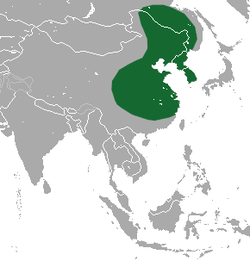
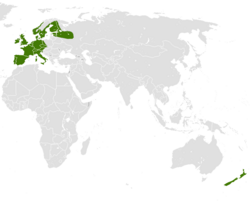
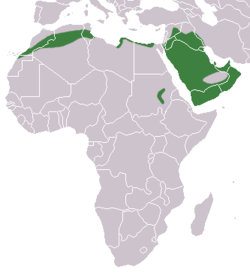
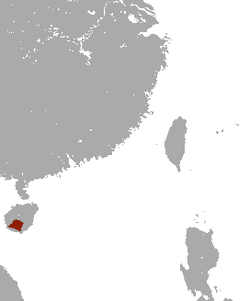
Erinaceidae is a family of small mammals in the order Eulipotyphla. A member of this family is called an erinaceid, and the family includes hedgehogs and gymnures. Erinaceidae is one of four families in the order Eulipotyphla. [1] They are found in Africa, Europe, and Asia, primarily in forests, shrublands, savannas, and grasslands, though some species can also be found in deserts, rocky areas, or caves. They range in size from the gymnures in the Hylomys genus, at 9 cm (4 in) plus a 1 cm (0.4 in) tail, to the moonrat, at 46 cm (18 in) plus a 30 cm (12 in) tail. Erinaceids are omnivorous and primarily eat insects and small vertebrates such as lizards, though they also consume plants, eggs, and fungi. Hedgehogs all have spines on their backs, while gymnures have fur. No erinaceids have population estimates, but the Hainan gymnure and Dinagat gymnure are categorized as endangered species.
Contents
- Conventions
- Classification
- Erinaceids
- Subfamily Erinaceinae
- Subfamily Galericinae
- References
- Sources
The twenty-four extant species of Erinaceidae are divided into two subfamilies: Erinaceinae, containing sixteen hedgehog species in five genera, and Galericinae, containing eight gymnure species in five genera. A few extinct prehistoric Erinaceidae species have been discovered, though due to ongoing research and discoveries the exact number and categorization is not fixed. [2]