| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|
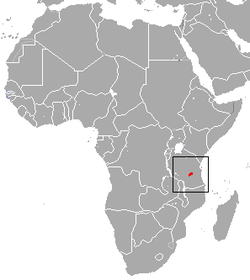
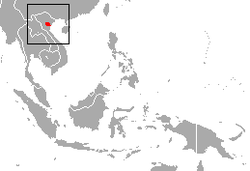
| Toque macaque  | M. sinica
(Linnaeus, 1771)
- M. s. aurifrons (Pale-fronted toque macaque)
- M. s. opisthomelas (Highland toque macaque)
- M. s. sinica (Common toque macaque)
| Sri Lanka
 | Size: 36–53 cm (14–21 in) long, plus at least 36–53 cm (14–21 in) tail [96]
Habitat: Forest [97]
Diet: Fruit as well as tree flowers, buds, and leaves [98] | EN
Unknown  [97] [97]
|
|---|
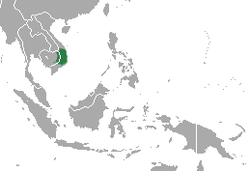
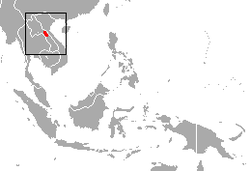
| Arunachal macaque  | M. munzala
Sinha, Datta, Madhusudan, Mishra, 2005 | Eastern Himalayas
 | Size: 36–77 cm (14–30 in) long, plus about 9–20 cm (4–8 in) tail [96]
Habitat: Forest [99]
Diet: Fruit, leaves, grains, buds, seeds, flowers, and bark, as well as insects and small invertebrates [96] | EN
250  [99] [99]
|
|---|
| Assam macaque  | M. assamensis
McClelland, 1840
- M. a. assamensis (Eastern Assamese macaque)
- M. a. pelops (Western Assamese macaque)
| Southeastern Asia
 | Size: 36–77 cm (14–30 in) long, plus about 9–20 cm (4–8 in) tail [96]
Habitat: Forest [100]
Diet: Fruit, leaves, grains, buds, seeds, flowers, and bark, as well as insects and small invertebrates [96] | NT
Unknown  [100] [100]
|
|---|
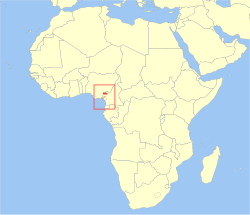
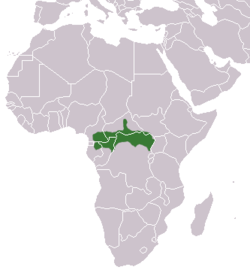
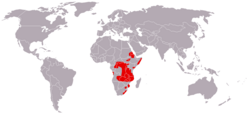
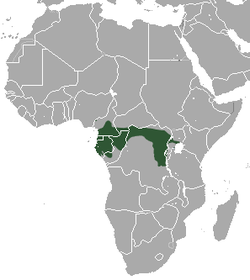
| Barbary macaque  | M. sylvanus
(Linnaeus, 1758) | Northwestern Africa
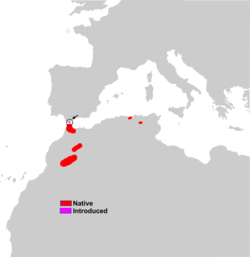 | Size: 45–60 cm (18–24 in) long, plus 1–2 cm (0–1 in) tail [101]
Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, rocky areas, and caves [102]
Diet: Plants, caterpillars, fruit, seeds, roots, and fungi [101] | EN
Unknown  [102] [102]
|
|---|
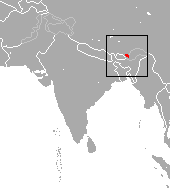
| Bonnet macaque  | M. radiata
(Geoffroy, 1812)
- M. r. diluta
- M. r. radiata
| Southern India
 | Size: 36–77 cm (14–30 in) long, plus about 9–20 cm (4–8 in) tail [96]
Habitat: Forest, savanna, and shrubland [103]
Diet: Fruit, foliage, and insects, as well as bird eggs and lizards [104] | VU
Unknown  [103] [103]
|
|---|
| Booted macaque  | M. ochreata
(Ogilby, 1841) | Island of Sulawesi in Indonesia
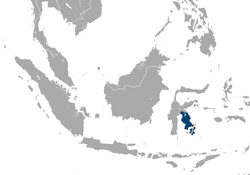 | Size: 36–77 cm (14–30 in) long, plus about 1–15 cm (0–6 in) tail [96]
