
Toxodon is an extinct genus of large ungulate native to South America from the Late Miocene to early Holocene epochs. Toxodon is a member of Notoungulata, an order of extinct South American native ungulates distinct from the two living ungulate orders that had been indigenous to the continent for over 60 million years since the early Cenozoic, prior to the arrival of living ungulates into South America around 2.5 million years ago during the Great American Interchange. Toxodon is a member of the family Toxodontidae, which includes medium to large sized herbivores. Toxodon was one of the largest members of Toxodontidae and Notoungulata, with Toxodon platensis having an estimated body mass of 1,000–1,200 kilograms (2,200–2,600 lb).
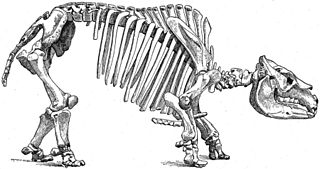
Notoungulata is an extinct order of ungulates that inhabited South America from the early Paleocene to the end of the Pleistocene, living from approximately 61 million to 11,000 years ago. Notoungulates were morphologically diverse, with forms resembling animals as disparate as rabbits and rhinoceroses. Notoungulata are the largest group of South American native ungulates, with over 150 genera in 14 families having been described, divided into two major subgroupings, Typotheria and Toxodontia. Notoungulates first diversified during the Eocene. Their diversity declined from the late Neogene onwards, with only the large toxodontids persisting until the end of the Pleistocene, perishing as part of the Late Pleistocene megafauna extinctions along with most other large mammals across the Americas. Collagen sequence analysis suggests that notoungulates are closely related to litopterns, another group of South American ungulates, and their closest living relatives being perissodactyls, including rhinoceroses, tapirs and equines as part of the clade Panperissodactyla. However their relationships to other South American ungulates are uncertain. Several groups of notoungulates separately evolved ever-growing cheek teeth.

Toxodontia is a suborder of the meridiungulate order Notoungulata. Most of the members of the five included families, including the largest notoungulates, share several dental, auditory and tarsal specializations. The group is named after Toxodon, the first example of the group to be discovered by science.

Peltephilus, the horned armadillo, is an extinct genus of armadillo xenarthran mammals that first inhabited Argentina during the Oligocene epoch, and became extinct in the Miocene epoch. Notably, the scutes on its head were so developed that they formed horns. Aside from the horned gophers of North America, it is the only known fossorial horned mammal. P. ferox had skull about 11.7 centimetres (4.6 in), and estimated body mass is around 11.07 kilograms (24.4 lb).

Theosodon is an extinct genus of litoptern mammal from the Early to Middle Miocene of South America.
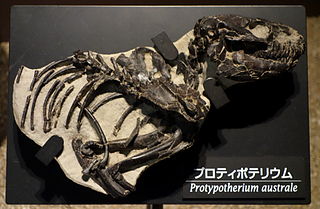
Protypotherium is an extinct genus of notoungulate mammals native to South America during the Oligocene and Miocene epochs. A number of closely related animals date back further, to the Eocene. Fossils of Protypotherium have been found in the Deseadan Fray Bentos Formation of Uruguay, Muyu Huasi and Nazareno Formations of Bolivia, Cura-Mallín and Río Frías Formations of Chile, and Santa Cruz, Salicas, Ituzaingó, Aisol, Cerro Azul, Cerro Bandera, Cerro Boleadoras, Chichinales, Sarmiento and Collón Curá Formations of Argentina.

Adinotherium is an extinct genus of Toxodontidae, large bodied hoofed ungulates which inhabited South America during the Middle to Late Miocene, from 17.5 to 6.8 Ma and existed for approximately 10.7 million years, Santacrucian to Huayquerian in the South American land mammal ages (SALMA). Fossils of Adinotherium have been found in the Santa Cruz and Ituzaingó Formations of Argentina and the Chucal and Río Frías Formations of Chile.
Scalabrinitherium is an extinct genus of mammals of the family Macraucheniidae. Fossils of this animal were found among the fossils of prehistoric xenarthrans in the Ituzaingó Formation of Argentina.

Toxodontidae is an extinct family of notoungulate mammals, known from the Oligocene to the Holocene of South America, with one genus, Mixotoxodon, also known from the Pleistocene of Central America and southern North America. Member of the family were medium to large-sized, ranging from around 350–400 kilograms (770–880 lb) in Nesodon to 1,000–1,200 kilograms (2,200–2,600 lb) in Toxodon, and had medium to high-crowned dentition, which in derived members of the group evolved into ever-growing cheek teeth. Isotopic analyses have led to the conclusion that Pleistocene members of the family were flexible mixed feeders.

Mesotheriidae is an extinct family of notoungulate mammals known from the Oligocene through the Pleistocene of South America. Mesotheriids were small to medium-sized herbivorous mammals adapted for digging.

Mixotoxodon is an extinct genus of notoungulate of the family Toxodontidae inhabiting South America, Central America and parts of southern North America during the Pleistocene epoch, from 1,800,000—12,000 years ago.

Patagornis is a genus of extinct flightless predatory birds of the family Phorusrhacidae. Known as "terror birds", these lived in what is now Argentina during the Early and Middle Miocene; the Santa Cruz Formation in Patagonia contains numerous specimens. Patagornis was an agile, medium sized Patagornithine and was likely a pursuit predator.

Psilopterus is an extinct genus of phorusrhacid from the Middle Oligocene to possibly the Late Pleistocene of Argentina and Uruguay. Compared to other phorusrhacids, members of the genus are both relatively gracile and diminutive, and include the smallest known species of terror bird: with the head raised P. bachmanni was 70–80 centimeters (2.3–2.6 ft) in height and weighed about 5 kilograms (11 lb), while the largest members of the genus were only about 8 kilograms (18 lb). The birds resemble the modern cariama, except with a heavier build and considerably smaller wings. Fossil finds in Uruguay indicate the genus may have survived until 96,040 ± 6,300 years ago, millions of years after the larger phorusrhacids became extinct.
The South American land mammal ages (SALMA) establish a geologic timescale for prehistoric South American fauna beginning 64.5 Ma during the Paleocene and continuing through to the Late Pleistocene. These periods are referred to as ages, stages, or intervals and were established using geographic place names where fossil materials where obtained.

Hegetotherium is an extinct genus of mammals from the Early to Middle Miocene of South America. Fossils of this genus have been found in the Cerro Bandera, Cerro Boleadoras, Chichinales, Collón Curá, Santa Cruz and Sarmiento Formations of Argentina, the Nazareno Formation of Bolivia, and the Galera and Río Frías Formations of Chile.
Fiandraia is an extinct monotypic genus of notoungulate that lived in Uruguay during the Oligocene and the Early Miocene. It was found in the Fray Bentos Formation, in rocks dated back from the Deseadan period.
Proterotherium is an extinct genus of litoptern mammal of the family Proterotheriidae that lived during the Late Miocene of Argentina and Chile. Fossils of this genus have been found in the Ituzaingó Formation of Argentina, and the Galera Formation of Chile.
Proadinotherium is an extinct genus of toxodontid. It lived between the Late Oligocene and the Early Miocene in what is now South America.
Eotypotherium is an extinct genus of mammal, belonging to the suborder Typotheria. It lived during the Early Miocene. Its fossilized remains were discovered in the Chucal Formation, in the Chilean altiplano, near the Salar de Surire, in South America.
Altitypotherium is an extinct genus of Notoungulate, belonging to the suborder Typotheria. It lived during the Early Miocene, and its fossilized remains were discovered in South America.

























