
Rhetoric is the art of persuasion. It is one of the three ancient arts of discourse (trivium) along with grammar and logic/dialectic. As an academic discipline within the humanities, rhetoric aims to study the techniques that speakers or writers use to inform, persuade, and motivate their audiences. Rhetoric also provides heuristics for understanding, discovering, and developing arguments for particular situations.

Scholasticism was a medieval school of philosophy that employed a critical organic method of philosophical analysis predicated upon the Aristotelian 10 Categories. Christian scholasticism emerged within the monastic schools that translated scholastic Judeo-Islamic philosophies, and "rediscovered" the collected works of Aristotle. Endeavoring to harmonize his metaphysics and its account of a prime mover with the Latin Catholic dogmatic trinitarian theology, these monastic schools became the basis of the earliest European medieval universities, and thus became the bedrock for the development of modern science and philosophy in the Western world. Scholasticism dominated education in Europe from about 1100 to 1700. The rise of scholasticism was closely associated with these schools that flourished in Italy, France, Portugal, Spain and England.
Dialectic, also known as the dialectical method, refers originally to dialogue between people holding different points of view about a subject but wishing to arrive at the truth through reasoned argumentation. Dialectic resembles debate, but the concept excludes subjective elements such as emotional appeal and rhetoric. It has its origins in ancient philosophy and continued to be developed in the Middle Ages.

The Frankfurt School is a school of thought in sociology and critical philosophy. It is associated with the Institute for Social Research founded at Goethe University Frankfurt in 1923. Formed during the Weimar Republic during the European interwar period, the first generation of the Frankfurt School was composed of intellectuals, academics, and political dissidents dissatisfied with the contemporary socio-economic systems of the 1930s: namely, capitalism, fascism, and communism.

Fredric Jameson is an American literary critic, philosopher and Marxist political theorist. He is best known for his analysis of contemporary cultural trends, particularly his analysis of postmodernity and capitalism. Jameson's best-known books include Postmodernism, or, The Cultural Logic of Late Capitalism (1991) and The Political Unconscious (1981).
Evald Vassilievich Ilyenkov was a Russian Marxist author and Soviet philosopher.

The Phenomenology of Spirit is the most widely-discussed philosophical work of Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel; its German title can be translated as either The Phenomenology of Spirit or The Phenomenology of Mind. Hegel described the work, published in 1807, as an "exposition of the coming to be of knowledge". This is explicated through a necessary self-origination and dissolution of "the various shapes of spirit as stations on the way through which spirit becomes pure knowledge".

Dialectic of Enlightenment is a work of philosophy and social criticism written by Frankfurt School philosophers Max Horkheimer and Theodor W. Adorno. The text, published in 1947, is a revised version of what the authors originally had circulated among friends and colleagues in 1944 under the title of Philosophical Fragments.
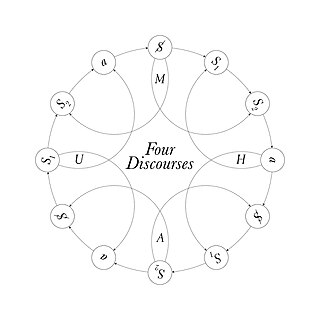
Four discourses is a concept developed by French psychoanalyst Jacques Lacan. He argued that there were four fundamental types of discourse. He defined four discourses, which he called Master, University, Hysteric and Analyst, and suggested that these relate dynamically to one another.

The lord–bondsman dialectic is a famous passage in Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel's The Phenomenology of Spirit. It is widely considered a key element in Hegel's philosophical system, and it has heavily influenced many subsequent philosophers.

Negative Dialectics is a 1966 book by the philosopher Theodor W. Adorno, in which he presents a critique of traditional Western philosophy and dialectical thinking. Adorno argues that the Enlightenment's emphasis on reason and progress has led to the domination of nature and the suppression of human individuality, and he develops the notion of negative dialectics as a critique of the positive, idealistic dialectics of Hegel and the Marxist dialectical materialism that grew out of it.
Relational dialectics is an interpersonal communication theory about close personal ties and relationships that highlights the tensions, struggles and interplay between contrary tendencies. The theory, proposed respectively by Leslie Baxter and Barbara Montgomery in 1988, defines communication patterns between relationship partners as the result of endemic dialectical tensions. Dialectics are described as the tensions an individual feels when experiencing paradoxical desires that we need and/ or want. The theory contains four assumptions, one of them being that relationships are not one dimensional, rather, they consist of highs and lows, without moving in only one direction. The second assumption claims that change is a key element in relational life, in other words, as our lives change, our relationships change with it. Third, is the assumption that, “contradictions or tensions between opposites never go away and never cease to provide tension,” which means, we will always experience the feelings of pressure that come with our contradictory desires. The fourth assumption is that communication is essential when it comes to working through these opposing feelings. Relationships are made in dialogue and they can be complicated and dialogue with similarities and differences are necessary. Relational communication theories allow for opposing views or forces to come together in a reasonable way. When making decisions, desires and viewpoints that often contradict one another are mentioned and lead to dialectical tensions. Leslie A. Baxter and Barbara M. Montgomery exemplify these contradictory statements that arise from individuals experience dialectal tensions using common proverbs such as "opposites attract", but "birds of a feather flock together"; as well as, "two's company; three's a crowd" but "the more the merrier". This does not mean these opposing tensions are fundamentally troublesome for the relationship; on the contrary, they simply bring forward a discussion of the connection between two parties.
Privacy regulation theory was developed by social psychologist Irwin Altman in 1975. This theory aims to explain why people sometimes prefer staying alone but at other times like get involved in social interactions, discussing privacy as "a selective control of access to the self or to one's group".

Interpersonal communication is an exchange of information between two or more people. It is also an area of research that seeks to understand how humans use verbal and nonverbal cues to accomplish several personal and relational goals. Communication includes utilizing communication skills within one's surroundings, including physical and psychological spaces. It is essential to see the visual/nonverbal and verbal cues regarding the physical spaces. In the psychological spaces, self-awareness and awareness of the emotions, cultures, and things that are not seen are also significant when communicating.
Jalari is one of the villages in Nadaun of Hamirpur, India.
The international film festival, Jalari in Corto, is held annually at Parco Jalari in Barcellona Pozzo di Gotto in Sicily. It began in the summer of 2004, having been conceived by young people of the cultural-ethnographic association Associazione Culturale Etnografica Ambientale “Jalari” and by Andrea Italiano. Its aim has been to promote, raise awareness and bring the art of cinema, and the communicative power of artistic expression in general, to as many people as possible through short films and meetings with authors, actors and critics. Year after year, the event has gained great fame, standing today as a springboard for both national and international young cinematic artists to gain exposure to a wider audience and increase visibility.
Dialectical logic is the system of laws of thought, developed within the Hegelian and Marxist traditions, which seeks to supplement or replace the laws of formal logic. The precise nature of the relation between dialectical and formal logic was hotly debated within the Soviet Union and China.
Dialectical materialism is a materialist theory based upon the writings of Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels that has found widespread applications in a variety of philosophical disciplines ranging from philosophy of history to philosophy of science. As a materialist philosophy, Marxist dialectics emphasizes the importance of real-world conditions and the presence of functional contradictions within and among social relations, which derive from, but are not limited to, the contradictions that occur in social class, labour economics, and socioeconomic interactions. Within Marxism, a contradiction is a relationship in which two forces oppose each other, leading to mutual development.
Formal scientists have attempted to combine formal logic and dialectic through formalisation of dialectic. These attempts include pre-formal and partially formal treatises on argument and dialectic, systems based on defeasible reasoning, and systems based on game semantics and dialogical logic.