Habitat: Forest and savanna [105]
Diet: Fruit, leaves, grains, buds, seeds, flowers, and bark, as well as insects and small invertebrates [96] | VU
Unknown  [105] [105]
|
|---|
| Celebes crested macaque  | M. nigra
(Desmarest, 1822) | Island of Sulawesi
 | Size: 44–57 cm (17–22 in) long, plus about 2 cm (1 in) tail [106]
Habitat: Forest [107]
Diet: Fruit, as well as insects, shoots, leaves, and stems [106] | CR
Unknown  [107] [107]
|
|---|
| Crab-eating macaque  | M. fascicularis
Raffles, 1821
- M. f. atriceps (Dark-crowned long-tailed macaque)
- M. f. aureus (Burmese long-tailed macaque)
- M. f. condorensis (Con Song long-tailed macaque)
- M. f. fascicularis (Common long-tailed macaque)
- M. f. fusca (Simeulue long-tailed macaque)
- M. f. karimondjawae (Kemujan long-tailed macaque)
- M. f. lasiae (Lasia long-tailed macaque)
- M. f. philippensis (Philippine long-tailed macaque)
- M. f. tua (Maratua long-tailed macaque)
- M. f. umbrosus (Nicobar long-tailed macaque)
| Southeastern Asia
 | Size: 40–47 cm (16–19 in) long, plus 50–60 cm (20–24 in) tail
Habitat: Forest, intertidal marine, caves, inland wetlands, grassland, shrubland, and savanna [108]
Diet: Fruit, crabs, flowers, insects, leaves, fungi, grasses, and clay [109] | EN
Unknown  [108] [108]
|
|---|
| Formosan rock macaque  | M. cyclopis
(Swinhoe, 1862) | Taiwan
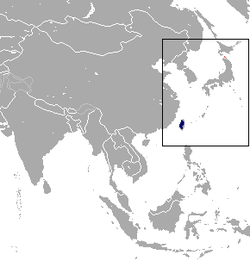 | Size: 36–45 cm (14–18 in) long, plus 26–46 cm (10–18 in) tail [110]
Habitat: Forest [111]
Diet: Fruit, leaves, berries, seeds, insects, and small vertebrates, buds, and shoots [110] | LC
Unknown  [111] [111]
|
|---|
| Gorontalo macaque  | M. nigrescens
(Temminck, 1849) | Island of Sulawesi
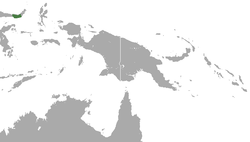 | Size: 36–77 cm (14–30 in) long, plus about 1–15 cm (0–6 in) tail [96]
Habitat: Forest [112]
Diet: Fruit, leaves, grains, buds, seeds, flowers, and bark, as well as insects and small invertebrates [96] | VU
Unknown  [112] [112]
|
|---|
| Heck's macaque
| M. hecki
(Matschie, 1901) | Island of Sulawesi
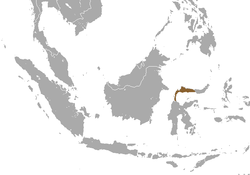 | Size: 36–77 cm (14–30 in) long, plus about 1–15 cm (0–6 in) tail [96]
Habitat: Forest and grassland [113]
Diet: Fruit, leaves, grains, buds, seeds, flowers, and bark, as well as insects and small invertebrates [96] | VU
100,000  [113] [113]
|
|---|
| Japanese macaque  | M. fuscata
Blyth, 1875
| Japan
