
Carcharodontosaurus is a genus of carnivorous theropod dinosaur that lived in North Africa from about 100 to 94 million years ago during the Cenomanian age of the Cretaceous. Two teeth of the genus, now lost, were first described from Algeria by French paleontologists Charles Depéret and Justin Savornin as Megalosaurus saharicus. A partial skeleton was collected by crews of German paleontologist Ernst Stromer during a 1914 expedition to Egypt. Stromer did not report the Egyptian find until 1931, in which he dubbed the novel genus Carcharodontosaurus, making the type species C. saharicus. Unfortunately, this skeleton was destroyed during the Second World War. In 1995 a nearly complete skull of C. saharicus, the first well-preserved specimen to be found in almost a century, was discovered in the Kem Kem Beds of Morocco; it was designated the neotype in 1996. Fossils unearthed from the Echkar Formation of northern Niger were described and named as another species, C. iguidensis, in 2007.

Sarcosuchus is an extinct genus of crocodyliform and distant relative of living crocodilians that lived during the Early Cretaceous, from the late Hauterivian to the early Albian, 133 to 112 million years ago of what is now Africa and South America. The genus name comes from the Greek σάρξ (sarx) meaning flesh and σοῦχος (souchus) meaning crocodile. It was one of the largest pseudosuchians, with the largest specimen of S. imperator reaching approximately 9–9.5 metres (29.5–31.2 ft) long and weighing up to 3.45–4.3 metric tons. It is known from two species; S. imperator from the early Albian Elrhaz Formation of Niger, and S. hartti from the Late Hauterivian of northeastern Brazil. Other material is known from Morocco and Tunisia and possibly Libya and Mali.

Ceratosaurs are members of the clade Ceratosauria, a group of dinosaurs defined as all theropods sharing a more recent common ancestor with Ceratosaurus than with birds. The oldest known ceratosaur, Saltriovenator, dates to the earliest part of the Jurassic, around 199 million years ago. Ceratosauria includes three major clades: Ceratosauridae, Noasauridae, and Abelisauridae, found primarily in the Southern Hemisphere. Originally, Ceratosauria included the above dinosaurs plus the Late Triassic to Early Jurassic Coelophysoidea and Dilophosauridae, implying a much earlier divergence of ceratosaurs from other theropods. However, most recent studies have shown that coelophysoids and dilophosaurids do not form a natural group with other ceratosaurs, and are excluded from this group.

Suchomimus is a genus of spinosaur dinosaur that lived between 125 and 112 million years ago in what is now Niger, North Africa, during the Aptian to early Albian stages of the Early Cretaceous Period. It was named and described by paleontologist Paul Sereno and colleagues in 1998, based on a partial skeleton from the Elrhaz Formation. Suchomimus's long and shallow skull, similar to that of a crocodile, earns it its generic name, while the specific name Suchomimus tenerensis alludes to the locality of its first remains, the Ténéré Desert.

Ouranosaurus is a genus of herbivorous basal hadrosauriform dinosaur that lived during the Aptian stage of the Early Cretaceous of modern-day Niger and Cameroon. Ouranosaurus measured about 7–8.3 metres (23–27 ft) long and weighed 2.2 metric tons. Two rather complete fossils were found in the Elrhaz Formation, Gadoufaoua deposits, Agadez, Niger, in 1965 and 1970, with a third indeterminate specimen known from the Koum Formation of Cameroon. The animal was named in 1976 by French paleontologist Philippe Taquet; the type species being Ouranosaurus nigeriensis. The generic name is a combination of ourane, a word with multiple meanings, and sauros, the Greek word for lizard. The specific epithet nigeriensis alludes to Niger, its country of discovery. And so, Ouranosaurus nigeriensis could be interpreted as "brave lizard originating from Niger".

Carcharodontosauridae is a group of carnivorous theropod dinosaurs. In 1931, Ernst Stromer named Carcharodontosauridae as a family, which, in modern paleontology, indicates a clade within Carnosauria. Carcharodontosaurids include some of the largest land predators ever known: Giganotosaurus, Mapusaurus, Carcharodontosaurus, and Tyrannotitan all rivaled Tyrannosaurus in size. Estimates give a maximum weight of 8–10 metric tons for the largest carcharodontosaurids, while the smallest carcharodontosaurids were estimated to have weighed at least 500 kilograms (1,100 lb).

Rugops is a monospecific genus of basal abelisaurid theropod dinosaur from Niger that lived during the Late Cretaceous period in what is now the Echkar Formation. The type and only species, Rugops primus, is known only from a partial skull. It was named and described in 2004 by Paul Sereno, Jeffery Wilson and Jack Conrad. Rugops has an estimated length of 4.4–5.3 metres (14–17 ft) and weight of 410 kilograms (900 lb). The top of its skull bears several pits which correlates with overlaying scale and the front of the snout would have had an armour-like dermis.

Cristatusaurus is a genus of theropod dinosaur that lived during the Early Cretaceous Period of what is now Niger, 112 million years ago. It was a baryonychine member of the Spinosauridae, a group of large bipedal carnivores with well-built forelimbs and elongated, crocodile-like skulls. The type species Cristatusaurus lapparenti was named in 1998 by scientists Philippe Taquet and Dale Russell, on the basis of jaw bones and some vertebrae. Two claw fossils were also later assigned to Cristatusaurus. The animal's generic name, which means "crested reptile", alludes to a sagittal crest on top of its snout; while the specific name is in honor of the French paleontologist Albert-Félix de Lapparent. Cristatusaurus is known from the Albian to Aptian Elrhaz Formation, where it would have coexisted with sauropod and iguanodontian dinosaurs, other theropods, and various crocodylomorphs.

