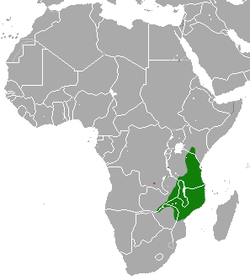
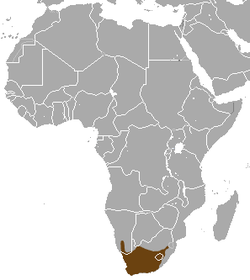
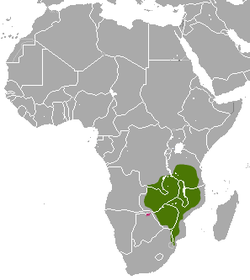
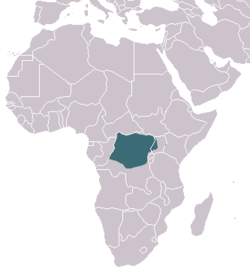
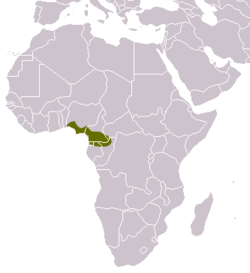
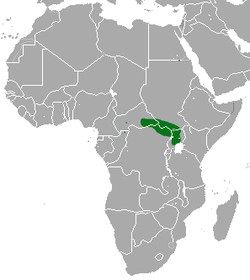
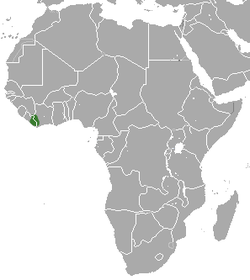
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|
| Collared mongoose  | U. semitorquata
(Gray, 1846)
- U. s. semitorquata
- U. s. uniforma
| Borneo in Southeast Asia
 | Size: 40–46 cm (16–18 in) long, plus 25–31 cm (10–12 in) tail [10]
Habitat: Forest [22]
Diet: Unknown [10] [22] | NT
Unknown  [22] [22]
|
|---|
| Crab-eating mongoose  | U. urva
(Hodgson, 1836)
- U. u. annamensis
- U. u. formosana
- U. u. sinensis
- U. u. urva
| Eastern and Southeast Asia
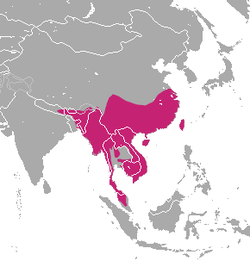 | Size: 45–50 cm (18–20 in) long, plus 25–30 cm (10–12 in) tail [23]
Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland [24]
Diet: Crustaceans, mammals, reptiles, insects, and amphibians [24] | LC
Unknown  [24] [24]
|
|---|
| Indian brown mongoose  | U. fusca
(Waterhouse, 1838)
- U. f. flavidens
- U. f. fusca
- U. f. maccarthiae
- U. f. rubidior
- U. f. siccata
| South India, Sri Lanka
 | Size: 33–48 cm (13–19 in) long, plus 20–33 cm (8–13 in) tail [23]
Habitat: Forest and grassland [25]
Diet: Believed to be a variety of small vertebrates and invertebrates [10] [25] | LC
Unknown  [25] [25]
|
|---|
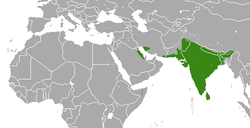
| Indian grey mongoose  | U. edwardsii
(Geoffroy, 1818)
- U. e. edwardsii
- U. e. ferruginea
- U. e. lanka
- U. e. montana
- U. e. nyula
| India, west Asia
 | Size: 36–45 cm (14–18 in) long, plus 32–45 cm (13–18 in) tail [23]
Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland [26]
Diet: Small mammals, birds, reptiles, eggs, and invertebrates [10] [26] | LC
Unknown  [26] [26]
|
|---|
| Javan mongoose  | U. javanica
(Geoffroy, 1818)
- U. j. exilis
- H. j. javanica
- U. j. orientalis
- U. j. peninsulae
- U. j. perakensis
- U. j. rafflesii
- U. j. rubrifrons
- U. j. siamensis
- U. j. tjerapai
| Southeast Asia
 | Size: 25–37 cm (10–15 in) long, plus 24–27 cm (9–11 in) tail [27]
Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands [28]
Diet: Invertebrates, as well as rodents, birds, snakes, lizards, frogs, fish, and fruit [27] [28] | LC
Unknown  [28] [28]
|
|---|
| Small Indian mongoose  | U. auropunctata
(Hodgson, 1836)
| West, south, and southeast Asia
 | Size: 25–37 cm (10–15 in) long, plus 24–27 cm (9–11 in) tail [27]
Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands [28]
Diet: Invertebrates, as well as rodents, birds, snakes, lizards, frogs, fish, and fruit [27] [28] | LC
Unknown  [28] [28]
|
|---|
| Ruddy mongoose  | U. smithii
(Gray, 1837)
- U. s. smithii
- U. s. thysanura
- U. s. zeylania
| India and Sri Lanka
 | Size: 39–45 cm (15–18 in) long, plus 35–47 cm (14–19 in) tail [23]
Habitat: Forest and shrubland [29]
Diet: Rodents, birds, and reptiles [10] [29] | LC
Unknown  [29] [29]
|
|---|
| Short-tailed mongoose  | U. brachyura
(Gray, 1837)
- U. b. brachyura
- U. b. hosei (Hose's mongoose)
- U. b. javanensis
- U. b. palawana
- U. b. parva
- U. b. sumatria
| Southeast Asia
 | Size: 38–45 cm (15–18 in) long, plus 20–25 cm (8–10 in) tail [30]
Habitat: Forest and shrubland [31]
Diet: Invertebrates and small vertebrates [31] | NT
Unknown  [31] [31]
|
|---|
| Stripe-necked mongoose  | U. vitticolla
(Bennett, 1835)
- U. v. inornata
- U. v. vitticolla
| Southern India and Sri Lanka
 | Size: 25–41 cm (10–16 in) long, plus 22–36 cm (9–14 in) tail [23]
Habitat: Forest and shrubland [32]
Diet: Small mammals, birds, birds' eggs, reptiles, fish, insects, and roots [32] | LC
Unknown  [32] [32]
|
|---|