 | Size: 36–77 cm (14–30 in) long, plus about 1–15 cm (0–6 in) tail [96]
Habitat: Forest [114]
Diet: Fruit, seeds, flowers, nectar, leaves, and fungi [115] | LC
Unknown  [114] [114]
|
|---|
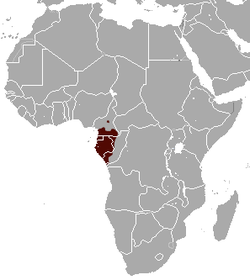
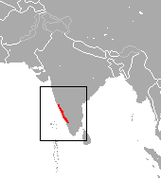
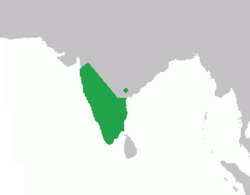
| Lion-tailed macaque  | M. silenus
(Linnaeus, 1758) | Southwestern India
 | Size: 40–61 cm (16–24 in) long, plus 24–38 cm (9–15 in) tail [116]
Habitat: Forest [117]
Diet: Fruit, as well as leaves, stems, flowers, buds, fungi, insects, lizards, tree frogs, and small mammals [116] | EN
2,400–2,500  [117] [117]
|
|---|
| Moor macaque  | M. maura
(Schinz, 1825) | Island of Sulawesi
 | Size: 36–77 cm (14–30 in) long, plus about 1–15 cm (0–6 in) tail [96]
Habitat: Forest and grassland [118]
Diet: Fruit, leaves, grains, buds, seeds, flowers, and bark, as well as insects and small invertebrates [96] | EN
Unknown  [118] [118]
|
|---|
| Muna-Buton macaque
| M. brunnescens
(Matschie, 1901) | Island of Sulawesi in Indonesia
 | Size: 36–77 cm (14–30 in) long, plus about 1–15 cm (0–6 in) tail [96]
Habitat: Forest [119]
Diet: Fruit, leaves, grains, buds, seeds, flowers, and bark, as well as insects and small invertebrates [96] | VU
Unknown  [119] [119]
|
|---|
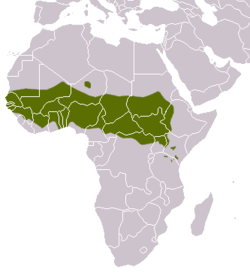
| Northern pig-tailed macaque  | M. leonina
(Blyth, 1863) | Southeastern Asia
 | Size: 36–77 cm (14–30 in) long, plus about 9–20 cm (4–8 in) tail [96]
Habitat: Forest [120]
Diet: Leaves, seeds, stems, roots, flowers, bamboo shoots, rice, gums, insects, larvae, termite eggs and spiders [120] | VU
Unknown  [120] [120]
|
|---|
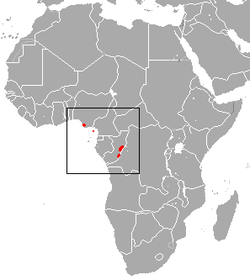
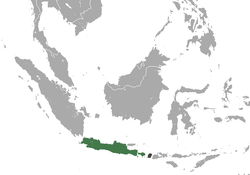
| Pagai Island macaque  | M. pagensis
(Miller, 1903) | Mentawai Islands in Indonesia
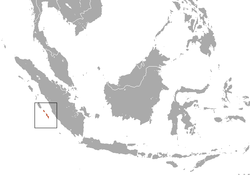 | Size: 36–77 cm (14–30 in) long, plus about 9–20 cm (4–8 in) tail [96]
Habitat: Forest [121]
Diet: Fruit, leaves, grains, buds, seeds, flowers, and bark, as well as insects and small invertebrates [96] | CR
2,100–3,700  [121] [121]
|
|---|
| Rhesus macaque  | M. mulatta
(Zimmermann, 1790) | Southern and southeastern Asia
 | Size: 45–64 cm (18–25 in) long, plus 19–32 cm (7–13 in) tail [122]
Habitat: Forest, savanna, and shrubland [123]
Diet: Fish, crabs, shellfish, bird eggs, honeycombs, crayfish, crabs, spiders, plants, gums and pith [123] | LC
