| Name | Year | Formation | Location | Notes | Images |
|---|
| Aardonyx | 2010 | Elliot Formation (Early Jurassic, Sinemurian) |  South Africa South Africa | Primarily bipedal but also capable of quadrupedal locomotion |  |
| Abrictosaurus | 1975 | Elliot Formation (Early Jurassic, Hettangian to Sinemurian) |  Lesotho Lesotho
 South Africa South Africa | Known from two skulls, one of which possesses tusks, which may be an indication of sexual dimorphism [1] |  |
| Adratiklit | 2020 | El Mers Group (Middle Jurassic, Bathonian) |  Morocco Morocco | One of the oldest known stegosaurs. Related to Late Jurassic European forms despite its early age [2] |  |
| Aegyptosaurus | 1932 | Bahariya Formation, Continental intercalaire?, Farak Formation? (Late Cretaceous, Cenomanian) |  Egypt Egypt
 Niger? Niger? | Its holotype specimen was destroyed in World War II |  |
| Afromimus | 2017 | Elrhaz Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian to Albian) |  Niger Niger | Originally described as an African ornithomimosaur, [3] but later redescribed as a possible noasaurid [4] |  |
| Afrovenator | 1994 | Tiourarén Formation (Middle Jurassic to Late Jurassic, Bathonian to Oxfordian) |  Niger Niger | Originally thought to hail from the Early Cretaceous |  |
| Ajnabia | 2021 | Ouled Abdoun Basin (Late Cretaceous, Maastrichtian) |  Morocco Morocco | The first hadrosaurid known from Africa. Closely related to European lambeosaurines [5] |  |
| Algoasaurus | 1904 | Kirkwood Formation (Early Cretaceous, Berriasian to Valanginian) |  South Africa South Africa | Today known from only a few bones. Several more may have been made into bricks before they could be studied [6] |  |
| Angolatitan | 2011 | Itombe Formation (Late Cretaceous, Coniacian) |  Angola Angola | The first non-avian dinosaur described from Angola |  |
| Antetonitrus | 2003 | Elliot Formation (Early Jurassic, Hettangian) |  South Africa South Africa | Had weight-bearing adaptations in all its limbs, although its forelimbs retain adaptations for grasping |  |
| Arcusaurus | 2011 | Elliot Formation (Early Jurassic, Pliensbachian) |  South Africa South Africa | Combines traits of basal and advanced sauropodomorphs | 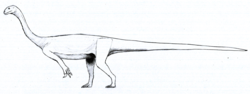 |
| Atlasaurus | 1999 | Guettioua Formation (Middle Jurassic, Bathonian to Callovian) |  Morocco Morocco | Possessed relatively elongated legs for a sauropod |  |
| Australodocus | 2007 | Tendaguru Formation (Late Jurassic, Kimmeridgian to Tithonian) |  Tanzania Tanzania | Potentially an early euhelopodid [7] |  |
| Bahariasaurus | 1934 | Bahariya Formation, Farak Formation? (Late Cretaceous, Cenomanian) |  Egypt Egypt
 Niger? Niger? | Large but known from very few remains |  |
| Berberosaurus | 2007 | Azilal Formation (Early Jurassic, Toarcian) |  Morocco Morocco | One of the oldest known ceratosaurs |  |
| Blikanasaurus | 1985 | Elliot Formation (Late Triassic, Norian) |  South Africa South Africa | A "hyper-robust" form that niche partitioned with other Late Triassic Elliot Formation sauropodomorphs [8] |  |
| Carcharodontosaurus | 1931 | Aïn el Guettar Formation?, Continental intercalaire, Echkar Formation, Elrhaz Formation?, Kem Kem Group, Wadi Milk Formation? (Late Cretaceous, Cenomanian) |  Algeria Algeria
 Morocco Morocco
 Niger Niger
 Sudan? Sudan?
