
Pyrotherium is an extinct genus of South American ungulate, of the order Pyrotheria, that lived in what is now Argentina and Bolivia, during the Late Oligocene. It was named Pyrotherium because the first specimens were excavated from an ancient volcanic ash deposit. Fossils of the genus have been found in the Deseado and Sarmiento Formations of Argentina and the Salla Formation of Bolivia.
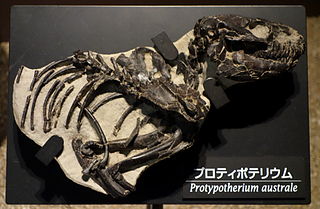
Protypotherium is an extinct genus of notoungulate mammals native to South America during the Oligocene and Miocene epochs. A number of closely related animals date back further, to the Eocene. Fossils of Protypotherium have been found in the Deseadan Fray Bentos Formation of Uruguay, Muyu Huasi and Nazareno Formations of Bolivia, Cura-Mallín and Río Frías Formations of Chile, and Santa Cruz, Salicas, Ituzaingó, Aisol, Cerro Azul, Cerro Bandera, Cerro Boleadoras, Chichinales, Sarmiento and Collón Curá Formations of Argentina.

Cramauchenia is an extinct genus of litoptern South American ungulate. Cramauchenia was named by Florentino Ameghino. The name has no literal translation. Instead, it is an anagram of the name of a related genus Macrauchenia. This genus was initially discovered in the Sarmiento Formation in the Chubut Province, in Argentina, and later it was found in the Chichinales Formation in the Río Negro Province and the Cerro Bandera Formation in Neuquén, also in Argentina, in sediments assigned to the SALMA Colhuehuapian, as well as the Agua de la Piedra Formation in Mendoza, in sediments dated to the Deseadan. In 1981 Soria made C. insolita a junior synonym of C. normalis. A specimen of C. normalis was described in 2010 from Cabeza Blanca in the Sarmiento Formation, in sediments assigned to the Deseadan SALMA.

Astrapotheria is an extinct order of South American and Antarctic hoofed mammals that existed from the late Paleocene to the Middle Miocene, 59 to 11.8 million years ago. Astrapotheres were large, rhinoceros-like animals and have been called one of the most bizarre orders of mammals with an enigmatic evolutionary history.
The Colhuehuapian age is a period of geologic time within the Early Miocene epoch of the Neogene, used more specifically within the SALMA classification in South America. It follows the Deseadan and precedes the Santacrucian age.

Astrapotherium is an extinct genus of large astrapotherian ungulate native to South America during the early-middle Miocene. It is the best known member of the group. The type species. A. magnus have been found in the Santa Cruz Formation in Argentina. Other fossils have been found in the Deseado, Sarmiento, and Aisol Formations of Argentina and Chile.

Astrapotheriidae is an extinct family of herbivorous South American land mammals that lived from the Late Eocene to the Middle Miocene 37.71 to 15.98 million years ago. The most derived of the astrapotherians, they were also the largest and most specialized mammals in the Tertiary of South America. There are two sister taxa: Eoastrapostylopidae and Trigonostylopidae.
Comahuetherium is an extinct genus of astrapotherian mammal from the Early Miocene. It is a basal astrapotheriid which lived in what is now Patagonia, Argentina. The holotype was found in the Cerro Bandera Formation in Neuquén Province, northern Patagonia and additional specimens were found at the Gran Barranca south of Lake Colhué Huapi, in Chubut Province of central Patagonia. It was first named by Alejandro Kramarz and Mariano Bond in 2011 and the type species is Comahuetherium coccaorum.

Xenastrapotherium is an extinct genus of astrapothere, a type of hoofed herbivorous mammal, native to South America, which lived in the Middle to Late Miocene period, typically during the Laventan stage. It is a member of the family Astrapotheriidae in the subfamily Uruguaytheriinae, large astrapotheres, equipped with a trunk-like nose and protruding teeth, similar to the elephants, but their tusks were the canine teeth, not the incisors. Xenastrapotherium was a genus widely distributed in northern South America, in contrast to other species of astrapotheres which lived in the area of the Southern Cone of the continent. It differed from other astrapotheres by having two lower incisors on each side of the jaw and the tusks have a pronounced longitudinal curvature, although their general shape and size are probably very similar to Astrapotherium, whose weight would be 900 to 1,500 kilograms, comparable to the current black rhinoceros.

Parastrapotherium is an extinct genus of South American land mammal that existed from the Late Oligocene to the Early Miocene. The genus includes some of the largest and smallest known astrapotherian, but at present no generally recognized description can adequately characterize it.

Hilarcotherium is an extinct genus of astrapotheriid mammals that lived in South America during the Middle Miocene (Laventan). The type species is H. castanedaii, found in sediments of the La Victoria Formation, part of the Honda Group in the department of Tolima in Colombia. In 2018, Carrillo et al. described a partial skull and mandible of a second species H. miyou from the Castilletes Formation in the Cocinetas Basin of northern Colombia, and estimated the body weight of the animal at 6,465 kilograms (14,253 lb).

Astraponotus is an extinct genus of astrapotheriids. It lived during the Middle-Late Eocene and its fossil remains have been found in the Sarmiento Formation of Argentina, South America.
Proadinotherium is an extinct genus of toxodontid. It lived between the Late Oligocene and the Early Miocene in what is now South America.

Propachyrucos is an extinct genus of hegetotheriid notoungulate. It lived from the Late Oligocene to the Early Miocene, in what is today South America.
Hegetotheriopsis is an extinct genus of hegetotheriid notoungulate. It lived from the Late Oligocene to the Early Miocene, and its fossilized remains are found in Argentina.

Prozaedyus is an extinct genus of chlamyphorid armadillo that lived during the Middle Oligocene and Middle Miocene in what is now South America.

The Cerro Bandera Formation is a geological formation in Neuquén Province, Argentina, in northern Patagonia, which dates to the Early Miocene, around 21 to 17.5 million years ago. It predominantly consists of pyroclastic deposits, which were deposited in a semi-arid environment. It is divided up into a number of members. The diverse fauna of the Cerro Bandera Formation include a variety of turtles and birds, also includes many mammals such as South American native ungulates as well as armadillos, and caviomorph rodents.
The Chichinales Formation is a geological formation in Río Negro Province, Argentina which dates from the Late Oligocene to the Early Miocene, around 23 to 17.5 million years ago. It predominantly consists of pyroclastic deposits, which were deposited in a semi-arid environment. It is divided up into a number of members. The diverse fauna of the Chichinales Formation, including a variety of turtles and birds, also includes many mammals such as South American native ungulates as well as armadillos, and caviomorph rodents.

Perimys is an extinct genus of neoepiblemid rodent that lived from the Early to Late Miocene in what is now South America. Fossils have been found in the Cerro Bandera, Cerro Boleadoras, Ituzaingó, Santa Cruz, and Sarmiento Formations of Argentina, and the Galera, Santa Cruz and Río Frías Formations of Chile.
Eoviscaccia is an extinct genus of chinchillid rodent that lived during the Early Oligocene (Tinguirirican) to the Early Miocene (Colhuehuapian) in what is now South America. Fossils of this genus have been found in the Cerro Bandera, Chichinales, Fray Bentos, and Sarmiento Formations of Argentina, the Salla Formation of Bolivia, and the Abanico Formation of Chile.






















