Litopterna is an extinct order of South American native ungulates that lived from the Paleocene to the end of the Pleistocene-early Holocene around 62.5 million-12,000 years ago, and were also present in Antarctica during the Eocene. They represent the second most diverse group of South American ungulates after Notoungulata. It is divided into nine families, with Proterotheriidae and Macraucheniidae being the most diverse and last surviving families.

South American native ungulates, commonly abbreviated as SANUs, are extinct ungulate-like mammals that were indigenous to South America from the Paleocene until the end of the Late Pleistocene. They represented a dominant element of South America's Cenozoic terrestrial mammal fauna prior to the arrival of living unguate groups in South America during the Pliocene and Pleistocene as part of the Great American Interchange. They comprise five major groups conventionally ranked as orders—Astrapotheria, Litopterna, Notoungulata, Pyrotheria, and Xenungulata—as well as the primitive "condylarth" groups Didolodontidae and Kollpaniinae. It has been proposed that some or all of the members of this group form a clade, named Meridiungulata, though the relationships of South American ungulates remain largely unresolved. The two largest groups of South American ungulates, the notoungulates and the litopterns, were the only groups to persist beyond the mid Miocene. Only a few species of notoungulates and litopterns survived until the end-Pleistocene extinction event around 12,000 years ago where they became extinct with most other large mammals in the Americas, shortly after the first arrival of humans into the region.

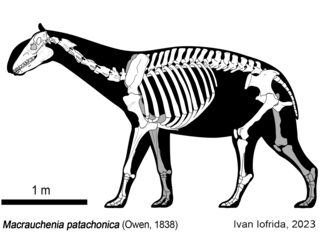
Macrauchenia is an extinct genus of large ungulate native to South America from the Pliocene or Middle Pleistocene to the end of the Late Pleistocene. It is a member of the extinct order Litopterna, a group of South American native ungulates distinct from the two orders which contain all living ungulates which had been present in South America since the early Cenozoic, over 60 million years ago, prior to the arrival of living ungulates in South America around 2.5 million years ago as part of the Great American Interchange. The bodyform of Macrauchenia has been described as similar to a camel, being one of the largest-known litopterns, with an estimated body mass of around 1 tonne. The genus gives its name to its family, Macraucheniidae, which like Macrauchenia typically had long necks and three-toed feet, as well as a retracted nasal region, which in Macrauchenia manifests as the nasal opening being on the top of the skull between the eye sockets. This has historically been argued to correspond to the presence of a tapir-like proboscis, though recent authors suggest a moose-like prehensile lip or a saiga antelope-like nose to filter dust are more likely.

Macraucheniidae is a family in the extinct South American ungulate order Litopterna, that resembled camelids. They had three functional digits on the fore and hind feet, as well as elongate necks. The family is generally divided up into two subfamilies, Cramaucheniinae and Macraucheniinae. The family shows retraction of the nasal region, most extremely to the top of the skull in derived macraucheniine taxa like Macrauchenia. which has been interpreted to have supported a probsocis, perhaps like that of a saiga antelope to filter dust, or a moose-like prehensile lip. The earliest unambiguous members of the family date to the late Oligocene around 30 million years ago. Polymorphis from the Eocene has historically been placed as a macraucheniid, but this has been doubted. Most early representatives had a body masses in the range of 80–120 kilograms (180–260 lb), though some like Llullataruca were as small as 35–55 kilograms (77–121 lb), and the last representatives of the family from the Pleistocene like Macrauchenia were over 1,000 kilograms (2,200 lb). The family reached its apex of diversity during the late Miocene around 10-6 million years ago, before declining to only a few species belong to the genera Macrauchenia and Xenorhinotherium by the Late Pleistocene.

Theosodon is an extinct genus of litoptern mammal from the Early to Middle Miocene of South America.
Paranauchenia is an extinct genus of South American litopterns belonging to the family Macraucheniidae. It is known only from fossil finds in Argentina. It possessed three toes and long limbs. The species Paranauchenia denticulata lived in the Miocene epoch in Argentina. Fossils have been found in the Arroyo Chasicó and Ituzaingó Formations of Argentina.
Huayqueriana is an extinct genus of South American litoptern, related to Macrauchenia, and belonging to the same family, Macraucheniidae. It was formerly known as Macrauchenidia latidens, described in 1939 by Cabrera, but redefined as Huayqueriana in 2016 based on the earlier name convention of Rovereto 1914. The genus is named after the Huayquerías Formation and the eponymous Huayquerian South American land mammal age defined at the formation.