 Tunisia? Tunisia? | One of the largest carnivorous dinosaurs. Two species are known |  |
| Chebsaurus | 2005 | Aïssa Formation (Middle Jurassic, Callovian) |  Algeria Algeria | Known from two juvenile specimens |  |
| Chenanisaurus | 2017 | Ouled Abdoun Basin (Late Cretaceous, Maastrichtian) |  Morocco Morocco | Potentially represents a lineage of abelisaurids endemic to Africa |  |
| Cristatusaurus | 1998 | Elrhaz Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian to Albian) |  Niger Niger | Usually seen as a synonym of Suchomimus , although some studies consider it to be a valid genus [9] |  |
| Deltadromeus | 1996 | Kem Kem Group (Late Cretaceous, Cenomanian) |  Morocco Morocco | Its precise phylogenetic position has been historically unstable, with multiple interpretations being suggested in the scientific literature [10] [11] [12] [13] |  |
| Dicraeosaurus | 1914 | Tendaguru Formation (Late Jurassic, Kimmeridgian to Tithonian) |  Tanzania Tanzania | A short-necked, low-browsing sauropod. Two species are known |  |
| Dracovenator | 2005 | Elliot Formation (Early Jurassic, Hettangian) |  South Africa South Africa | Only known from fragments of a skull, but those are enough to tell that it was related to Dilophosaurus |  |
| Dysalotosaurus | 1919 | Tendaguru Formation (Late Jurassic, Kimmeridgian) |  Tanzania Tanzania | Known from multiple remains that revealed much about its life history, [14] diet [15] and even disease [16] |  |
| Elaphrosaurus | 1920 | Tendaguru Formation (Late Jurassic, Kimmeridgian) |  Tanzania Tanzania | Possessed a relatively shallow chest for a medium-sized theropod |  |
| Elrhazosaurus | 2009 | Elrhaz Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) |  Niger Niger | Closely related to Valdosaurus |  |
| Eocarcharia | 2008 | Elrhaz Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian to Albian) |  Niger Niger | Originally thought to be a carcharodontosaurid but later research found it to be chimeric, with the holotype postorbital and referred skull roof likely belonging to a spinosaurid closely related to the contemporaneous Suchomimus , and the referred maxilla belonging to a distinct carcharodontosaurid [17] |  |
| Eocursor | 2007 | Elliot Formation (Early Jurassic, Sinemurian) |  South Africa South Africa | One of the most completely known early ornithischians |  |
| Eucnemesaurus | 1920 | Elliot Formation (Late Triassic, Carnian to Norian) |  South Africa South Africa | Some fossils assigned to this genus were originally interpreted as those of a giant herrerasaurid |  |
| Euskelosaurus | 1866 | Elliot Formation (Late Triassic, Norian to Rhaetian) |  Lesotho Lesotho
 South Africa South Africa
 Zimbabwe Zimbabwe | Originally thought to have been bow-legged |  |
| Geranosaurus | 1911 | Clarens Formation (Early Jurassic, Pliensbachian to Toarcian) |  South Africa South Africa | Poorly known but potentially a heterodontosaurid |  |
| Giraffatitan | 1988 | Tendaguru Formation (Late Jurassic, Kimmeridgian to Tithonian) |  Tanzania Tanzania | Popularly associated with Brachiosaurus but several differences between the two have been noted [18] |  |
| Gryponyx | 1911 | Elliot Formation (Early Jurassic, Hettangian to Sinemurian) |  South Africa South Africa | Although usually seen as a synonym of Massospondylus , at least one study has found it to be distantly related [19] |  |
| Heterodontosaurus | 1962 | Clarens Formation, Elliot Formation (Early Jurassic, Hettangian to Sinemurian) |  South Africa South Africa | Possessed three types of teeth, including analogues of incisors and tusks, as well as a keratinous beak |  |
| Igai | 2023 | Quseir Formation (Late Cretaceous, Campanian) |  Egypt Egypt | More closely related to European titanosaurs than to southern African ones |  |
| Ignavusaurus | 2010 | Elliot Formation (Early Jurassic, Hettangian) |  Lesotho Lesotho | Only known from a single, mostly articulated juvenile skeleton with a badly crushed skull |  |
| Inosaurus | 1960 | Bahariya Formation?, Echkar Formation?, Tegama Group? (Early Cretaceous, Albian?) |  Egypt? Egypt?
