
Carnotaurus is a genus of theropod dinosaur that lived in South America during the Late Cretaceous period, probably sometime between 72 and 69 million years ago. The only species is Carnotaurus sastrei. Known from a single well-preserved skeleton, it is one of the best-understood theropods from the Southern Hemisphere. The skeleton, found in 1984, was uncovered in the Chubut Province of Argentina from rocks of the La Colonia Formation. Carnotaurus is a derived member of the Abelisauridae, a group of large theropods that occupied the large predatorial niche in the southern landmasses of Gondwana during the late Cretaceous. Within the Abelisauridae, the genus is often considered a member of the Brachyrostra, a clade of short-snouted forms restricted to South America.

Rajasaurus is a genus of carnivorous abelisaurid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of India, containing one species: Rajasaurus narmadensis. The bones were excavated from the Lameta Formation in the Gujarat state of Western India, probably inhabiting what is now the Narmada River Valley. It was formally described by palaeontologist Jeffrey A. Wilson and colleagues in 2003 based on a partial skeleton comprising the braincase, spine, hip bone, legs, and tail–a first for an Indian theropod. The dinosaur likely measured 6.6 metres (22 ft), and had a single horn on the forehead which was probably used for display and head-butting. Like other abelisaurids, Rajasaurus was probably an ambush predator.

Rugops is a monospecific genus of basal abelisaurid theropod dinosaur from Niger that lived during the Late Cretaceous period in what is now the Echkar Formation. The type and only species, Rugops primus, is known only from a partial skull. It was named and described in 2004 by Paul Sereno, Jeffery Wilson and Jack Conrad. Rugops has an estimated length of 4.4–5.3 metres (14–17 ft) and weight of 410 kilograms (900 lb). The top of its skull bears several pits which correlates with overlaying scale and the front of the snout would have had an armour-like dermis.

Paranthodon is a genus of stegosaurian dinosaur that lived in what is now South Africa during the Early Cretaceous, between 139 and 131 million years ago. Discovered in 1845, it was one of the first stegosaurians found. Its only remains, a partial skull, isolated teeth, and fragments of vertebrae, were found in the Kirkwood Formation. British paleontologist Richard Owen initially identified the fragments as those of the pareiasaur Anthodon. After remaining untouched for years in the British Museum of Natural History, the partial skull was identified by South African paleontologist Robert Broom as belonging to a different genus; he named the specimen Palaeoscincus africanus. Several years later, Hungarian paleontologist Franz Nopcsa, unaware of Broom's new name, similarly concluded that it represented a new taxon, and named it Paranthodon owenii. Since Nopcsa's species name was assigned after Broom's, and Broom did not assign a new genus, both names are now synonyms of the current binomial, Paranthodon africanus. The genus name combines the Ancient Greek para (near) with the genus name Anthodon, to represent the initial referral of the remains.

Majungasaurus is a genus of abelisaurid theropod dinosaur that lived in Madagascar from 70 to 66 million years ago, at the end of the Cretaceous Period, making it one of the last-known non-avian dinosaurs that went extinct during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. The genus contains a single species, Majungasaurus crenatissimus. This dinosaur is also called Majungatholus, a name which is considered a junior synonym of Majungasaurus.

Ekrixinatosaurus is a genus of abelisaurid theropod which lived approximately 100 to 97 million years ago during the Late Cretaceous period. Its fossils have been found in Argentina. Only one species is currently recognized, Ekrixinatosaurus novasi, from which the specific name honors of Dr. Fernando Novas for his contributions to the study of abelisaurid theropods, while the genus name refers to the dynamiting of the holotype specimen. It was a large abelisaur, measuring between 6.5 and 8 m in length and weighing 800 kg (1,800 lb).

Mahajangasuchus is an extinct genus of crocodyliform which had blunt, conical teeth. The type species, M. insignis, lived during the Late Cretaceous; its fossils have been found in the Maevarano Formation in northern Madagascar. It was a fairly large predator, measuring up to 4 metres (13 ft) long.

Anatosuchus is an extinct genus of notosuchian crocodyliforms discovered in Gadoufaoua, Niger, and described by a team of palaeontologists led by the American Paul Sereno in 2003, in the Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology.
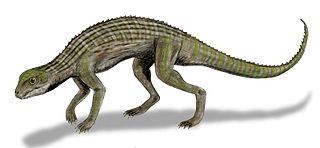
Adamantinasuchus is an extinct genus of notosuchian crocodylomorph from and named after the Late Cretaceous Adamantina Formation of Brazil. It is known from only one fossil, holotype UFRJ-DG 107-R, collected by William Nava. The fossil consists of a partial skull, fragmentary limb bones and a few broken vertebrae, and was found 25 kilometres (16 mi) southwest of the town of Marilia, near a reservoir dam. Adamantinasuchus was approximately 60 centimetres (24 in) long from nose to tail, and would have only weighed a few kilograms.

