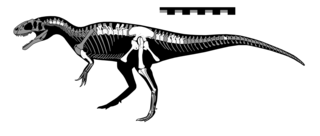
Gasosaurus is a genus of tetanuran theropod that lived approximately 171.6 to 161.2 million years ago during the middle of the Jurassic Period. The name "Gasosaurus" is derived from the English "gasoline" and the Greek σαῦρος. Only one species is currently recognised, G. constructus, from which the specific name honours the gasoline company that found the Dashanpu fossil quarry in Sichuan Province, China, now named as the Lower Shaximiao Formation.

Afrovenator is a genus of megalosaurid theropod dinosaur from the Middle or Late Jurassic Period on the Tiourarén Formation and maybe the Irhazer II Formation of the Niger Sahara region in northern Africa. Afrovenator represents the only properly identified Gondwanan megalosaur, with proposed material of the group present in the Late Jurassic on Tacuarembó Formation of Uruguay and the Tendaguru Formation of Tanzania.
Metriacanthosaurus is a genus of metriacanthosaurid dinosaur from the upper Oxford Clay of England, dating to the Late Jurassic period, about 160 million years ago.

Allosauridae is a family of medium to large bipedal, carnivorous allosauroid theropod dinosaurs from the Late Jurassic. Allosauridae is a fairly old taxonomic group, having been first named by the American paleontologist Othniel Charles Marsh in 1878. Allosaurids are characterized by an astragalus with a restriction of the ascending process to the lateral part of the bone, a larger medial than lateral condyle, and a horizontal groove across the face of the condyles.

Elaphrosaurus is a genus of ceratosaurian theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 154 to 150 million years ago during the Late Jurassic Period in what is now Tanzania in Africa. Elaphrosaurus was a medium-sized but lightly built member of the group that could grow up to 6.2 m (20 ft) long. Morphologically, this dinosaur is significant in two ways. Firstly, it has a relatively long body but is very shallow-chested for a theropod of its size. Secondly, it has very short hindlimbs in comparison with its body. Phylogenetic analyses indicate that this genus is likely a ceratosaur. Earlier suggestions that it is a late surviving coelophysoid have been examined but generally dismissed. Elaphrosaurus is currently believed to be a very close relative of Limusaurus, an unusual beaked ceratosaurian which may have been either herbivorous or omnivorous.

Monolophosaurus is an extinct genus of tetanuran theropod dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic Shishugou Formation in what is now Xinjiang, China. It was named for the single crest on top of its skull. Monolophosaurus was a mid-sized theropod at about 5–5.5 metres (16–18 ft) long and weighed 475 kilograms (1,047 lb).

Siamotyrannus is a genus of theropod dinosaur from the early Cretaceous of Thailand.

Megalosauroidea is a superfamily of tetanuran theropod dinosaurs that lived from the Middle Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous period. The group is defined as Megalosaurus bucklandii and all taxa sharing a more recent common ancestor with it than with Allosaurus fragilis or Passer domesticus. Members of the group include Spinosaurus, Megalosaurus, and Torvosaurus. They are possibly paraphyletic in nature with respect to Allosauroidea.

Xuanhanosaurus is a genus of theropod dinosaur that lived during the Middle Jurassic (Bathonian) of the Sichuan Basin, China, around 166 million years ago. This taxon represents one of the various non-coelurosaurian tetanuran taxa found on the Middle Jurassic of the region, uncovered in the Lower Shaximiao Formation. Although it has been known for more than 40 years, this taxon has been the subject of very few studies, although most seem to agree that it is a tetanuran, possibly a basal allosauroid, highlighting the fact that it has a vestigial fourth metacarpal.

Magnosaurus was a genus of theropod dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic of England. It is based on fragmentary remains and has often been confused with or included in Megalosaurus.
Chuandongocoelurus is a genus of carnivorous tetanuran theropod dinosaur from the Jurassic of China.

