
The foot is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws or nails.

The human leg, in the general word sense, is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh and even the hip or gluteal region. However, the definition in human anatomy refers only to the section of the lower limb extending from the knee to the ankle, also known as the crus or, especially in non-technical use, the shank. Legs are used for standing, and all forms of locomotion including recreational such as dancing, and constitute a significant portion of a person's mass. Female legs generally have greater hip anteversion and tibiofemoral angles, but shorter femur and tibial lengths than those in males.

In human anatomy, the ulnar nerve is a nerve that runs near the ulna bone. The ulnar collateral ligament of elbow joint is in relation with the ulnar nerve. The nerve is the largest in the human body unprotected by muscle or bone, so injury is common. This nerve is directly connected to the little finger, and the adjacent half of the ring finger, innervating the palmar aspect of these fingers, including both front and back of the tips, perhaps as far back as the fingernail beds.

In human anatomy, the metacarpal bones or metacarpus, form the intermediate part of the skeletal hand located between the phalanges of the fingers and the carpal bones of the wrist which forms the connection to the forearm. The metacarpal bones are analogous to the metatarsal bones in the foot.

In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock.

The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.

The opponens digiti minimi is a muscle in the hand. It is of a triangular form, and placed immediately beneath the palmaris brevis, abductor digiti minimi and flexor digiti minimi brevis. It is one of the three hypothenar muscles that control the little finger.

The Adductor hallucis arises by two heads—oblique and transverse and is responsible for adducting the big toe. It has two heads, both are innervated by the lateral plantar nerve.

The plantar nerves are a pair of nerves innervating the sole of the foot. They arise from the posterior branch of the tibial nerve.
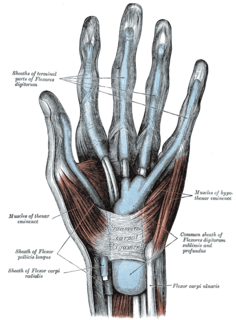
The hypothenar muscles are a group of three muscles of the palm that control the motion of the little finger.
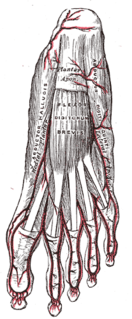
The abductor digiti minimi is a muscle which lies along the lateral (outer) border of the foot, and is in relation by its medial margin with the lateral plantar artery, vein and nerves.

In human anatomy, the abductor digiti minimi is a skeletal muscle situated on the ulnar border of the palm of the hand. It forms the ulnar border of the palm and its spindle-like shape defines the hypothenar eminence of the palm together with the skin, connective tissue, and fat surrounding it. Its main function is to pull the little finger away from the other fingers.

The flexor digiti minimi brevis is a hypothenar muscle in the hand that flexes the little finger at the metacarpophalangeal joint. It lies lateral to the abductor digiti minimi when the hand is in anatomical position.

The sole is the bottom of the foot.

The lateral plantar nerve is a branch of the tibial nerve, in turn a branch of the sciatic nerve and supplies the skin of the fifth toe and lateral half of the fourth, as well as most of the deep muscles, its distribution being similar to that of the ulnar nerve in the hand.

The lateral plantar artery, much larger than the medial, passes obliquely lateralward and forward to the base of the fifth metatarsal bone.

The peroneus muscles are a group of muscles in the leg. While the muscle group exists in many variations, it is normally composed of three muscles: peroneus longus, brevis and tertius. The peroneus muscles originates from lower two-thirds of the lateral surface of the shaft of the fibula and the anterior and posterior inter-muscular septa of the leg. It inserts onto the metatarsals.

The fifth metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot, and is palpable along the distal outer edges of the feet. It is the second smallest of the five metatarsal bones. The fifth metatarsal is analogous to the fifth metacarpal bone in the hand
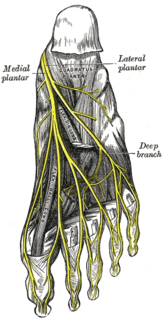
The superficial branch of the lateral plantar nerve splits into a proper and a common plantar digital nerve:
In human anatomy, a brevis muscle derives its name from the Latin brevis meaning "short", and can refer to:


