 Niger Niger | Very poorly known | |
| Iyuku | 2022 | Kirkwood Formation (Early Cretaceous, Valanginian) |  South Africa South Africa | Uniquely known from an assemblage of mostly hatchling and juvenile fossils | |
| Janenschia | 1991 | Tendaguru Formation (Late Jurassic, Kimmeridgian to Tithonian) |  Tanzania Tanzania | Potentially a close relative of Bellusaurus , Haestasaurus and Tehuelchesaurus , all of which may form a unique clade of eusauropods with possible turiasaur affinities [7] [20] [21] |  |
| Jobaria | 1999 | Tiourarén Formation (Middle Jurassic to Late Jurassic, Bathonian to Oxfordian) |  Niger Niger | Known from an almost complete skeleton |  |
| Kangnasaurus | 1915 | Kalahari Deposits Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) |  South Africa South Africa | Comparisons have been made with dryosaurids [22] but at least two studies suggest a position within Elasmaria [23] [24] |  |
| Karongasaurus | 2005 | Dinosaur Beds (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) |  Malawi Malawi | Described from only a mandible and isolated teeth | 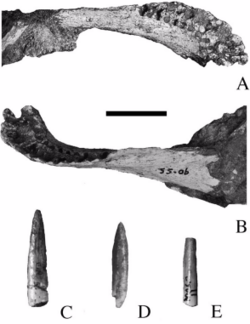 |
| Kentrosaurus | 1915 | Tendaguru Formation (Late Jurassic, Kimmeridgian to Tithonian) |  Tanzania Tanzania | Possessed two rows of plates that gradually transitioned into spikes towards the tail, as well as a long spike on each shoulder |  |
| Kholumolumo | 2020 | Elliot Formation (Late Triassic, Norian) |  Lesotho Lesotho | Before its formal description, it had been informally referred to as "Kholumolumosaurus" and "Thotobolosaurus". The latter name means "trash heap lizard" in Sesotho, referring to how the holotype was originally found close to a trash heap |  |
| Kryptops | 2008 | Elrhaz Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian to Albian) |  Niger Niger | Postcranial remains referred to this genus have been later found to come from an allosauroid, perhaps a metriacanthosaurid [17] |  |
| Ledumahadi | 2018 | Elliot Formation (Early Jurassic, Hettangian to Sinemurian) |  South Africa South Africa | One of the largest Early Jurassic dinosaurs, estimated as weighing 12 tonnes (26,000 lb) despite lacking columnar limbs like later sauropods [25] |  |
| Lesothosaurus | 1978 | Clarens Formation, Elliot Formation (Early Jurassic, Hettangian to Sinemurian) |  Lesotho Lesotho
 South Africa South Africa | Possibly an opportunistic omnivore, feeding on meat during seasons when plants are not available [26] |  |
| Lurdusaurus | 1999 | Elrhaz Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian to Albian) |  Niger Niger | The proportions of its body and limbs suggest it may have been a semiaquatic herbivore similar to a hippopotamus [27] |  |
| Lycorhinus | 1924 | Elliot Formation (Early Jurassic, Hettangian to Sinemurian) |  South Africa South Africa | Originally misidentified as a cynodont |  |
| Malawisaurus | 1993 | Dinosaur Beds (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) |  Malawi Malawi | Known from abundant material, including elements from the skull and osteoderms, but they may not represent a single taxon [28] |  |
| Mansourasaurus | 2018 | Quseir Formation (Late Cretaceous, Campanian) |  Egypt Egypt | One of the few Late Cretaceous sauropods known from Africa [29] |  |
| Massospondylus | 1854 | Bushveld Sandstone, Clarens Formation, Elliot Formation, Forest Sandstone (Early Jurassic, Hettangian to Pliensbachian) |  Lesotho Lesotho
 South Africa South Africa
 Zimbabwe Zimbabwe | Abundant remains have been discovered. Several specimens were once assigned to their own genera and species |  |
| Mbiresaurus | 2022 | Pebbly Arkose Formation (Late Triassic, Carnian) |  Zimbabwe Zimbabwe | One of the oldest dinosaurs known from Africa. Its discovery proves that the earliest dinosaurs were restricted to high latitudes [30] | |
