Related Research Articles

Alcoholism is the continued drinking of alcohol despite it causing problems. Some definitions require evidence of dependence and withdrawal. Problematic use of alcohol has been mentioned in the earliest historical records. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimated there were 283 million people with alcohol use disorders worldwide as of 2016. The term alcoholism was first coined in 1852, but alcoholism and alcoholic are sometimes considered stigmatizing and to discourage seeking treatment, so diagnostic terms such as alcohol use disorder or alcohol dependence are often used instead in a clinical context.

Alcohol intoxication, commonly described in higher doses as drunkenness or inebriation, and known in overdose as alcohol poisoning, is the behavior and physical effects caused by recent consumption of alcohol. The technical term intoxication in common speech may suggest that a large amount of alcohol has been consumed, leading to accompanying physical symptoms and deleterious health effects. Mild intoxication is mostly referred to by slang terms such as tipsy or buzzed. In addition to the toxicity of ethanol, the main psychoactive component of alcoholic beverages, other physiological symptoms may arise from the activity of acetaldehyde, a metabolite of alcohol. These effects may not arise until hours after ingestion and may contribute to a condition colloquially known as a hangover.

Drinking culture is the set of traditions and social behaviours that surround the consumption of alcoholic beverages as a recreational drug and social lubricant. Although alcoholic beverages and social attitudes toward drinking vary around the world, nearly every civilization has independently discovered the processes of brewing beer, fermenting wine, and distilling spirits, among other practices. Many countries have developed their own regional cultures based on unique traditions around the fermentation and consumption of alcohol, which may also be known as a beer culture, wine culture etc. after a particularly prominent type of drink.

Liquor or distilled beverages are alcoholic drinks produced by the distillation of grains, fruits, vegetables, or sugar that have already gone through alcoholic fermentation. Other terms for liquor include spirit, spirituous liquor or hard liquor. While the word liquor ordinarily refers to distilled alcoholic spirits rather than beverages produced by fermentation alone, it can sometimes be used more broadly to refer to any alcoholic beverage.
Alcohol has a number of effects on health. Short-term effects of alcohol consumption include intoxication and dehydration. Long-term effects of alcohol include changes in the metabolism of the liver and brain, with increased risk of several types of cancer and alcohol use disorder. Alcohol intoxication affects the brain, causing slurred speech, clumsiness, and delayed reflexes. There is an increased risk of developing an alcohol use disorder for teenagers while their brain is still developing. Adolescents who drink have a higher probability of injury including death.
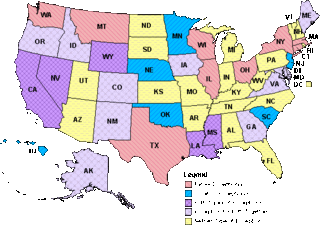
Although the minimum legal age to purchase alcohol is 21 in all U.S. states and most territories, the legal details for consumption vary greatly. Although some states completely ban alcohol usage for people under 18, the majority have exceptions that permit consumption.
Alcohol is any organic compound in which a hydroxyl functional group (-OH) is bound to a carbon atom, usually connected to other carbon or hydrogen atoms. An important class are the simple acyclic alcohols, the general formula for which is CnH2n+1OH. Of those, ethanol (C2H5OH) is the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, and in common speech the word alcohol refers specifically to ethanol. Articles related to alcohol include:

A hangover is the experience of various unpleasant physiological and psychological effects usually following the consumption of alcohol, such as wine, beer, and liquor. Hangovers can last for several hours or for more than 24 hours. Typical symptoms of a hangover may include headache, drowsiness, concentration problems, dry mouth, dizziness, fatigue, gastrointestinal distress, absence of hunger, light sensitivity, depression, sweating, hyper-excitability, irritability, and anxiety.

An alcoholic beverage is a beverage containing alcohol (ethanol). Alcoholic drinks are typically divided into three classes—beers, wines, and spirits—and typically their alcohol content is between 3% and 50%.

Binge drinking, or heavy episodic drinking, is drinking alcoholic beverages with an intention of becoming intoxicated by heavy consumption of alcohol over a short period of time, but definitions vary considerably.

Alcohol is commonly consumed and available at pubs and liquor stores in Australia – all of which are private enterprises. Spirits can be purchased at liquor stores and pubs, whereas most grocery stores do not sell them, although they may have separate liquor stores on their premises. Alcohol consumption is higher, according to WHO studies, than in most European countries and several Central Asian and African countries, although consumption is just as high in Australia as in North America. After tobacco, alcohol is the second leading preventable cause of death and hospitalisation in Australia.

