| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|
| Cowan's shrew tenrec  | M. cowani
Thomas, 1882 | Madagascar
 | Size: 6–10 cm (2–4 in) long, plus 6–8 cm (2–3 in) tail [58]
Habitat: Forest [59]
Diet: Insects and other invertebrates, as well as small vertebrates [60] | LC
Unknown  [59] [59]
|
|---|
| Drouhard's shrew tenrec  | M. drouhardi
Grandidier, 1934 | Eastern Madagascar
 | Size: 6–9 cm (2–4 in) long, plus 5–9 cm (2–4 in) tail [61]
Habitat: Forest [62]
Diet: Insects and other invertebrates, as well as small vertebrates [60] | LC
Unknown  [62] [62]
|
|---|
| Dryad shrew tenrec
| M. dryas
Jenkins, 1992 | Northeastern Madagascar
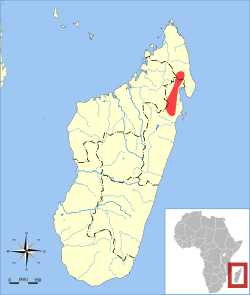 | Size: 17–18 cm (7–7 in) long, plus tail [63]
Habitat: Forest [64]
Diet: Invertebrates [63] | VU
Unknown  [64] [64]
|
|---|
| Gracile shrew tenrec
| M. gracilis
(Major, 1896) | Eastern Madagascar
 | Size: 16–19 cm (6–7 in) long, plus tail [65]
Habitat: Forest [66]
Diet: Believed to be insects, earthworms, and other invertebrates [65] | LC
Unknown  [66] [66]
|
|---|
| Grandidier's shrew tenrec
| M. grandidieri
Olson, Rakotomalala, Hildebrandt, Lanier, Raxworthy, Goodman, 2009 | Western Madagascar | Size: 5–8 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 3–4 cm (1–2 in) tail [67]
Habitat: Forest and shrubland [68]
Diet: Believed to be insects and other invertebrates [67] | LC
Unknown  [68] [68]
|
|---|
| Greater long-tailed shrew tenrec
| M. principula
Thomas, 1926 | Eastern Madagascar
 | Size: 7–8 cm (3 in) long, plus 14–18 cm (6–7 in) tail [69]
Habitat: Forest [70]
Diet: Insects and other invertebrates, as well as small vertebrates [60] | LC
Unknown  [70] [70]
|
|---|
| Jenkins's shrew tenrec
| M. jenkinsae
Goodman, Soarimalala, 2004 | Southwestern Madagascar | Size: 7–8 cm (3 in) long, plus 7–9 cm (3–4 in) tail [71]
Habitat: Forest and shrubland [72]
Diet: Insects and other invertebrates [60] | EN
Unknown  [72] [72]
|
|---|
| Least shrew tenrec
| M. pusilla
Major, 1896 | Eastern Madagascar
 | Size: 4–6 cm (2 in) long, plus 6–8 cm (2–3 in) tail [73]
Habitat: Forest and inland wetlands [74]
Diet: Insects and other invertebrates [60] | LC
Unknown  [74] [74]
|
|---|
| Lesser long-tailed shrew tenrec
| M. longicaudata
Thomas, 1882 | Central and northern Madagascar
 | Size: 6–8 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 11–16 cm (4–6 in) tail [60]
Habitat: Forest [75]
Diet: Insects, arachnids, crustaceans, and other invertebrates [76] | LC
Unknown  [75] [75]
|
|---|
| Major's long-tailed tenrec
| M. majori
Thomas, 1918 | Madagascar
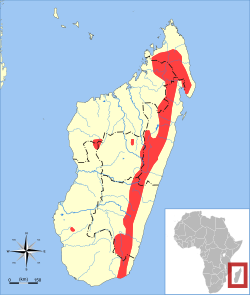 | Size: 5–7 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 10–14 cm (4–6 in) tail [77]
Habitat: Forest [78]
Diet: Insects and other invertebrates [60] | LC
Unknown  [78] [78]
|
|---|
| Montane shrew tenrec
| M. monticola
Goodman, Jenkins, 1998 | Northeastern Madagascar