| Melanorosaurus | 1924 | Elliot Formation (Late Triassic, Norian) |  South Africa South Africa | A robust, quadrupedal herbivore. Some specimens assigned to this genus may not represent the same taxon [8] |  |
| Meroktenos | 2016 | Elliot Formation (Late Triassic, Norian to Rhaetian) |  Lesotho Lesotho | Its femur was unusually robust for an animal of its size |  |
| Minqaria | 2024 | Ouled Abdoun Basin (Late Cretaceous, Maastrichtian) |  Morocco Morocco | Known from a partial skull |  |
| Mnyamawamtuka | 2019 | Galula Formation (Early Cretaceous to Late Cretaceous, Aptian to Cenomanian) |  Tanzania Tanzania | Its specific name, moyowamkia, is Kiswahili for "heart tail", which references the heart-shaped cross-section of its caudal vertebrae |  |
| Musankwa | 2024 | Pebbly Arkose Formation, (Late Triassic, Norian) |  Zimbabwe Zimbabwe | The fourth dinosaur genus to be named from Zimbabwe |  |
| Ngwevu | 2019 | Clarens Formation (Early Jurassic, Pliensbachian to Toarcian) |  South Africa South Africa | Known from a skull originally assigned to Massospondylus . It was assigned to its own genus based on its unique proportions |  |
| Nigersaurus | 1999 | Elrhaz Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian to Albian) |  Niger Niger | All of its teeth were at the front of its jaws, which were wider than the rest of its skull, an adaptation to low browsing |  |
| Nqwebasaurus | 2000 | Kirkwood Formation (Early Cretaceous, Berriasian) |  South Africa South Africa | The first non-avian coelurosaur named from mainland Africa |  |
| Orosaurus | 1867 | Elliot Formation? (Late Triassic, Norian to Rhaetian) |  South Africa South Africa | Probably a synonym of Euskelosaurus | |
| Ostafrikasaurus | 2012 | Tendaguru Formation (Late Jurassic, Tithonian) |  Tanzania Tanzania | Described from a single tooth as an early spinosaurid [31] but ceratosaurid affinities have also been proposed [32] |  |
| Ouranosaurus | 1976 | Elrhaz Formation (Early Cretaceous, Aptian) |  Niger Niger | Had long neural spines that projected from its vertebrae, which may have supported a sail or hump in life |  |
| Paralititan | 2001 | Bahariya Formation (Late Cretaceous, Cenomanian) |  Egypt Egypt | Would have lived in a tidal flat environment dominated by mangroves |  |
| Paranthodon | 1929 | Kirkwood Formation (Early Cretaceous, Berriasian to Valanginian) |  South Africa South Africa | Although only known from fragmentary specimens, they are enough to tell that it was a stegosaur |  |
| Pegomastax | 2012 | Elliot Formation (Early Jurassic, Sinemurian) |  South Africa South Africa | The morphology of its jaws and beak suggests a diet of tough plants |  |
| Plateosauravus | 1932 | Elliot Formation (Late Triassic, Norian) |  South Africa South Africa | Known from multiple specimens, including those of juveniles |  |
| Pulanesaura | 2015 | Elliot Formation (Early Jurassic, Hettangian to Sinemurian) |  South Africa South Africa | A low browser that lacked the extremely long neck of later sauropods | 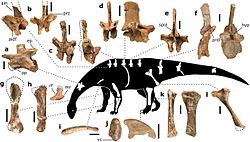 |
| Rebbachisaurus | 1954 | Kem Kem Group (Late Cretaceous, Cenomanian) |  Morocco Morocco | Carried a row of elongated neural spines, which would have supported a ridge or low sail on its back |  |
| Rugops | 2004 | Echkar Formation (Late Cretaceous, Cenomanian) |  Niger Niger | Preserves two rows of holes on the top of its skull, which may have anchored a display structure [33] or an armor-like dermis [34] |  |
| Rukwatitan | 2014 | Galula Formation (Early Cretaceous to Late Cretaceous, Albian to Cenomanian) |  Tanzania Tanzania | One of the few titanosaurs known from central Africa, filling in a gap in their evolutionary history |  |