Alcohol laws are laws relating to manufacture, use, being under the influence of and sale of alcohol or alcoholic beverages. Common alcoholic beverages include beer, wine, (hard) cider, and distilled spirits. Definition of alcoholic beverage varies internationally, e.g., the United States defines an alcoholic beverage as "any beverage in liquid form which contains not less than one-half of one percent of alcohol by volume". Alcohol laws can restrict those who can produce alcohol, those who can buy it, when one can buy it, labelling and advertising, the types of alcoholic beverage that can be sold, where one can consume it, what activities are prohibited while intoxicated, and where one can buy it. In some cases, laws have even prohibited the use and sale of alcohol entirely.
Binge drinking is the practice of consuming excessive amounts of alcohol in a short period of time. Due to the idiosyncrasies of the human body, the exact amount of alcohol that would constitute binge drinking differs among individuals. The definitions of binge drinking are also nuanced across cultures and population subgroups. For example, many studies use gender-specific measures of binge drinking. The epidemiology of binge drinking likewise differs across cultures and population subgroups.

A caffeinated alcoholic drink is a drink that contains both alcohol and a significant amount of caffeine. Caffeine, a stimulant, masks some of the depressant effects of alcohol. However, in 2010 and 2011, this type of drink faced criticism for posing health risks to its drinkers. In some places there is a ban on caffeinated alcoholic drinks.

The 17 November 2010 United States ban on caffeinated alcoholic drinks is a ban which prevents the marketing and distribution of any prepackaged caffeinated alcoholic drink.
The legal drinking age varies from country to country. In the United States, the legal drinking age is currently 21. To curb excessive alcohol consumption by younger people, instead of raising the drinking age, other countries have raised the prices of alcohol beverages and encouraged the general public to drink less. Setting a legal drinking age of 21 is designed to discourage reckless alcohol consumption by youth, limiting consumption to those who are more mature, who can be expected to make reasonable and wise decisions when it comes to drinking.
In the alcoholic beverages industry, congeners are substances produced during fermentation other than the desired type of alcohol (ethanol). These substances include small amounts of chemicals such as methanol and other alcohols, acetone, acetaldehyde, esters, tannins, and aldehydes. Congeners are responsible for most of the taste and aroma of distilled alcoholic beverages, and contribute to the taste of non-distilled drinks. Brandy, rum and red wine have the highest amount of congeners, while vodka and beer have the least.

Alcohol, sometimes referred to by the chemical name ethanol, is the second most consumed psychoactive drug globally behind caffeine, and alcohol use disorders are the most prevalent of all substance use disorders worldwide. Alcohol is a central nervous system (CNS) depressant, decreasing electrical activity of neurons in the brain. The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies alcohol as a toxic, psychoactive, dependence-producing, and carcinogenic substance.

Teetotalism is the practice of never consuming alcohol, specifically in alcoholic drinks. A person who practices teetotalism is called a teetotaler (US) or teetotaller (UK), or said to be teetotal. Globally, almost half of adults do not drink alcohol. A number of temperance organisations have been founded in order to promote teetotalism and provide spaces for non-drinkers to socialise.

Many students attending colleges, universities, and other higher education institutions consume alcoholic beverages. The laws and social culture around this practice vary by country and institution type, and within an institution, some students may drink heavily whereas others may not drink at all. In the United States, drinking tends to be particularly associated with fraternities.
References
- 1 2 "Drinking Levels and Patterns Defined | National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA)". www.niaaa.nih.gov.
- ↑ "What Is Intermittent Sobriety—and Why Is Everyone Talking About It Right Now?". Real Simple.
- ↑ "Are You Trying 'Sober October'? Experts Reveal the Surprising Benefits of 'Intermittent Sobriety'". Health.
- ↑ "NHIS - Adult Alcohol Use - Glossary". www.cdc.gov. 10 May 2019.
- ↑ "NHIS - Adult Alcohol Use - Glossary". www.cdc.gov. 10 May 2019.
- ↑ "NHIS - Adult Alcohol Use - Glossary". www.cdc.gov. 10 May 2019.
- ↑ Goddiksen MK (4 January 2023). "Sober Curious er det nye sort'" [Sober Curious is the new kind] (in Danish).