Brachyrostra is a clade within the theropod dinosaur family Abelisauridae. It includes the famous genera Carnotaurus, Abelisaurus, Aucasaurus as well as their close relatives from the Cretaceous Period of Argentina and Brazil plus Caletodraco from France. The group was first proposed in an analysis conducted by Juan Canale and colleagues in 2008. They found that all South American abelisaurids described up to that point grouped together as a sub-clade of Abelisauridae, which they named based on the relatively unusual shape of their skulls. They defined the clade Brachyrostra as "all the abelisaurids more closely related to Carnotaurus sastrei than to Majungasaurus crenatissimus."

Biseridens is an extinct genus of anomodont therapsid, and one of the most basal anomodont genera known. Originally known from a partial skull misidentified as an eotitanosuchian in 1997, another well-preserved skull was found in the Qingtoushan Formation in the Qilian Mountains of Gansu, China, in 2009 that clarified its relationships to anomodonts, such as the dicynodonts.

Polonosuchus is a genus of rauisuchid known from the late Triassic of Poland. It was a huge predator about 5–6 metres in length and, like all rauisuchians, was equipped with a large head of long sharp teeth. The legs were placed almost underneath the body, unlike most reptiles, which would have made it quite fast and a powerful runner. The appearance was very similar to that of the more known Postosuchus, of North America, and shared with the latter the ecological niche of the apex predator.

Eoabelisaurus is a genus of abelisauroid theropod dinosaur from the Lower Jurassic Cañadón Asfalto Formation of the Cañadón Asfalto Basin in Argentina, South America. The generic name combines a Greek ἠώς, (eos), "dawn", with the name Abelisaurus, in reference to the fact it represents an early relative of the latter. Only one species is currently recognized, E. mefi; the specific name honours the MEF, the Museo Paleontológico "Egidio Feruglio", where discoverer Diego Pol is active. It is characterized by reduced forelimb proportions that show primitive characteristics of the Abelisauridae family.

Arcovenator is an extinct genus of abelisaurid theropod dinosaurs hailing from the Late Cretaceous of France and possibly Spain. The type and only described species is Arcovenator escotae.
This Glossary explains technical terms commonly employed in the description of dinosaur body fossils. Besides dinosaur-specific terms, it covers terms with wider usage, when these are of central importance in the study of dinosaurs or when their discussion in the context of dinosaurs is beneficial. The glossary does not cover ichnological and bone histological terms, nor does it cover measurements.
Panguraptor is a genus of coelophysid theropod dinosaur known from fossils discovered in Lower Jurassic rocks of southern China. The type and only known species is Panguraptor lufengensis. The generic name refers to the deity Pangu but also to the supercontinent Pangaea for which in a geological context the same characters are used: 盘古. Raptor means "seizer", "robber" in Latin. The specific name is a reference to the Lufeng Formation. The holotype specimen was recovered on 12 October 2007 from the Lufeng Formation of Yunnan, which is noted for sauropodomorph fossils. It was described in 2014 by You Hai-Lu and colleagues.

Akainacephalus is a monospecific genus of ankylosaurid dinosaur from southern Utah that lived during the Late Cretaceous in what is now the Horse Mountain Gryposaur Quarry of the Kaiparowits Formation. The type and only species, Akainacephalus johnsoni, is known from the most complete ankylosaur specimen ever discovered from southern Laramidia, including a complete skull, tail club, a number of osteoderms, limb elements and part of its pelvis, among other remains. It was described in 2018 by Jelle P. Wiersma and Randall B. Irmis. It is closely related and shares similar cranial anatomy to Nodocephalosaurus.
Tralkasaurus is a genus of abelisaurid dinosaur from the Huincul Formation from Río Negro Province in Argentina. The type and only species is Tralkasaurus cuyi, named in 2020 by Mauricio Cerroni and colleagues based on an incomplete skeleton. A medium-sized abelisaurid, Tralkasaurus exhibits a conflicting blend of characteristics found among the early-diverging abelisauroids with others that characterize the highly specialized clade Brachyrostra, and thus its position within the clade is poorly-resolved.

Bagualia, is an extinct genus of eusauropod dinosaur, from the Early Jurassic Epoch in what is now the Chubut Province of Argentina. The type species, B. alba, was formally described in 2020. Bagualia represents the oldest definitive Eusauropod, and due to the completeness of its material it represents one of the most important taxa for understanding the early evolution of the group.

Baiyinosaurus is an extinct genus of stegosaurian dinosaurs from the Middle Jurassic Wangjiashan Formation of China. The genus contains a single species, B. baojiensis, known from a partial skeleton including cranial bones. The skeletal anatomy of Baiyinosaurus demonstrates transitional features between basal thyreophorans and stegosaurs. While many stegosaurs are known from China, Baiyinosaurus is the only one currently named from Gansu Province.
































