount of radiation emitted by an object increases with temperature; therefore, thermography allows one to see variations in temperature. When viewed through a thermal imaging camera, warm objects stand out well against cooler backgrounds; humans and other warm-blooded animals become easily visible against the environment, day or night. As a result, thermography is particularly useful to the military and other users of surveillance cameras.

Far infrared (FIR) or long wave refers to a specific range within the infrared spectrum of electromagnetic radiation. It encompasses radiation with wavelengths ranging from 15 μm (micrometers) to 1 mm, which corresponds to a frequency range of approximately 20 THz to 300 GHz. This places far infrared radiation within the CIE IR-B and IR-C bands. The longer wavelengths of the FIR spectrum overlap with a range known as terahertz radiation. Different sources may use different boundaries to define the far infrared range. For instance, astronomers often define it as wavelengths between 25 μm and 350 μm. Infrared photons possess significantly lower energy than photons in the visible light spectrum, with tens to hundreds of times less energy.

Multispectral imaging captures image data within specific wavelength ranges across the electromagnetic spectrum. The wavelengths may be separated by filters or detected with the use of instruments that are sensitive to particular wavelengths, including light from frequencies beyond the visible light range. It can allow extraction of additional information the human eye fails to capture with its visible receptors for red, green and blue. It was originally developed for military target identification and reconnaissance. Early space-based imaging platforms incorporated multispectral imaging technology to map details of the Earth related to coastal boundaries, vegetation, and landforms. Multispectral imaging has also found use in document and painting analysis.

A passive infrared sensor is an electronic sensor that measures infrared (IR) light radiating from objects in its field of view. They are most often used in PIR-based motion detectors. PIR sensors are commonly used in security alarms and automatic lighting applications.

A motion detector is an electrical device that utilizes a sensor to detect nearby motion. Such a device is often integrated as a component of a system that automatically performs a task or alerts a user of motion in an area. They form a vital component of security, automated lighting control, home control, energy efficiency, and other useful systems. It can be achieved by either mechanical or electronic methods. When it is done by natural organisms, it is called motion perception.

Ultraviolet photography is a photographic process of recording images by using radiation from the ultraviolet (UV) spectrum only. Images taken with ultraviolet radiation serve a number of scientific, medical or artistic purposes. Images may reveal deterioration of art works or structures not apparent under light. Diagnostic medical images may be used to detect certain skin disorders or as evidence of injury. Some animals, particularly insects, use ultraviolet wavelengths for vision; ultraviolet photography can help investigate the markings of plants that attract insects, while invisible to the unaided human eye. Ultraviolet photography of archaeological sites may reveal artifacts or traffic patterns not otherwise visible.

An electric eye is a photodetector used for detecting obstruction of a light beam. An example is the door safety system used on garage door openers that use a light transmitter and receiver at the bottom of the door to prevent closing if there is any obstruction in the way that breaks the light beam. The device does not provide an image; only the presence of light is detectable. Visible light may be used, but infrared radiation conceals the operation of the device and typically is used in modern systems. Originally, systems used lamps powered by direct current or the power line alternating current frequency, but modern photodetector systems use an infrared light-emitting diode modulated at a few kilohertz, which allows the detector to reject stray light and improves the range, sensitivity, and security of the device.

A nondispersive infrared sensor is a simple spectroscopic sensor often used as a gas detector. It is non-dispersive in the fact that no dispersive element is used to separate out the broadband light into a narrow spectrum suitable for gas sensing. The majority of NDIR sensors use a broadband lamp source and an optical filter to select a narrow band spectral region that overlaps with the absorption region of the gas of interest. In this context narrow may be 50-300nm bandwidth. Modern NDIR sensors may use Microelectromechanical systems (MEMs) or mid IR LED sources, with or without an optical filter.
A gas detector is a device that detects the presence of gases in an area, often as part of a safety system. A gas detector can sound an alarm to operators in the area where the leak is occurring, giving them the opportunity to leave. This type of device is important because there are many gases that can be harmful to organic life, such as humans or animals.
Electro-optical MASINT is a subdiscipline of Measurement and Signature Intelligence, (MASINT) and refers to intelligence gathering activities which bring together disparate elements that do not fit within the definitions of Signals Intelligence (SIGINT), Imagery Intelligence (IMINT), or Human Intelligence (HUMINT).

Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) is a technique used to obtain an infrared spectrum of absorption or emission of a solid, liquid, or gas. An FTIR spectrometer simultaneously collects high-resolution spectral data over a wide spectral range. This confers a significant advantage over a dispersive spectrometer, which measures intensity over a narrow range of wavelengths at a time.

A missile approach warningsystem (MAW) is part of the avionics package on some military aircraft. A sensor detects attacking missiles. Its automatic warning cues the pilot to make a defensive maneuver and deploy the available countermeasures to disrupt missile tracking.

A Quantum Well Infrared Photodetector (QWIP) is an infrared photodetector, which uses electronic intersubband transitions in quantum wells to absorb photons. In order to be used for infrared detection, the parameters of the quantum wells in the quantum well infrared photodetector are adjusted so that the energy difference between its first and second quantized states match the incoming infrared photon energy. QWIPs are typically made of gallium arsenide, a material commonly found in smartphones and high-speed communications equipment. Depending on the material and the design of the quantum wells, the energy levels of the QWIP can be tailored to absorb radiation in the infrared region from 3 to 20 μm.
Infrared open-path gas detectors send out a beam of infrared light, detecting gas anywhere along the path of the beam. This linear 'sensor' is typically a few metres up to a few hundred metres in length. Open-path detectors can be contrasted with infrared point sensors.

An optical beam smoke detector is a device that uses a projected beam of light to detect smoke across large areas, typically as an indicator of fire. They are used to detect fires in buildings where standard point smoke detectors would either be uneconomical or restricted for use by the height of the building. Optical beam smoke detectors are often installed in warehouses as a cost-effective means of protecting large open spaces.
























