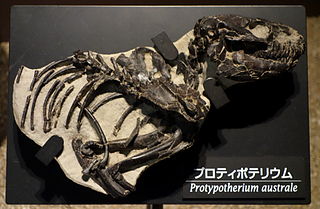
Protypotherium is an extinct genus of notoungulate mammals native to South America during the Oligocene and Miocene epochs. A number of closely related animals date back further, to the Eocene. Fossils of Protypotherium have been found in the Deseadan Fray Bentos Formation of Uruguay, Muyu Huasi and Nazareno Formations of Bolivia, Cura-Mallín and Río Frías Formations of Chile, and Santa Cruz, Salicas, Ituzaingó, Aisol, Cerro Azul, Cerro Bandera, Cerro Boleadoras, Chichinales, Sarmiento and Collón Curá Formations of Argentina.

Cramauchenia is an extinct genus of litoptern South American ungulate. Cramauchenia was named by Florentino Ameghino. The name has no literal translation. Instead, it is an anagram of the name of a related genus Macrauchenia. This genus was initially discovered in the Sarmiento Formation in the Chubut Province, in Argentina, and later it was found in the Chichinales Formation in the Río Negro Province and the Cerro Bandera Formation in Neuquén, also in Argentina, in sediments assigned to the SALMA Colhuehuapian, as well as the Agua de la Piedra Formation in Mendoza, in sediments dated to the Deseadan. In 1981 Soria made C. insolita a junior synonym of C. normalis. A specimen of C. normalis was described in 2010 from Cabeza Blanca in the Sarmiento Formation, in sediments assigned to the Deseadan SALMA.

Mesotheriidae is an extinct family of notoungulate mammals known from the Oligocene through the Pleistocene of South America. Mesotheriids were small to medium-sized herbivorous mammals adapted for digging.

The Malargüe Group is a group of geologic formations of the Neuquén Basin of the Mendoza, Neuquén, Río Negro and La Pampa Provinces in northern Patagonia, Argentina. The formations of the Malargüe Group range in age between the middle Campanian to Deseadan, an Oligocene age of the SALMA classification, straddling the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, about 79 million to 30 million years in age. The group overlies the older Neuquén Group, separated by an unconformity dated to 79 Ma. The rocks of the Malargüe Group comprise both marine and continental deposits which are over 400 m (1312 ft) thick in total.

Hegetotherium is an extinct genus of mammals from the Early to Middle Miocene of South America. Fossils of this genus have been found in the Cerro Bandera, Cerro Boleadoras, Chichinales, Collón Curá, Santa Cruz and Sarmiento Formations of Argentina, the Nazareno Formation of Bolivia, and the Galera and Río Frías Formations of Chile.

Prohegetotherium is an extinct genus of hegetotheriid notoungulates from the Late Oligocene to Early Miocene of the Agua de la Piedra, Mariño & Sarmiento Formations of Argentina, the Petaca and Salla Formations of Bolivia, and Fray Bentos Formation of Uruguay.
The Agua de la Piedra Formation is a Late Oligocene geologic formation of the Malargüe Group that crops out in the southernmost Precordillera and northernmost Neuquén Basin in southern Mendoza Province, Argentina.

Prosotherium is an extinct genus of hegetotheriid notoungulate. It lived during the Late Oligocene, and its fossilized remains were found in South America.
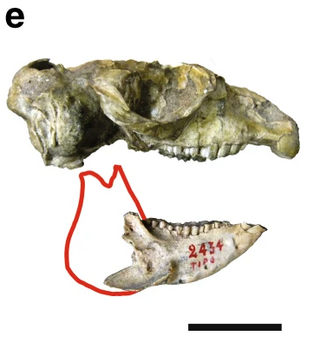
Tremacyllus is an extinct genus of hegetotheriids. It lived from the Late Miocene to the Late Pleistocene and its fossilized remains were discovered in South America.
Proadinotherium is an extinct genus of toxodontid. It lived between the Late Oligocene and the Early Miocene in what is now South America.
Ethegotherium is an extinct genus of Notoungulates, belonging to the suborder Typotheria. It lived from the Lower to the Middle Miocene, and its fossilized remains were discovered in South America. It might be a synonym of the genus Prohegetotherium.
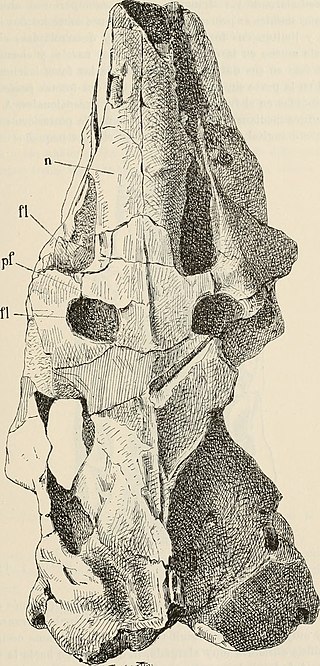
Hemihegetotherium is an extinct genus of hegetotheriid notoungulate that lived from the Middle to the Late Miocene of what is now Argentina.
Propachyrucos is an extinct genus of hegetotheriid notoungulate. It lived from the Late Oligocene to the Early Miocene, in what is today South America.
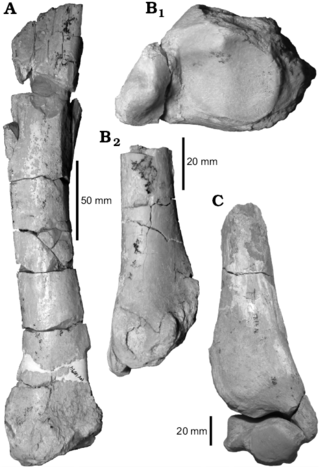
Gualta is an extinct genus of leontiniid notoungulates. It lived during the Late Oligocene of what is now Argentina.
Anayatherium is an extinct genus of notoungulate belonging to the family Leontiniidae. It lived during the Late Oligocene, and its fossilized remains were discovered in South America.

Notopithecus is an extinct genus of Notoungulate, belonging to the suborder Typotheria. It lived from the Middle to the Late Eocene and its fossilized remains were discovered in South America.
Sallatherium is an extinct genus of Notoungulate, belonging to the suborder Typotheria. It lived during the Late Oligocene, and its fossilized remains were discovered in South America.
Rosendo is an extinct genus of notohippid notoungulates that lived during the Early Oligocene in what is now Argentina and Chile. Fossils of this genus have been found in the Sarmiento Formation and the Abanico Formations of Argentina and Chile.
Moqueguahippus is an extinct genus of notohippid notoungulates that lived during the Late Oligocene of what is now Peru. Fossils of this genus have been found in the Moquegua Formation of Peru, which it was named after.
Federicoanaya is an extinct genus of interatheriine notoungulates that lived during the Late Oligocene in what is now Bolivia. Fossils of this genus have been found in the Salla Formation of Bolivia.



















