
Condylarthra is an informal group – previously considered an order – of extinct placental mammals, known primarily from the Paleocene and Eocene epochs. They are considered early, primitive ungulates. It is now largely considered to be a wastebasket taxon, having served as a dumping ground for classifying ungulates which had not been clearly established as part of either Perissodactyla or Artiodactyla, being composed thus of several unrelated lineages.

Bisonalveus is an extinct genus of shrew-like mammals that were presumably ground-dwelling and fed on plants and insects. Bisonalveus fossils have been discovered in the upper Great Plains region of North America, including sites in modern-day Wyoming, North Dakota, Montana, and Alberta. The fossils have been dated to 60 million years ago, during the Tiffanian North American Stage of the Palaeocene epoch. Bisonalveus is the last known genus of the Pentacodontinae sub-family to have arisen, replacing the genus Coriphagus in the early Tiffanian. Bisonalveus itself appears to have gone extinct by the middle Tiffanian.

Pyrotheria is an order of extinct meridiungulate mammals. These elephant-like ungulates include the genera Baguatherium, Carolozittelia, Colombitherium, Griphodon, Propyrotherium, Proticia, and Pyrotherium.

Xenungulata is an order of extinct and primitive South American hoofed mammals that lived from the Late Paleocene to Early Eocene. Fossils of the order are known from deposits in Brazil, Argentina, Peru, and Colombia. The best known member of this enigmatic order is the genus Carodnia, a tapir-like and -sized animal with a gait similar to living African elephants.
Victorlemoinea is an extinct litoptern genus of the family Sparnotheriodontidae, that lived from the Early to Middle Eocene. Fossils of Victorlemoinea have been found in the Las Flores, Sarmiento and Koluel Kaike Formations of Argentina, the Itaboraí Formation of Brazil and La Meseta Formation, Antarctica.

Carodnia is an extinct genus of South American ungulate known from the Early Eocene of Brazil, Argentina, and Peru. Carodnia is placed in the order Xenungulata together with Etayoa and Notoetayoa.

Astrapotheria is an extinct order of South American and Antarctic hoofed mammals that existed from the late Paleocene to the Middle Miocene, 59 to 11.8 million years ago. Astrapotheres were large, rhinoceros-like animals and have been called one of the most bizarre orders of mammals with an enigmatic evolutionary history.

The Itaboraian age is a period within the Early Eocene geologic time epoch of the Paleogene, used more specifically with South American land mammal ages (SALMA). It follows the Riochican and precedes the Casamayoran age.
Hunter-Schreger bands, commonly abbreviated as HSB, are features of the enamel of the teeth in mammals, mostly placentals. In HSB, enamel prisms are arranged in layers of varying thickness at about right angles to each other. HSB strengthen the enamel and prevent cracks from propagating through the tooth.

Polydolopimorphia is an extinct order of metatherians, more closely related to extant marsupials than other extinct mammals. Known from the Paleocene-Pliocene of South America and the Eocene of Antarctica, they were a diverse group during the Paleogene, filling many niches, before declining and becoming extinct at the end of the Neogene. It is divided into two suborders, Bonapartheriiformes, and Polydolopiformes Most members are only known from jaw fragments, which have their characteristically generally bunodont teeth. The morphology of their teeth has led to proposals that polydolopimorphians may be crown group marsupials, nested within Australidelphia, though this proposal, and the monophyly of the order as a whole has been questioned, with other analyses finding them outside of crown-group Marsupialia. The group contained omnivorous, frugivorous and herbivorous forms.

The Itaboraí Formation is a highly fossiliferous geologic formation and Lagerstätte of the Itaboraí Basin in Rio de Janeiro, southeastern Brazil. The formation reaching a thickness of 100 metres (330 ft) is the defining unit for the Itaboraian South American land mammal age (SALMA), dating to the Early Eocene, approximately 53 to 50 Ma.
Ernestokokenia is an extinct genus of mammal, belonging to the Didolodontidae. It lived during the Early Eocene and the Middle Eocene, and its fossils were discovered in South America.
Paulogervaisia is an extinct genus of mammal, belonging to the family Didolodontidae. Its fossilized remains have been found in South America.
Sparnotheriodontidae is an enigmatic extinct family of litopterns known primarily from teeth. Sparnotheriodontids are one of two South American native ungulate clades known to have reached Antarctica, the other being astrapotheres.
Tetragonostylops is an extinct genus of mammal, related to Astrapotheria. It lived during the Late Paleocene, and its fossils were discovered in South America.
Asmithwoodwardia is an extinct genus of mammals, from the order Litopterna. It lived during the Late Paleocene and the Early Eocene, and its fossilized remains were found in South America.
Protolipterna is an extinct genus of mammal, belonging to the order Litopterna. It lived during the Late Paleocene and the Early Eocene, in what is now South America.
Polymorphis is an extinct genus of litopterns belonging to the family Macraucheniidae. It lived during the Middle Eocene of Argentina.

Anisolambda is an extinct genus of litoptern. It lived from the Late Paleocene to the Middle Eocene in what is now Argentina.
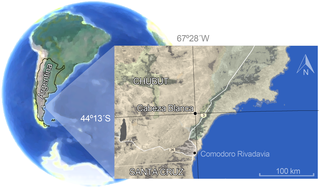
The Sarmiento Formation, in older literature described as the Casamayor Formation, is a geological formation in Chubut Province, Argentina, in central Patagonia, which spans around 30 million years from the mid-Eocene to the early Miocene. It predominantly consists of pyroclastic deposits, which were deposited in a semi-arid environment. It is divided up into a number of members. The diverse fauna of the Sarmiento Formation, including a variety of birds, crocodilians, turtles and snakes, also includes many mammals such as South American native ungulates as well as armadillos, and caviomorph rodents.


















