Related Research Articles

Muslin is a cotton fabric of plain weave. It is made in a wide range of weights from delicate sheers to coarse sheeting. It is commonly believed that it gets its name from the city of Mosul, Iraq.
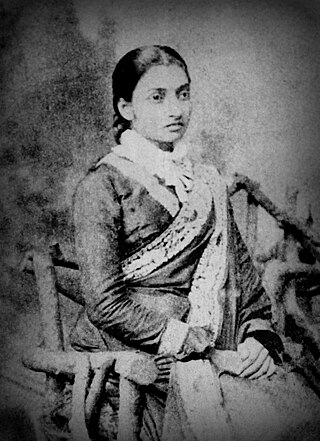
A sari is a women's garment from the Indian subcontinent. It consists of an un-stitched stretch of woven fabric arranged over the body as a robe, with one end attached to the waist, while the other end rests over one shoulder as a stole (shawl), sometimes baring a part of the midriff. It may vary from 4.1 to 8.2 metres in length, and 60 to 120 centimetres in breadth, and is a form of ethnic wear in India, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Bangladesh, Pakistan. There are various names and styles of sari manufacture and draping, the most common being the Nivi style. The sari is worn with a fitted bodice also called a choli and a petticoat called ghagra, parkar, or ul-pavadai. It remains fashionable in the Indian subcontinent today.
Ikat is a dyeing technique from Southeast Asia used to pattern textiles that employs resist dyeing on the yarns prior to dyeing and weaving the fabric. In Southeast Asia, where it is the most widespread, ikat weaving traditions can be divided into two general groups of related traditions. The first is found among Daic-speaking peoples. The second, larger group is found among the Austronesian peoples and spread via the Austronesian expansion to as far as Madagascar. It is most prominently associated with the textile traditions of Indonesia in modern times, from where the term ikat originates. Similar unrelated dyeing and weaving techniques that developed independently are also present in other regions of the world, including India, Central Asia, Japan, Africa, and the Americas.

Khadi, derived from khaddar, is a hand-spun and woven natural fibre cloth promoted by Mahatma Gandhi as swadeshi (self-sufficiency) for the freedom struggle of the Indian subcontinent, and the term is used throughout India, Pakistan and Bangladesh. The first piece of the hand-woven cloth was manufactured in the Sabarmati Ashram during 1917–18. The coarseness of the cloth led Gandhi to call it khadi. The cloth is made from cotton, but it may also include silk or wool, which are all spun into yarn on a charkha. It is a versatile fabric that remains cool in summer and warm in winter. To improve its appearance, khadi is sometimes starched to give it a stiffer feel. It is widely accepted in various fashion circles.

A Banarasi sari is a sari made in Varanasi, an ancient city which is also called Benares (Banaras). The saris are among the finest saris in India and are known for their gold and silver brocade or zari, fine silk and opulent embroidery. The saris are made of finely woven silk and are decorated with intricate designs, and, because of these engravings, are relatively heavy.
Kotpad is a town and a notified area committee in Koraput district in the Indian state of Odisha. Nearest railway station to Kotpad is Kotpad Road station which is a part of East Coast railway.

A Sambalpuri sari is a traditional handwoven bandha (ikat) sari wherein the warp and the weft are tie-dyed before weaving. It is produced in the Sambalpur, Balangir, Bargarh, Boudh and Sonepur districts of Odisha, India. The sari is a traditional female garment in the Indian subcontinent consisting of a strip of unstitched cloth ranging from four to nine meters in length that is draped over the body in various styles.

Tussar silk is produced from larvae of several species of silkworms belonging to the moth genus Antheraea, including A. assamensis, A. paphia, A. pernyi, A. roylei, and A. yamamai. These silkworms live in the wild forests in trees belonging to Terminalia species and Shorea robusta, as well as other food plants such as jamun and oak found in South Asia, eating the leaves of the trees on which they live. Tussar silk is valued for its rich texture and natural, deep-gold colour, and varieties are produced in many countries, including China, India, Japan, and Sri Lanka.
Weaving and cloth trading communities of Western India particularly of Gujarat are called Vankar/Wankar/Vaniya. The four major woven fabrics produced by these communities are cotton, silk, khadi and linen. Today majority of these community members are not engaged in their ancestral weaving occupation still some population of these community contribute themselves in traditional handloom weaving of famous Patola of Patan, Kachchh shawl of Bhujodi in Kutch, Gharchola and Crotchet of Jamnagar, Zari of Surat, Mashroo of Patan and Mandvi in Kutch, Bandhani of Jamnagar, Anjar and Bhuj, Motif, Leheria, Dhamakda and Ajrak, Nagri sari, Tangaliya Shawl, Dhurrie, Kediyu, Heer Bharat, Abhala, Phento and art of Gudri. Vankar is described as a caste as well as a community.

Bomkai sari or Bomkai Saree is a handloom saree from Odisha, India. It is an origin of Bomkai village from Ganjam district, however later it is mainly produced by the Bhulia community of Subarnapur district. Bomkai is one of the identified Geographical Indications of India. Bomkai Sarees are popular items displayed at various fashion shows.

Baluchari Sari is a type of sari, a garment worn by women in the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura and Assam and the country of Bangladesh. This particular type of sari originated in West Bengal and is known for depictions of mythological scenes on the anchal of the sari. It used to be produced in Murshidabad but presently Bishnupur and its surrounding areas of West Bengal are the only place where authentic Baluchari saris are produced. It takes approximately one week to produce one such sari. In 2011, the Baluchari Sari was granted the status of Geographical Indication for West Bengal in India.

Pochampally sari or Pochampalli ikat is a saree made in Bhoodan Pochampally, Yadadri Bhuvanagiri district, Telangana State, India. They have traditional geometric patterns in "Paagadu Bandhu" (Ikat) style of dyeing. The intricate geometric designs find their way into sarees and dress materials. The Indian government's official airplane company, Air India, has its cabin crew wear specially designed Pochampally silk sarees.

Gajam Anjaiah, an Indian master handloom designer, who is widely recognised in the handloom industry for his innovations and developments of Tie and Dye handloom products along with Telia Rumal technique of weaving based on Ikat tie-dye process. He received Padma Shri from Government of India under Art category in 2013. He is known for his excellence in traditional handloom design works, such as Puttapaka Sarees in Tie and dye skill, that is the traditional art of designing on paper and then transferring it on to cloth. His dedication to the Handloom Industry has kept the Indian tradition of weaving alive, brought livelihood to the weavers and gave exclusive/unique designed handloom products to the people in India.

Handloom saris are a traditional textile art of Bangladesh and India. The production of handloom saris is important for economic development in rural India.
Mangalagiri sarees and fabrics are produced by performing handicraft weaving in Mangalagiri, a town in Guntur district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It was registered as one of the handicrafts in the geographical indication from Andhra Pradesh by Geographical Indications of Goods Act, 1999.

Habaspuri is a cotton-based traditional handloom textiles of Odisha, India. Habaspuri sari is a major product of this textile. The Bhulia weavers of Chicheguda, Kalahandi district, Odisha are originally attributed for weaving of the Habaspuri fabric. For its uniqueness in weaving, design and production, it has been identified as one of the 14 Geographical Indications of Odisha.

Odisha Ikat, is a kind of ikat known as Bandhakala and Bandha, a resist dyeing technique, originating from Indian state of Odisha. Traditionally known as "Bandhakala"', "Bandha", '"Bandha of Odisha", it is a geographically tagged product of Odisha since 2007. It is made through a process of tie-dyeing the warp and weft threads to create the design on the loom prior to weaving. It is unlike any other ikat woven in the rest of the country because of its design process, which has been called "poetry on the loom". This design is in vogue only at the western and eastern regions of Odisha; similar designs are produced by community groups called the Bhulia, Kostha Asani, and Patara. The fabric gives a striking curvilinear appearance. Saris made out of this fabric feature bands of brocade in the borders and also at the ends, called anchal or pallu. Its forms are purposefully feathered, giving the edges a "hazy and fragile" appearance. There are different kinds of bandha saris made in Odisha, notably Khandua, Sambalpuri, Pasapali, Kataki and Manibandhi.
Gobardhan Panika is an Indian master weaver of Kotpad handloom a traditional tribal craft. The Government of India awarded him the fourth highest civilian honour of the Padma Shri, in 2018, for his contributions to the art of weaving.

Shantipur Handloom Industry, also known Shantipur Handloom Cluster, is a handloom weaving industry in Nadia district of West Bengal. It is one of the foremost handloom centers of India. This handloom industry is world famous for the production of cotton Sari (saree). The two main centers of this industrial zone are Shantipur and Phulia. Shantipur has an old reputation for cotton sarees, known as Shantipuri sarees, and Phulia is well known for Tangail-Jamdani sarees.
Block printing in India holds an important part in the country's rich cultural heritage and artistic traditions. Dating back thousands of years, this special ancient technique of textile decoration involves the meticulous carving of intricate designs onto wooden blocks, which are then dipped in natural dyes and stamped onto fabric to create vibrant patterns and motifs. This was a creative outlet for many.
References
- ↑ "Kotpad Weavers Co-operative Society 0". www.gocoop.com. Archived from the original on 28 August 2015. Retrieved 31 January 2016.
- ↑ "Sweet to get origin identity". The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 27 May 2015. Retrieved 31 January 2016.
- ↑ "Geographical Indications Registry". Geographical Indications. 2005.
- ↑ "I aspire to take Kotpad story to global audience: Odisha filmmaker". Odisha Sun Times. Bhubaneswar. 26 March 2018. Archived from the original on 31 March 2018.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ↑ "Reels of Kotpad". Bhubaneswar. 4 August 2018.
- ↑ "Padma Awards". Padma Awards. Government of India. 17 May 2018. Archived from the original on 15 October 2018. Retrieved 17 May 2018.
- ↑ "Kotpad Organic Dyed Cloth". www.orissahandloom.com. Retrieved 31 January 2016.
