
Rhynchippus is an extinct genus of notoungulate mammals from the Late Oligocene of South America. The genus was first described by Florentino Ameghino in 1897 and the type species is R. equinus, with lectotype MACN A 52–31. Fossils of Rhynchippus have been found in the Agua de la Piedra and Sarmiento Formations of Argentina, the Salla and Petaca Formations of Bolivia, the Tremembé Formation of Brazil, and the Moquegua Formation of Peru.

Leontiniidae is an extinct family comprising eighteen genera of notoungulate mammals known from the Middle Eocene (Mustersan) to Late Miocene (Huayquerian) of South America.

Mesotheriidae is an extinct family of notoungulate mammals known from the Oligocene through the Pleistocene of South America. Mesotheriids were small to medium-sized herbivorous mammals adapted for digging.
The Deseadan age is a period of geologic time within the Oligocene epoch of the Paleogene to the Early Miocene epoch of the Neogene, used more specifically within the SALMA classification of South America. It follows the Tinguirirican and precedes the Colhuehuapian age.

The Malargüe Group is a group of geologic formations of the Neuquén Basin of the Mendoza, Neuquén, Río Negro and La Pampa Provinces in northern Patagonia, Argentina. The formations of the Malargüe Group range in age between the middle Campanian to Deseadan, an Oligocene age of the SALMA classification, straddling the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, about 79 million to 30 million years in age. The group overlies the older Neuquén Group, separated by an unconformity dated to 79 Ma. The rocks of the Malargüe Group comprise both marine and continental deposits which are over 400 m (1312 ft) thick in total.
Cuyo Basin is a sedimentary basin in Mendoza Province, western Argentina. The Cuyo Basin has a NNW-SSE elongated shape and is limited to the west by the Sierra Pintada System and to the east by the Pampean pericraton. To the north the basin reaches the area around the city of Mendoza.

Archaeohyrax is a genus of extinct notoungulate mammal known from the Middle Eocene to Oligocene of Argentina and Bolivia.

Prohegetotherium is an extinct genus of hegetotheriid notoungulates from the Late Oligocene to Early Miocene of the Agua de la Piedra, Mariño & Sarmiento Formations of Argentina, the Petaca and Salla Formations of Bolivia, and Fray Bentos Formation of Uruguay.
The Agua de la Piedra Formation is a Late Oligocene geologic formation of the Malargüe Group that crops out in the southernmost Precordillera and northernmost Neuquén Basin in southern Mendoza Province, Argentina.
Proadinotherium is an extinct genus of toxodontid. It lived between the Late Oligocene and the Early Miocene in what is now South America.
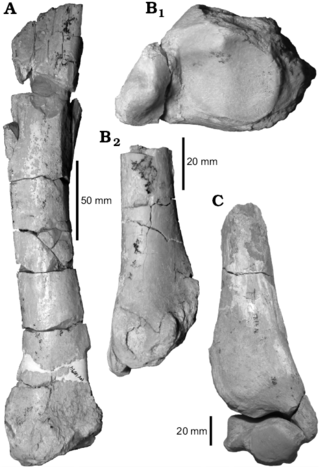
Gualta is an extinct genus of leontiniid notoungulates. It lived during the Late Oligocene of what is now Argentina.
Asmodeus is an extinct genus of mammal, belonging to the order Notoungulata. It lived during the Late Oligocene, in what is today South America.

Interatheriinae is an extinct subfamily of interatheriids that consisted of notoungulates dating from the Early Eocene to the Early Pliocene. The subfamily includes the genera Archaeophylus, Argyrohyrax, Boleatherium, Brucemacfaddenia, Caenophilus, Choichephilum, Cochilius, Eopachyrucos, Federicoanaya, Interatherium, Juchuysillu, Miocochilius, Neoicochilus, Patriarchus, Proargyrohyrax, Progaleopithecus, Protypotherium, and Santiagorothia. They were small to medium sized interatheres, and when compared to the other subfamily, Notopithecinae, interatheriines are found to occupy an advanced, derived position in the family.
Argyrohyrax is an extinct genus of interatheriid notoungulate that lived during the Late Oligocene, of what is now Argentina and Bolivia.

Cochilius is an extinct genus of interatheriid notoungulate that lived between the Late Oligocene and the lower Miocene in what is now Argentina.
Hegetotheriopsis is an extinct genus of hegetotheriid notoungulate. It lived from the Late Oligocene to the Early Miocene, and its fossilized remains are found in Argentina.
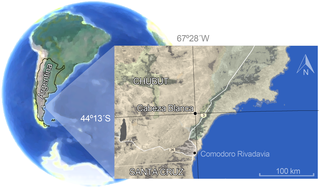
The Sarmiento Formation, in older literature described as the Casamayor Formation, is a geological formation in Chubut Province, Argentina, in central Patagonia, which spans around 30 million years from the mid-Eocene to the early Miocene. It predominantly consists of pyroclastic deposits, which were deposited in a semi-arid environment. It is divided up into a number of members. The diverse fauna of the Sarmiento Formation, including a variety of birds, crocodilians, turtles and snakes, also includes many mammals such as South American native ungulates as well as armadillos, and caviomorph rodents.
Moqueguahippus is an extinct genus of notohippid notoungulates that lived during the Late Oligocene of what is now Peru. Fossils of this genus have been found in the Moquegua Formation of Peru, which it was named after.
Progaleopithecus is an extinct genus of interatheriid notoungulate that lived during the Late Oligocene of Argentina. Fossils of this genus have been found in the Agua de la Piedra, Deseado, and Sarmiento Formations of Argentina.
Federicoanaya is an extinct genus of interatheriine notoungulates that lived during the Late Oligocene in what is now Bolivia. Fossils of this genus have been found in the Salla Formation of Bolivia.


















