
Adenosine monophosphate (AMP), also known as 5'-adenylic acid, is a nucleotide. AMP consists of a phosphate group, the sugar ribose, and the nucleobase adenine. It is an ester of phosphoric acid and the nucleoside adenosine. As a substituent it takes the form of the prefix adenylyl-.
A nucleoside triphosphate is a nucleoside containing a nitrogenous base bound to a 5-carbon sugar, with three phosphate groups bound to the sugar. They are the molecular precursors of both DNA and RNA, which are chains of nucleotides made through the processes of DNA replication and transcription. Nucleoside triphosphates also serve as a source of energy for cellular reactions and are involved in signalling pathways.
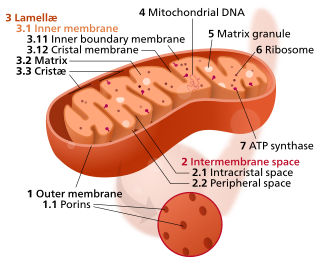
In the mitochondrion, the matrix is the space within the inner membrane. The word "matrix" stems from the fact that this space is viscous, compared to the relatively aqueous cytoplasm. The mitochondrial matrix contains the mitochondrial DNA, ribosomes, soluble enzymes, small organic molecules, nucleotide cofactors, and inorganic ions.[1] The enzymes in the matrix facilitate reactions responsible for the production of ATP, such as the citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, oxidation of pyruvate, and the beta oxidation of fatty acids.
Translocase is a general term for a protein that assists in moving another molecule, usually across a cell membrane. These enzymes catalyze the movement of ions or molecules across membranes or their separation within membranes. The reaction is designated as a transfer from “side 1” to “side 2” because the designations “in” and “out”, which had previously been used, can be ambiguous. Translocases are the most common secretion system in Gram positive bacteria.
In molecular biology, the protein domain SAICAR synthase is an enzyme which catalyses a reaction to create SAICAR. In enzymology, this enzyme is also known as phosphoribosylaminoimidazolesuccinocarboxamide synthase. It is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a beta-glucan-transporting ATPase (EC 3.6.3.42) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a capsular-polysaccharide-transporting ATPase (EC 7.6.2.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glycerol-3-phosphate-transporting ATPase (EC 3.6.3.20) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a maltose-transporting ATPase (EC 3.6.3.19) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a molybdate-transporting ATPase (EC 3.6.3.29) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a monosaccharide-transporting ATPase (EC 3.6.3.17) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a Na+-exporting ATPase (EC 3.6.3.7) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a nickel-transporting ATPase (EC 3.6.3.24) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a nonpolar-amino-acid-transporting ATPase (EC 3.6.3.22) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a nucleoplasmin ATPase (EC 3.6.4.11) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a phosphate-transporting ATPase (EC 3.6.3.27) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a sulfate-transporting ATPase (EC 3.6.3.25) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a teichoic-acid-transporting ATPase (EC 3.6.3.40) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a xenobiotic-transporting ATPase (EC 3.6.3.44) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Steroid-transporting ATPase (EC 3.6.3.45, pleiotropic-drug-resistance protein, PDR protein) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP phosphohydrolase (steroid-exporting). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction



