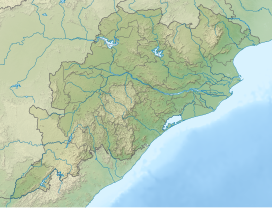
Odisha, formerly Orissa, is an Indian state located in Eastern India. It is the eighth-largest state by area, and the eleventh-largest by population, with over 41 million inhabitants. The state also has the third-largest population of Scheduled Tribes in India. It neighbours the states of Jharkhand and West Bengal to the north, Chhattisgarh to the west, and Andhra Pradesh to the south. Odisha has a coastline of 485 kilometres (301 mi) along the Bay of Bengal in the Indian Ocean. The region is also known as Utkaḷa and is mentioned by this name in India's national anthem, Jana Gana Mana. The language of Odisha is Odia, which is one of the Classical languages of India.
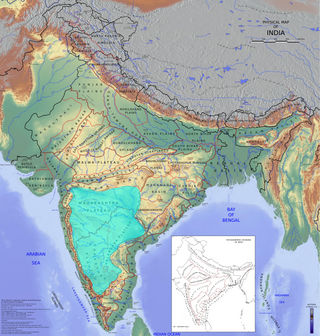
The Deccan is a large plateau and region of the Indian subcontinent located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada River. To the north, it is bounded by the Satpura and Vindhya Ranges. It covers the modern-day Indian States of Maharashtra, Telangana, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh

The Mahanadi River is a major river in East Central India. It drains an area of around 132,100 square kilometres (51,000 sq mi) and has a total length of 900 kilometres (560 mi). Mahanadi is also known for the Hirakud Dam which was the first major multipurpose river valley project after India's independence in 1947. The river flows through the states of Chhattisgarh and Odisha, before finally ending in the Bay of Bengal.

The Chota Nagpur Plateau is a plateau in eastern India, which covers much of Jharkhand state as well as adjacent parts of Chhattisgarh, Odisha, West Bengal and Bihar. The Indo-Gangetic plain lies to the north and east of the plateau, and the basin of the Mahanadi river lies to the south. The total area of the Chota Nagpur Plateau is approximately 65,000 square kilometres (25,000 sq mi).

Sambalpur District is a district in the western part of state of Odisha, India. The historic city of Sambalpur is the district headquarters.

The Brahmani is a major seasonal river in the Odisha state of eastern India. The Brahmani is formed by the confluence of the Sankh and South Koel rivers, and flows through the districts of Sundargarh, Deogarh, Angul, Dhenkanal, Cuttack, Jajapur and Kendrapara. Also South Koel can be considered as upper reaches of Brahmani. Together with the river Baitarani, Brahmani forms a large delta before emptying into the Bay of Bengal at Dhamra. It is the second widest river in Odisha after Mahanadi.
The Utkal Plain is part of the East Coastal Plain of India. It is a coastal plain in the Odisha state of eastern India. It includes the delta of the Mahanadi River, Brahmani River, Baitarani River. The most prominent physiographic feature of this plain is the Chilka Lake. It is the biggest lake in the country and its area varies between 780 km2 in winter to 1,144 km2 in the monsoon months.

Nuapada district is an area of Odisha state in India. Nuapada town is the headquarters of the district. It has one subdivision: Nuapada, and five blocks: Khariar, Sinapali, Boden, Komna, and Nuapada. Nuapada District has three Notified Area Councils: Khariar, Khariar Road, and Nuapada, six tehsils and more villages such as Gandabahali, Tukla, Hatibandha, Duajher, Bargaon, Tarbod, Udyanbandh, and Larka.

Jashpur District is a district of the central Indian state of Chhattisgarh bordering Jharkhand and Odisha. Jashpur Nagar is the administrative headquarters of the district. The district was formerly a princely state before Independence. Highly mountainous and forested, Jashpur is known for its natural environment.

The Central Provinces was a province of British India. It comprised British conquests from the Mughals and Marathas in central India, and covered parts of present-day Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra states. Nagpur was the primary winter capital while Pachmarhi served as the regular summer retreat. It became the Central Provinces and Berar in 1903.

The Eastern Highlands moist deciduous forests, presently known as East Deccan moist deciduous forests, is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion in east-central India. The ecoregion covers an area of 341,100 square kilometers (131,700 sq mi), extending across portions of Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha, and Telangana states.

Bargarh District is an administrative district of Odisha state in eastern India. The city of Bargarh is its district headquarters. The district was carved out of the erstwhile district of Sambalpur on 1 April 1993.
Malkangiri, historically known as Malikamardhangiri, is a town and municipality in Malkangiri district in the Indian state of Odisha. It is the headquarter of the Malkangiri district. Malkangiri has been the new home of the East Bengali refugees from erstwhile East Pakistan, who have been rehabilitated since 1965 under the Dandakaranya Project. Some Sri Lankan Tamil refugees were also rehabilitated in the town, following the armed struggle of the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE) in the early 1990s, although most of them have now returned to their country. Currently, it is one of the most naxalite-affected areas of the state, and is a part of the Red Corridor.

Sambalpur is the fourth largest city in the Indian State of Odisha. It is located on the banks of river Mahanadi, with a population of 335,761. Prehistoric settlements have been recorded there. It is the home of the Sambalpuri sari.
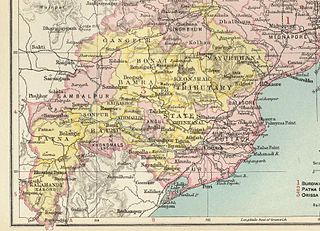
The Orissa Tributary States, also known as the Gadajats (ଗଡ଼ଜାତ) and as the Orissa Feudatory States, were a group of princely states of British India now part of the present-day Indian state of Odisha.

Chhattisgarh Division was an administrative division of the Central Provinces of British India. It was located in the east of the Central Provinces and encompassed the upper Mahanadi River basin, in the central part of present-day Chhattisgarh state of India.
Western Odisha is the western part of the state of Odisha in India, extending from the Kalahandi district in the south to the Sundargarh district in the north.

Odisha is one of the 28 states in the Republic of India. Odisha is located in the eastern part of the Indian peninsula and the Bay of Bengal lies to its East while Chhattisgarh shares its border in the west and north-west. The state also shares geographic boundaries with West Bengal in the north-east, Jharkhand in the north and Andhra Pradesh in the south. The state is spread over an area of 1,55,707 km2 and extends for 700 km from north to south and 500 kilometres from east to west. Its coastline is 450 km long. The state is divided into 30 districts which are further subdivided into 314
blocks called tahasil.

The Jharsuguda–Vizianagaram line is a railway line in eastern India. It connects Jharsuguda,516 km (321 mi) from Howrah on the Howrah–Nagpur–Mumbai line, and Titlagarh, which in turn is connected with Vizianagaram, 820 km (510 mi) from Howrah on the Howrah–Chennai main line, and Raipur Junction, 830 km (516 mi) from Howrah on the Howrah–Nagpur–Mumbai line. There are several branch lines, like the 176 km (109 mi) line connecting Rayagada with Koraput on the Kothavalasa–Kirandul line. The line traverses Western Odisha and connects the Howrah–Nagpur–Mumbai line with the Howrah–Chennai main line. It covers small portions of Chhattisgarh and Andhra Pradesh.

Gandabahali is a village in Sinapali Block in the south of Nuapada District in Odisha, India.