Related Research Articles

Frankfort is the capital city of the U.S. state of Kentucky and the seat of Franklin County. It is a home rule-class city. The population was 28,602 at the 2020 United States census. Located along the Kentucky River, Frankfort is the principal city of the Frankfort, Kentucky Micropolitan Statistical Area, which includes all of Franklin and Anderson counties. It is the 4th least populous state capital in the United States, and the 13th most populous city in Kentucky.

Madison County is a county located in the central part of the U.S. state of Kentucky. At the 2020 census, its population was 92,701. Its county seat is Richmond. The county is named for Virginia statesman James Madison, who later became the fourth President of the United States.

Scouting in Kentucky has a long history, from the 1910s to the present day, serving thousands of youth in programs that suit the environment in which they live. Kentucky has a very early Scouting heritage, as the home state of Daniel Carter Beard.

Louisa is a home-rule class city located in eastern Kentucky, United States, at the merger of the Levisa and Tug Forks into the Big Sandy River, which forms part of the state's border with West Virginia. It is the seat of Lawrence County. The population was 2,467 at the 2010 census and an estimated 2,375 in 2018.
John Taylor (1752–1833) was a pioneer Baptist preacher, religious writer, frontier historian and planter in north and central Kentucky. His two histories of early Baptist churches in Kentucky provide insight into the frontier society of the early decades of the 19th century. His 1820 pamphlet entitled "Thoughts on Missions" put him at the center of the controversy within frontier Baptist congregations about supporting mission societies. In buying and selling land on the frontier, Taylor acquired 2,000 acres (8.1 km2) and 20 African-American slaves by the end of the first decade of the 19th century, thus entering the planter class.

John Brown was an American lawyer and statesman who participated in the development and formation of the State of Kentucky after the American Revolutionary War.

U.S. Route 421 is a diagonal northwest–southeast United States Numbered Highway in the states of North Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia, Kentucky, and Indiana. The highway runs for 941 miles (1,514 km) from Fort Fisher, North Carolina, to US 20 in Michigan City, Indiana. Along its routing, US 421 serves several cities including Wilmington, North Carolina; Greensboro, North Carolina; Bristol, Tennessee and Virginia; Lexington, Kentucky; and Indianapolis, Indiana. US 421 is a spur route of US 21, which it meets west of Yadkinville, North Carolina.

The Wilderness Road was one of two principal routes used by colonial and early national era settlers to reach Kentucky from the East. Although this road goes through the Cumberland Gap into southern Kentucky and northern Tennessee, the other is sometimes called the "Cumberland Road" because it started in Fort Cumberland in Maryland. Despite Kentucky Senator Henry Clay's advocacy of this route, early in the 19th century, the northern route was selected for the National Road, connecting near Washington, Pennsylvania into the Ohio Valley of northern Kentucky and Ohio.

The Cumberland Gap is a pass in the eastern United States through the long ridge of the Cumberland Mountains, within the Appalachian Mountains and near the tripoint of Kentucky, Virginia, and Tennessee. At an elevation of 1,631 feet (497 m) above sea level, it is famous in American colonial history for its role as a key passageway through the lower central Appalachians.
William Christian was a military officer, planter and politician from the western part of the Colony of Virginia. He represented Fincastle County in the House of Burgesses and as relations with Britain soured, signed the Fincastle Resolutions. He later represented western Virginia in the Virginia Senate and founded Fort William, as well as helped negotiate the Treaty of Long Island of the Holston, which made peace between the Overmountain Men and Cherokees in 1777. He was killed in 1786 at the outset of the Northwest Indian War, leading an expedition against Native Americans near what is now Jeffersonville, Indiana.

Historic Jamestown is the cultural heritage site that was the location of the 1607 James Fort and the later 17th-century town of Jamestown in America. It is located on Jamestown Island, on the James River at Jamestown, Virginia and operated as a partnership between Preservation Virginia and the U.S. National Park Service as part of Colonial National Historical Park.

Richard Henderson was an American jurist, land speculator and politician who was best known for attempting to create the Transylvania Colony in frontier Kentucky. Henderson County and its seat Henderson, Kentucky are named for him. He also sold land to an early settlement that went on to become Nashville, Tennessee.