Xenorhinotherium is an extinct genus of macraucheniine macraucheniids, native to northern South America during the Pleistocene epoch, closely related to Macrauchenia of Patagonia. The type species is X. bahiense.

Cramauchenia is an extinct genus of litoptern South American ungulate. Cramauchenia was named by Florentino Ameghino. The name has no literal translation. Instead, it is an anagram of the name of a related genus Macrauchenia. This genus was initially discovered in the Sarmiento Formation in the Chubut Province, in Argentina, and later it was found in the Chichinales Formation in the Río Negro Province and the Cerro Bandera Formation in Neuquén, also in Argentina, in sediments assigned to the SALMA Colhuehuapian, as well as the Agua de la Piedra Formation in Mendoza, in sediments dated to the Deseadan. In 1981 Soria made C. insolita a junior synonym of C. normalis. A specimen of C. normalis was described in 2010 from Cabeza Blanca in the Sarmiento Formation, in sediments assigned to the Deseadan SALMA.
Scalabrinitherium is an extinct genus of mammals of the family Macraucheniidae. Fossils of this animal were found among the fossils of prehistoric xenarthrans in the Ituzaingó Formation of Argentina.

Proterotheriidae is an extinct family of litoptern ungulates known from the Eocene-Late Pleistocene of South America. Members of the group were small-medium sized cursorial herbivores with brachydont teeth, with their toes showing progressive reduction, with later members of the group bearing weight on a single large toe similar to living horses.

Neolicaphrium is an extinct genus of ungulate mammal belonging to the extinct order Litopterna. This animal lived from the Late Pliocene (Chapadmalalan) to the Late Pleistocene (Lujanian) in southern South America, being the last survivor of the family Proterotheriidae.
Cullinia is an extinct genus of litoptern, an order of South American native ungulates that included horse-like and camel-like animals such as Macrauchenia. It is only known from fragmentary remains. Cullinia levis is known from Chasicoan remains found in the Arroyo Chasicó Formation of Argentina, and remains from the Brazilian state of Acre and the Huayquerian Ituzaingó Formation have been assigned to Cullinia sp..

Cramaucheniinae is a paraphyletic subfamily of macraucheniids that originated in the middle Eocene. The size range of the group ranged from small, basal forms to larger and more derived forms. During their evolution, the cramaucheniines undergone a trend from evolving from small basal forms such as Polymorphis into larger, more derived taxa such as Theosodon.
Promacrauchenia is an extinct genus of macraucheniids that lived during the Late Miocene to Late Pliocene epochs of what is now Argentina and Bolivia. It belongs to the subfamily Macraucheniinae, which also includes Huayqueriana, Macrauchenia, and Xenorhinotherium. Fossils of this genus have been found in the Ituzaingó, Andalhuala, and Cerro Azul Formations of Argentina.
Windhausenia is an extinct genus of mammals belonging to the family Macraucheniidae and the order Litopterna. While it reached the size of its better known relative Macrauchenia, its constitution was lighter. Remains from the genus have been uncovered in Argentina.
Sparnotheriodontidae is an enigmatic extinct family of litopterns known primarily from teeth. Sparnotheriodontids are one of two South American native ungulate clades known to have reached Antarctica, the other being astrapotheres.
Polymorphis is an extinct genus of litopterns belonging to the family Macraucheniidae. It lived during the Middle Eocene of Argentina.

Paramacrauchenia is an extinct genus of proterotheriid litopterns from the Early Miocene of what is now Argentina and Chile. Its fossils have been found in the Sarmiento and Santa Cruz Formations of Argentina and Chile.
Pternoconius is an extinct genus of macraucheniid litoptern from the Late Oligocene and Early Miocene of Argentina. Fossils of this genus have been found in the Sarmiento Formation of Argentina.

