Unknown  [123] [123]
|
|---|
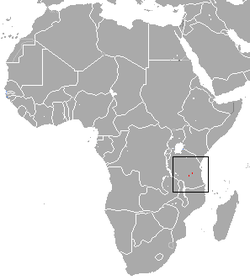
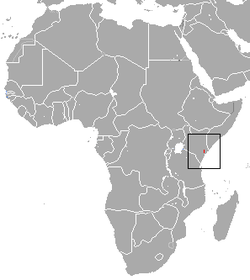
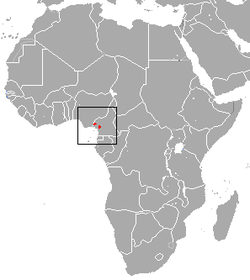
| Siberut macaque
| M. siberu
Fuentes, 1995 | Siberut island in Indonesia
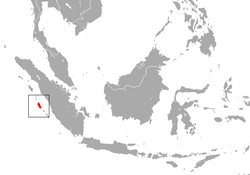 | Size: 36–77 cm (14–30 in) long, plus about 9–20 cm (4–8 in) tail [96]
Habitat: Forest [124]
Diet: Fruit, as well as mushrooms, leaves, crabs, crayfish, pith, sap, shoots and flowers [124] | EN
Unknown  [124] [124]
|
|---|
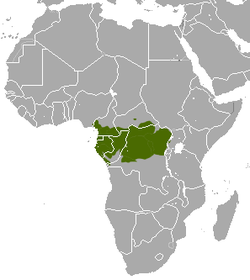
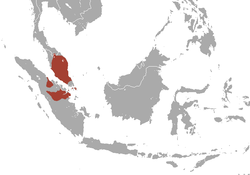
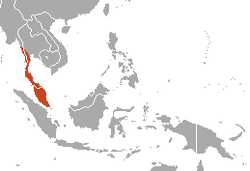
| Southern pig-tailed macaque  | M. nemestrina
(Linnaeus, 1766) | Southeastern Asia
 | Size: 46–57 cm (18–22 in) long, plus 13–26 cm (5–10 in) tail [125]
Habitat: Forest and shrubland [126]
Diet: Fruit, insects, seeds, leaves, dirt, and fungus, as well as birds, termite eggs and larvae, and river crabs [125] | EN
Unknown  [126] [126]
|
|---|
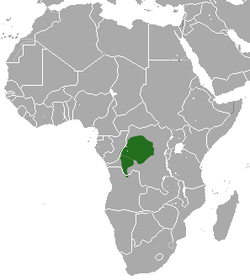
| Stump-tailed macaque  | M. arctoides
(Geoffroy, 1831) | Southeastern Asia
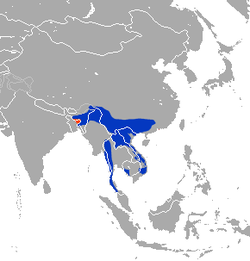 | Size: 48–65 cm (19–26 in) long, plus 3–7 cm (1–3 in) tail [127]
Habitat: Forest [128]
Diet: Fruit, seeds, flowers, roots, leaves, frogs, crabs, birds, and bird eggs [127] | VU
Unknown  [128] [128]
|
|---|
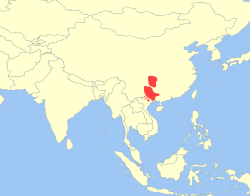
| Tibetan macaque  | M. thibetana
(H. Milne-Edwards, 1870)
- M. t. esau
- M. t. guiahouensis
- M. t. huangshanensis
- M. t. thibetana
| East China
 | Size: 36–77 cm (14–30 in) long, plus about 1–15 cm (0–6 in) tail [96]
Habitat: Forest and caves [129]
Diet: Fruit, as well as flowers, berries, seeds, leaves, stems, stalks, and invertebrates [129] | NT
Unknown  [129] [129]
|
|---|
| Tonkean macaque  | M. tonkeana
(von Meyer, 1899) | Island of Sulawesi
 | Size: 36–77 cm (14–30 in) long, plus about 1–15 cm (0–6 in) tail [96]
Habitat: Forest [130]
Diet: Fruit, leaves, grains, buds, seeds, flowers, and bark, as well as insects and small invertebrates [96] | VU
Unknown  [130] [130]
|
|---|
| White-cheeked macaque  | M. leucogenys
Li, Zhao, Fan, 2015 | Northeastern India | Size: 36–77 cm (14–30 in) long, plus about 9–20 cm (4–8 in) tail [96]
Habitat: Forest [131]
Diet: Fruit, leaves, grains, buds, seeds, flowers, and bark, as well as insects and small invertebrates [96] | EN
Unknown  [131] [131]
|
|---|