| Sauroniops | 2013 | Kem Kem Group (Late Cretaceous, Cenomanian) |  Morocco Morocco | Only known from a single, thickened frontal. Suggested to be a synonym of Carcharodontosaurus [13] but this has been refuted [35] |  |
| Sefapanosaurus | 2015 | Elliot Formation (Early Jurassic, Hettangian) |  South Africa South Africa | Had a distinctive cross-shaped astragalus | |
| Shingopana | 2017 | Galula Formation (Late Cretaceous, Campanian to Maastrichtian) |  Tanzania Tanzania | Most closely related to South American titanosaurs | |
| Spicomellus | 2021 | El Mers Group (Middle Jurassic, Bathonian) |  Morocco Morocco | The oldest ankylosaur known and the first one from Africa. Uniquely, its osteoderms were fused directly to its ribs [36] and had very long spikes in its neck and pelvis [37] |  |
| Spinophorosaurus | 2009 | Irhazer Shale (Middle Jurassic, Bajocian to Bathonian) |  Niger Niger | Originally described as possessing a "thagomizer" similar to those of stegosaurs, [38] but these turned out to be misidentified clavicles. [39] A high browser with tall shoulders and an elevated neck [40] |  |
| Spinosaurus | 1915 | Aïn el Guettar Formation?, Bahariya Formation, Kem Kem Group (Late Cretaceous, Cenomanian) |  Algeria Algeria
 Egypt Egypt
 Morocco Morocco
 Tunisia? Tunisia? | Possessed a myriad of features that have been suggested to be evidence of a semiaquatic lifestyle, including webbed feet [41] and a paddle-like tail. [42] However, it is debated if it was a marine piscivore [43] or a shoreline generalist [44] |  |
| Spinostropheus | 2004 | Tiourarén Formation (Middle Jurassic to Late Jurassic, Bathonian to Oxfordian) |  Niger Niger | Although often considered a close relative of Elaphrosaurus , these inferences are based on a specimen that cannot actually be referred to this genus [45] |  |
| Suchomimus | 1998 | Elrhaz Formation (Early Cretaceous, Barremian to Albian) |  Niger Niger | Similar to Baryonyx but with a low sail on its back |  |
| Taleta | 2025 | Ouled Abdoun Basin (Late Cretaceous, Maastrichtian) |  Morocco Morocco | Closely related to and contemporary with Ajnabia and Minqaria [46] |  |
| Tameryraptor | 2025 | Bahariya Formation (Late Cretaceous, Cenomanian) |  Egypt Egypt | Based on destroyed fossils originally referred to Carcharodontosaurus |  |
| Tataouinea | 2013 | Aïn el Guettar Formation (Early Cretaceous, Albian) |  Tunisia Tunisia | Its bones were extensively pneumatized, supporting the theory that sauropods had bird-like respiratory systems |  |
| Tazoudasaurus | 2004 | Azilal Formation (Early Jurassic, Toarcian) |  Morocco Morocco | One of the few Early Jurassic sauropods known from reasonably complete remains |  |
| Tendaguria | 2000 | Tendaguru Formation (Late Jurassic, Tithonian) |  Tanzania Tanzania | The first definitive turiasaur known from Africa [7] |  |
| Thyreosaurus | 2024 | El Mers Group (Middle Jurassic, Bathonian) |  Morocco Morocco | May have possessed a recumbent dermal armor, an unusual feature among stegosaurs [47] |  |
| Tornieria | 1911 | Tendaguru Formation (Late Jurassic, Kimmeridgian to Tithonian) |  Tanzania Tanzania | Has been assigned to different genera throughout its history |  |
| Veterupristisaurus | 2011 | Tendaguru Formation (Late Jurassic, Kimmeridgian to Tithonian) |  Tanzania Tanzania | Known from a few vertebrae somewhat similar to those of Acrocanthosaurus |  |
| Vulcanodon | 1972 | Forest Sandstone (Early Jurassic, Sinemurian to Pliensbachian) |  Zimbabwe Zimbabwe | Theropod teeth were found associated with the holotype |  |
| Wamweracaudia | 2019 | Tendaguru Formation (Late Jurassic, Tithonian) |  Tanzania Tanzania | The first definitive mamenchisaurid known from outside Asia | |