Szechuanosaurus is an extinct genus of carnivorous theropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic. Fossils referred to the genus have been found in China, Asia in the Oxfordian-?Tithonian. Its type species is based on several undiagnostic teeth from the Kuangyuan Series. Additional possible specimens of Szechuanosaurus were also reported from the Kalaza Formation, also located in China.

Condorraptor is an extinct genus of megalosauroid theropod dinosaur. Its genus name means 'robber from Cerro Condor', referencing a nearby village, while its species name, currumili, is named after Hipolito Currumil, the landowner and discoverer of the locality. It was among the earliest large South American theropods, having been found in Lower Jurassic strata of the Cañadón Asfalto Formation in the Cañadón Asfalto Basin of Argentina. The type species, described in 2005, is Condorraptor currumili. It is based on a tibia, with an associated partial skeleton that may belong to the same individual. Initially described as a basal tetanuran, Benson (2010) found it to be a piatnitzkysaurid megalosauroid and the sister taxon of Piatnitzkysaurus, a finding supported by later studies.

Dubreuillosaurus is a genus of carnivorous dinosaur from the middle Jurassic Period. It is a megalosaurid theropod. Its fossils were found in France. The only named species, Dubreuillosaurus valesdunensis, was originally described as a species of Poekilopleuron, Poekilopleuron? valesdunensis, which is still formally the type species of the genus. It was later renamed Dubreuillosaurus valesdunensis when, in 2005, Allain came to the conclusion that it was not part of the genus Poekilopleuron. Its type specimen, MNHN 1998-13, is only rivalled in the number of preserved elements in this group by that of Eustreptospondylus. Dubreuillosaurus is considered to be the sister species of Magnosaurus. It did not show signs of insular dwarfism even though it was uncovered on an island.

Streptospondylus is a genus of tetanuran theropod dinosaur known from the Late Jurassic period of France, 161 million years ago. It was a medium-sized predator with an estimated length of 6 meters (19.5 ft) and a weight of 500 kg (1,100 lbs).

Spinostropheus is a genus of carnivorous neotheropod theropod dinosaur that lived in the Middle Jurassic period and has been found in the Tiouraren Formation, Niger. The type and only species is S. gautieri.

Noasauridae is an extinct family of theropod dinosaurs belonging to the group Ceratosauria. They were closely related to the short-armed abelisaurids, although most noasaurids had much more traditional body types generally similar to other theropods. Their heads, on the other hand, had unusual adaptations depending on the subfamily. 'Traditional' noasaurids, sometimes grouped in the subfamily Noasaurinae, had sharp teeth which splayed outwards from a downturned lower jaw.

Shidaisaurus is a genus of metriacanthosaurid dinosaur. Its fossil was found in early Middle Jurassic-age rocks of the Chuanjie Formation in Yunnan, China. It is known from a partial skeleton, holotype DML-LCA 9701-IV, found at the bottom of an assemblage of nine dinosaur individuals, lacking most of the tail vertebrae, ribs, pectoral girdle, and limb bones. Shidaisaurus was described in 2009 by Wu and colleagues. The type species is Shidaisaurus jinae. Generic name and specific name in combination refer to the Jin-Shidai Company that oversaw excavation and inspection of the Jurassic World Park near the site.
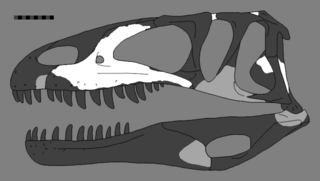
Leshansaurus is a genus of theropod dinosaur from the Late Jurassic Shaximiao Formation of what is now China. It was described in 2009 by a team of Chinese paleontologists. The type species is Leshansaurus qianweiensis. Fossils of Leshansaurus were discovered in strata from the Shangshaximiao Formation, a formation rich in dinosaur fossils. Li et al. referred this taxon to Sinraptoridae – a group of carnosaurian theropods, but it may belong to Megalosauridae instead.

Orionides is a clade of tetanuran theropod dinosaurs from the Middle Jurassic to the Present. The clade includes most theropod dinosaurs, including birds.


































