
Xenungulata is an order of extinct and primitive South American hoofed mammals that lived from the Late Paleocene to Early Eocene. Fossils of the order are known from deposits in Brazil, Argentina, Peru, and Colombia. The best known member of this enigmatic order is the genus Carodnia, a tapir-like and -sized animal with a gait similar to living African elephants.

Trigonostylops is an extinct genus of South American meridiungulatan ungulate, from the Late Paleocene to Late Eocene of South America and Antarctica. It is the only member of the family Trigonostylopidae.

Pyrotherium is an extinct genus of South American ungulate, of the order Pyrotheria, that lived in what is now Argentina and Bolivia, during the Late Oligocene. It was named Pyrotherium because the first specimens were excavated from an ancient volcanic ash deposit. Fossils of the genus have been found in the Deseado and Sarmiento Formations of Argentina and the Salla Formation of Bolivia.
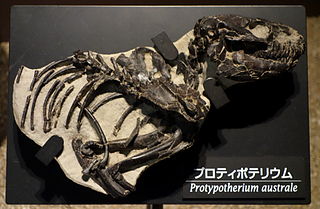
Protypotherium is an extinct genus of notoungulate mammals native to South America during the Oligocene and Miocene epochs. A number of closely related animals date back further, to the Eocene. Fossils of Protypotherium have been found in the Deseadan Fray Bentos Formation of Uruguay, Muyu Huasi and Nazareno Formations of Bolivia, Cura-Mallín and Río Frías Formations of Chile, and Santa Cruz, Salicas, Ituzaingó, Aisol, Cerro Azul, Cerro Bandera, Cerro Boleadoras, Chichinales, Sarmiento and Collón Curá Formations of Argentina.

Cramauchenia is an extinct genus of litoptern South American ungulate. Cramauchenia was named by Florentino Ameghino. The name has no literal translation. Instead, it is an anagram of the name of a related genus Macrauchenia. This genus was initially discovered in the Sarmiento Formation in the Chubut Province, in Argentina, and later it was found in the Chichinales Formation in the Río Negro Province and the Cerro Bandera Formation in Neuquén, also in Argentina, in sediments assigned to the SALMA Colhuehuapian, as well as the Agua de la Piedra Formation in Mendoza, in sediments dated to the Deseadan. In 1981 Soria made C. insolita a junior synonym of C. normalis. A specimen of C. normalis was described in 2010 from Cabeza Blanca in the Sarmiento Formation, in sediments assigned to the Deseadan SALMA.

Astrapotheria is an extinct order of South American and Antarctic hoofed mammals that existed from the late Paleocene to the Middle Miocene, 59 to 11.8 million years ago. Astrapotheres were large, rhinoceros-like animals and have been called one of the most bizarre orders of mammals with an enigmatic evolutionary history.

Astrapotherium is an extinct genus of large astrapotherian ungulate native to South America during the early-middle Miocene. It is the best known member of the group. The type species. A. magnus have been found in the Santa Cruz Formation in Argentina. Other fossils have been found in the Deseado, Sarmiento, and Aisol Formations of Argentina and Chile.

Granastrapotherium is an extinct genus of ungulate mammals, described from remains found in rocks of the Honda Group in the Tatacoa Desert, in the Colombian departments of Huila and Tolima, at the Miocene fossil site La Venta. The only species formally recognized is Granastrapotherium snorki. Remains found in Bolivia and Peru, seem to belong to Granastrapotherium or a very similar animal.

Hilarcotherium is an extinct genus of astrapotheriid mammals that lived in South America during the Middle Miocene (Laventan). The type species is H. castanedaii, found in sediments of the La Victoria Formation, part of the Honda Group in the department of Tolima in Colombia. In 2018, Carrillo et al. described a partial skull and mandible of a second species H. miyou from the Castilletes Formation in the Cocinetas Basin of northern Colombia, and estimated the body weight of the animal at 6,465 kilograms (14,253 lb).

Astraponotus is an extinct genus of astrapotheriids. It lived during the Middle-Late Eocene and its fossil remains have been found in the Sarmiento Formation of Argentina, South America.
The Río Loro Formation is a geological formation of the Sierras Pampeanas in Tucumán Province Argentina whose strata date back to the Late Paleocene of the Paleogene, or Riochican in the SALMA classification.
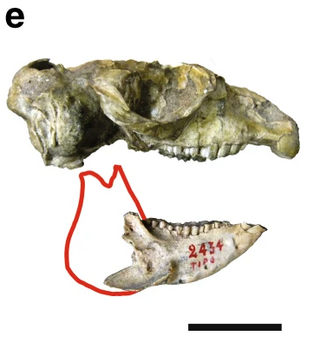
Tremacyllus is an extinct genus of hegetotheriids. It lived from the Late Miocene to the Late Pleistocene and its fossilized remains were discovered in South America.
Ernestokokenia is an extinct genus of mammal, belonging to the Didolodontidae. It lived during the Early Eocene and the Middle Eocene, and its fossils were discovered in South America.
Tetragonostylops is an extinct genus of mammal, related to Astrapotheria. It lived during the Late Paleocene, and its fossils were discovered in South America.
Astrapothericulus is an extinct genus of mammals, belonging to the order Astrapotheria. It lived during the Lower Miocene in what is now South America.
Notonychops is an extinct genus of mammal, belonging to the order Litopterna, that lived during the Middle to Late Paleocene in what is today South America.
Proectocion is an extinct genus of adianthid litoptern. It lived during the Early Eocene, in what is now South America.

Notopithecus is an extinct genus of Notoungulate, belonging to the suborder Typotheria. It lived from the Middle to the Late Eocene and its fossilized remains were discovered in South America.
The Sarmiento Formation, in older literature described as the Casamayor Formation, is a geological formation in Chubut Province, Argentina, in central Patagonia, which spans around 30 million years from the mid-Eocene to the early Miocene. It predominantly consists of pyroclastic deposits, which were deposited in a semi-arid environment. It is divided up into a number of members. The diverse fauna of the Sarmiento Formation, including a variety of birds, crocodilians, turtles and snakes, also includes many mammals such as South American native ungulates as well as armadillos, and caviomorph rodents.
Liarthrus is a genus of astrapotheriid mammal known from the Late Oligocene Sarmiento Formation of Santa Cruz Province, Argentina. It was described by the Argentine paleontologist Florentino Ameghino in 1895 along with several other genera from the "Pyrotherium Beds", which were then believed to date to the Cretaceous period. Ameghino described Liarthus on the basis of fragmentary, being only a right astragalus, premolar 4, and an incomplete premolar from the upper jaws. Only one species was described, L. copei, the species name honoring the American paleontologist Edward Drinker Cope, who lived during the same interval as Ameghino. Liarthrus was synonymized with the other astrapothere Parastrapotherium in 1914 by American mammologist Frederic Loomis, though it was revalidated by a 2008 analysis of Parastrapotherium. Liarthrus was a herbivorous mammal, being an astrapothere, which had large tusks on their skulls and mandibles in addition to a large body size.






















