
Integrins are transmembrane receptors that help cell-cell and cell-extracellular matrix (ECM) adhesion. Upon ligand binding, integrins activate signal transduction pathways that mediate cellular signals such as regulation of the cell cycle, organization of the intracellular cytoskeleton, and movement of new receptors to the cell membrane. The presence of integrins allows rapid and flexible responses to events at the cell surface.
Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) are a subset of cell surface proteins that are involved in the binding of cells with other cells or with the extracellular matrix (ECM), in a process called cell adhesion. In essence, CAMs help cells stick to each other and to their surroundings. CAMs are crucial components in maintaining tissue structure and function. In fully developed animals, these molecules play an integral role in generating force and movement and consequently ensuring that organs are able to execute their functions normally. In addition to serving as "molecular glue", CAMs play important roles in the cellular mechanisms of growth, contact inhibition, and apoptosis. Aberrant expression of CAMs may result in a wide range of pathologies, ranging from frostbite to cancer.

DSCAM and Dscam are both abbreviations for Down syndrome cell adhesion molecule. In humans, DSCAM refers to a gene that encodes one of several protein isoforms.

Eph receptors are a group of receptors that are activated in response to binding with Eph receptor-interacting proteins (Ephrins). Ephs form the largest known subfamily of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs). Both Eph receptors and their corresponding ephrin ligands are membrane-bound proteins that require direct cell-cell interactions for Eph receptor activation. Eph/ephrin signaling has been implicated in the regulation of a host of processes critical to embryonic development including axon guidance, formation of tissue boundaries, cell migration, and segmentation. Additionally, Eph/ephrin signaling has been identified to play a critical role in the maintenance of several processes during adulthood including long-term potentiation, angiogenesis, and stem cell differentiation and cancer.
Semaphorins are a class of secreted and membrane proteins that were originally identified as axonal growth cone guidance molecules. They primarily act as short-range inhibitory signals and signal through multimeric receptor complexes. Semaphorins are usually cues to deflect axons from inappropriate regions, especially important in the neural system development. The major class of proteins that act as their receptors are called plexins, with neuropilins as their co-receptors in many cases. The main receptors for semaphorins are plexins, which have established roles in regulating Rho-family GTPases. Recent work shows that plexins can also influence R-Ras, which, in turn, can regulate integrins. Such regulation is probably a common feature of semaphorin signalling and contributes substantially to our understanding of semaphorin biology.

VEGF receptors (VEGFRs) are receptors for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). There are three main subtypes of VEGFR, numbered 1, 2 and 3. Depending on alternative splicing, they may be membrane-bound (mbVEGFR) or soluble (sVEGFR).

A plexin is a protein which acts as a receptor for semaphorin family signaling proteins. It is classically known for its expression on the surface of axon growth cones and involvement in signal transduction to steer axon growth away from the source of semaphorin. Plexin also has implications in development of other body systems by activating GTPase enzymes to induce a number of intracellular biochemical changes leading to a variety of downstream effects.

Ephrin B1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EFNB1 gene. It is a member of the ephrin family. The encoded protein is a type I membrane protein and a ligand of Eph-related receptor tyrosine kinases. It may play a role in cell adhesion and function in the development or maintenance of the nervous system.

Cadherin EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CELSR3 gene.

Cadherin EGF LAG seven-pass G-type receptor 1 also known as flamingo homolog 2 or cadherin family member 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CELSR1 gene.

Taste receptor type 2 member 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TAS2R10 gene. The protein is responsible for bitter taste recognition in mammals. It serves as a defense mechanism to prevent consumption of toxic substances which often have a characteristic bitter taste.
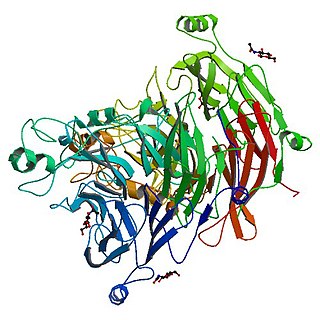
The Sema domain is a structural domain of semaphorins, which are a large family of secreted and transmembrane proteins, some of which function as repellent signals during axon guidance. Sema domains also occur in the hepatocyte growth factor receptor, Plexin-A3 and in viral proteins.

EPH receptor A2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EPHA2 gene.
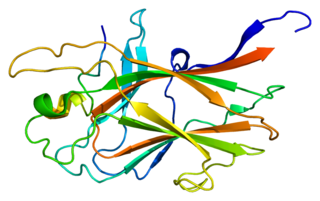
Ephrin type-B receptor 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EPHB4 gene.

Semaphorin-4D (SEMA4D) also known as Cluster of Differentiation 100 (CD100), is a protein of the semaphorin family that in humans is encoded by the SEMA4D gene.

Plexin B1 is a protein of the plexin family that in humans is encoded by the PLXNB1 gene.

Contactin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CNTN2 gene.

Ephrin type-B receptor 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EPHB3 gene.
WH1 domain is an evolutionary conserved protein domain found on WASP proteins, which are often involved in actin polymerization.

The growth cone is a highly dynamic structure of the developing neuron, changing directionality in response to different secreted and contact-dependent guidance cues; it navigates through the developing nervous system in search of its target. The migration of the growth cone is mediated through the interaction of numerous trophic and tropic factors; netrins, slits, ephrins and semaphorins are four well-studied tropic cues (Fig.1). The growth cone is capable of modifying its sensitivity to these guidance molecules as it migrates to its target; this sensitivity regulation is an important theme seen throughout development.
