Lurdusaurus is a genus of massive and unusually shaped iguanodont dinosaur from the Elrhaz Formation in Niger. It contains one species, L. arenatus. The formation dates to the Early Cretaceous, roughly 112 million years ago. Lurdusaurus has a highly atypical body plan for an iguanodont, with a small skull, long neck, rotund torso, and powerful forelimbs and claws, somewhat reminiscent of a ground sloth. Its metacarpals are fused and reinforced into a large block, and the thumb spike is remarkably enormous. These would have allowed the hand to have functioned almost like a ball-and-chain flail. Lurdusaurus is estimated to have been 7–9 m (23–30 ft) long and 2 m high when on all-fours, but its stomach would have been only 70 cm off the ground. It may have weighed 2.5–5.5 t, conspicuously heavy for an iguanodontid this size.

Kelmayisaurus is an extinct genus of carcharodontosaurid theropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous. It was roughly 10–12 meters long and its name refers to the petroleum-producing city of Karamay in the Xinjiang province of western China near where it was found.

Stephen Louis "Steve" Brusatte FRSE is an American paleontologist, author, and evolutionary biologist who specializes in the anatomy and evolution of dinosaurs. He was educated at the University of Chicago for his Bachelor's degree, at the University of Bristol for his Master's of Science on a Marshall Scholarship, and finally at the Columbia University for Master's in Philosophy and Doctorate. He is currently Professor of Palaeontology and Evolution at the University of Edinburgh. In April 2024, Brusatte was elected to fellowship of the Royal Society of Edinburgh.

Kryptops is a genus of abelisaurid theropod dinosaur from the Early Cretaceous of Niger. It is known from a partial skeleton found at the Gadoufaoua locality in the western Ténéré Desert, in rocks of the Aptian–Albian-age Elrhaz Formation. This dinosaur was described by paleontologists Paul Sereno and Stephen Brusatte in 2008. The genus name means "covered face", in reference to evidence that the face bore a tightly adhering covering. The type species is K. palaios, which means "old".

Nigersaurus is a genus of rebbachisaurid sauropod dinosaur that lived during the middle Cretaceous period, about 115 to 105 million years ago. It was discovered in the Elrhaz Formation in an area called Gadoufaoua, in Niger. Fossils of this dinosaur were first described in 1976, but it was only named Nigersaurus taqueti in 1999, after further and more complete remains were found and described. The genus name means "Niger reptile", and the specific name honours the palaeontologist Philippe Taquet, who discovered the first remains.
The Elrhaz Formation is a geological formation in Niger, West Africa.

Elrhazosaurus is a genus of basal iguanodontian dinosaur, known from isolated bones found in Early Cretaceous rocks of Niger. These bones were initially thought to belong to a species of the related dryosaurid Valdosaurus, but have since been reclassified.
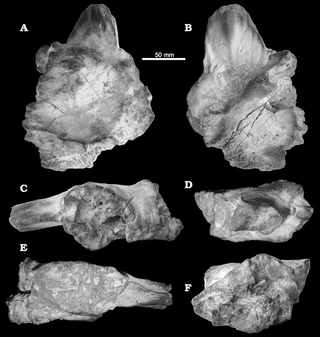
Sauroniops is a controversial genus of carnivorous basal carcharodontosaurid theropod dinosaur known from the Late Cretaceous Gara Sbaa Formation, and possibly also the Kem Kem Formation, both of Morocco. The type, and currently only, species is S. platytholus.

This timeline of ceratosaur research is a chronological listing of events in the history of paleontology focused on the ceratosaurs, a group of relatively primitive, often horned, predatory theropod dinosaurs that became the apex predators of the southern hemisphere during the Late Cretaceous. The nature and taxonomic composition of the Ceratosauria has been controversial since the group was first distinguished in the late 19th century. In 1884 Othniel Charles Marsh described the new genus and species Ceratosaurus nasicornis from the Late Jurassic Morrison Formation of the western United States. He felt that it belonged in a new family that he called the Ceratosauridae. He created the new taxon Ceratosauria to include both the Ceratosauridae and the ostrich-like ornithomimids. The idea of the Ceratosauria was soon contested, however. Later that same decade both Lydekker and Marsh's hated rival Edward Drinker Cope argued that the taxon was invalid.
Tralkasaurus is a genus of abelisaurid dinosaur from the Huincul Formation from Río Negro Province in Argentina. The type and only species is Tralkasaurus cuyi, named in 2020 by Mauricio Cerroni and colleagues based on an incomplete skeleton. A medium-sized abelisaurid, Tralkasaurus exhibits a conflicting blend of characteristics found among the early-diverging abelisauroids with others that characterize the highly specialized clade Brachyrostra, and thus its position within the clade is poorly-resolved.

Eorhynchocyon is an extinct mammal genus from the macroscelidid superfamily.

Chakisaurus is an extinct genus of elasmarian ornithopod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Huincul Formation of Argentina. The genus contains a single species, C. nekul, known from multiple partial skeletons belonging to individuals of different ages. Chakisaurus represents the first ornithischian species to be named from the Huincul Formation.




