 | Size: 7–10 cm (3–4 in) long, plus 9–12 cm (4–5 in) tail [79]
Habitat: Forest [80]
Diet: Insects and other invertebrates [60] | VU
Unknown  [80] [80]
|
|---|
| Naked-nosed shrew tenrec
| M. gymnorhyncha
Jenkins, Goodman, Raxworthy, 1996 | Eastern Madagascar
 | Size: 13–18 cm (5–7 in) long, plus tail [81]
Habitat: Forest [82]
Diet: Insects, as well as small mammals, amphibians, vegetation, and potentially carrion [81] | LC
Unknown  [82] [82]
|
|---|
| Nasolo's shrew tenrec
| M. nasoloi
Jenkins, 1999 | Western Madagascar
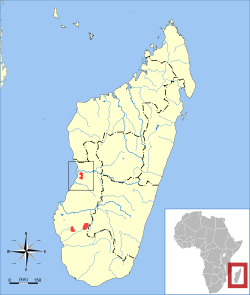 | Size: About 8 cm (3 in) long, plus 5 cm (2 in) tail [83]
Habitat: Forest [84]
Diet: Insects and other invertebrates [60] | VU
Unknown  [84] [84]
|
|---|
| Northern shrew tenrec
| M. jobihely
Goodman, Raxworthy, Maminirina, Olson, 2006 | Eastern and northern Madagascar
 | Size: 4–7 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 4–6 cm (2 in) tail [85]
Habitat: Forest [86]
Diet: Insects and other invertebrates [60] | EN
Unknown  [86] [86]
|
|---|
| Pale shrew tenrec
| M. fotsifotsy
Jenkins, Raxworthy, Nussbaum, 1997 | Eastern and northern Madagascar
 | Size: 6–9 cm (2–4 in) long, plus 7–10 cm (3–4 in) tail [79]
Habitat: Forest [87]
Diet: Insects and other invertebrates [60] | LC
Unknown  [87] [87]
|
|---|
| Pygmy shrew tenrec
| M. parvula
Grandidier, 1934 | Eastern and northern Madagascar
 | Size: 5–7 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 4–7 cm (2–3 in) tail [88]
Habitat: Forest [89]
Diet: Insects and other invertebrates [60] | LC
Unknown  [89] [89]
|
|---|
| Short-tailed shrew tenrec
| M. brevicaudata
Grandidier, 1899 | Western and northern Madagascar
 | Size: 6–7 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 3 cm (1 in) tail [90]
Habitat: Forest and shrubland [91]
Diet: Insects and small vertebrates [90] | LC
Unknown  [91] [91]
|
|---|
| Shrew-toothed shrew tenrec
| M. soricoides
Jenkins, 1993 | Eastern Madagascar
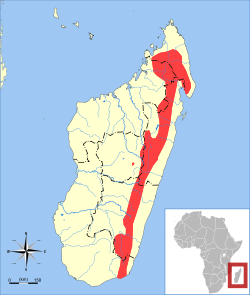 | Size: 7–11 cm (3–4 in) long, plus 8–11 cm (3–4 in) tail [92]
Habitat: Forest [93]
Diet: Insects and other invertebrates, as well as small vertebrates [60] | LC
Unknown  [93] [93]
|
|---|
| Taiva shrew tenrec
| M. taiva
Major, 1896 | Eastern Madagascar
 | Size: 5–8 cm (2–3 in) long, plus 7–9 cm (3–4 in) tail [85]
Habitat: Forest [94]
Diet: Insects and other invertebrates [60] | LC
Unknown  [94] [94]
|
|---|
| Thomas's shrew tenrec
| M. thomasi
Major, 1896 | Eastern Madagascar
 | Size: 7–12 cm (3–5 in) long, plus 5–8 cm (2–3 in) tail [77]
Habitat: Forest [95]
Diet: Insects and other invertebrates [60] | LC
Unknown  [95] [95]
|
|---|
| Web-footed tenrec
| M. mergulus
Major, 1896 | Eastern Madagascar
 | Size: 12–17 cm (5–7 in) long, plus 11–17 cm (4–7 in) tail
Habitat: Forest and inland wetlands
Diet: Insects, as well as tadpoles and crayfish | VU
Unknown 
|
|---|