The prehistory and history of Kentucky span thousands of years, and have been influenced by the state's diverse geography and central location. Archaeological evidence of human occupation in Kentucky begins approximately 9,500 BCE. A gradual transition began from a hunter-gatherer economy to agriculture c. 1800 BCE. Around 900 CE, the Mississippian culture took root in western and central Kentucky; the Fort Ancient culture appeared in eastern Kentucky. Although they had many similarities, the Fort Ancient culture lacked the Mississippian's distinctive, ceremonial earthen mounds.
Captain Isaac Ruddell was an 18th-century American Virginia State Line officer during the American Revolutionary War and a Kentucky frontiersman. He was an officer commanding a company under BGEN George Rogers Clark (1777–1782). He was the founder of Ruddell's Station, or fort, on the Licking River in present-day Harrison County, Kentucky. In 1780, during the Revolutionary War, the settlement was destroyed by joint British Canadian and Eastern Woodlands Indian forces under British officer Captain Henry Bird. He and his family were held prisoner in Detroit for over two years before their release. Two of his sons were later taken captive by Shawnee, one of them becoming adopted brother of the famed warrior Tecumseh.

Corner in Celebrities Historic District is a neighborhood located in the north section of Frankfort, Kentucky, that is designated an historic district because of the high concentration of structures that previously belonged to notable residents. The area contains the historic homes of George M. Bibb, Benjamin G. Brown, James Brown, John Brown, John J. Crittenden, Thomas Crittenden, James Harlan, John Marshall Harlan, Robert P. Letcher, William Lindsay, Thomas Metcalfe, Charles Slaughter Morehead, William Owsley, Hugh Rodman, Charles S. Todd, Thomas Todd, George G. Vest, John C. Watson, and Simeon Willis. The area was added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places in 1971.
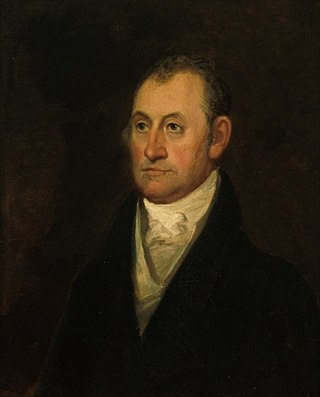
Thomas Todd was an Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1807 to 1826. Raised in the Colony of Virginia, he studied law and later participated in the founding of Kentucky, where he served as a clerk, judge, and justice. He was married twice and had a total of eight children. Todd joined the U.S. Supreme Court in 1807 and his handful of legal opinions there mostly concerned land claims. He was labeled the most insignificant U.S. Supreme Court justice by Frank H. Easterbrook in The Most Insignificant Justice: Further Evidence, 50 U. Chi. L. Rev. 481 (1983).

U.S. Route 421 (US 421) in the U.S. state of Kentucky is a 250.536-mile-long (403.199 km) north–south United States highway that traverses twelve counties in the central and eastern parts of the state. It travels in a southeast-to-northwest path from the Virginia state line near Pennington Gap to the Indiana state line, on the Ohio River at Milton, Kentucky and Madison, Indiana.
Thomas Lewis was an American Revolutionary War veteran who figured prominently in the early development of Lexington, Kentucky and the Commonwealth of Kentucky. He administered the oath of office to Kentucky's first governor, Isaac Shelby, in 1792.

The Westervelt massacre, also known as the Westerfield massacre, was an attack by Native Americans on a caravan of Dutch American settlers on June 27, 1780, near the frontier. Occurring amidst the backdrop of the Revolutionary War, the attack remains one of the largest massacres in the history of Kentucky.

The Travelling Church was a large group of pioneering settlers in the late 1700s that emigrated from Spotsylvania County, Virginia, to the Kentucky District of Virginia. It was the largest group that migrated to the area in a single movement. The group was led by the Reverend Lewis Craig, one of three pastor sons of Toliver Craig Sr., and its core was his Baptist congregation. The group of about 600 people arrived at Gilbert's Creek, Kentucky, in December 1781. Other preachers in the Travelling Church were Lewis Craig's younger brother Rev. Joseph Craig and his beloved slave Peter Durrett, who later became a pioneering black minister in Lexington, Kentucky. Lewis Craig's other brother who was a minister, Rev. Elijah Craig, did not come with the rest of the Church, as he remained for a while in Virginia to help James Madison establish constitutional religious liberty assurances before joining the group later. The group's pioneering members were to found many churches, settlements, and other institutions that continue to this day.
References
- ↑ "Leestown, Ky".
- ↑ "Leestown". Register of Kentucky State Historical Society, Vol. 29, No. 89 (October, 1931).
- ↑ "Historical Marker Database".
- ↑ "Leestown Historical Market 103".
