| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|
| Abyssinian hare  | L. habessinicus
Hemprich, Ehrenberg, 1832
- L. h. angolensis
- L. h. microtis
- L. h. senegalensis
- L. h. whytei
| Horn of Africa
 | Size: 44–45 cm (17–18 in) long [9]
Habitat: Savanna, grassland, and desert [10]
Diet: Grass, shrubs, and forbs [9] | LC
Unknown  [10] [10]
|
|---|
| African savanna hare  | L. victoriae
Heuglin, 1865 | Sub-Saharan Africa
 | Size: 41–58 cm (16–23 in) long [11]
Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, and grassland [12]
Diet: Variety of plants [12] | LC
Unknown  [12] [12]
|
|---|
| Alaskan hare  | L. othus
Merriam, 1900
- L. o. othus
- L. o. tschuktschorum
| Western Alaska
 | Size: 50–60 cm (20–24 in) long, plus 6–11 cm (2–4 in) tail [13]
Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland [14]
Diet: Dwarf willow, grass, sedges, and other plants [14] | LC
Unknown  [14] [14]
|
|---|
| Antelope jackrabbit  | L. alleni
Mearns, 1890
- L. a. alleni
- L. a. palitans
- L. a. tiburonensis
| Southwestern North America
 | Size: 43–70 cm (17–28 in) long, plus 5–14 cm (2–6 in) tail [15]
Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and desert [16]
Diet: Grass, velvet mesquite, and cacti [16] | LC
Unknown  [16] [16]
|
|---|
| Arctic hare  | L. arcticus
Ross, 1819
- L. a. arcticus
- L. a. bangsii
- L. a. groenlandicus
- L. a. monstrabilis
| Arctic North America
 | Size: 56–66 cm (22–26 in) long, plus 4–10 cm (2–4 in) tail [17]
Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland [18]
Diet: Woody plants [18] | LC
Unknown  [18] [18]
|
|---|
| Black jackrabbit  | L. insularis
Bryant, 1891 | Tip of Baja California
 | Size: 54–61 cm (21–24 in) long, plus 6–12 cm (2–5 in) tail [19]
Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, caves, desert, and coastal marine [20]
Diet: Grass, as well as tree bark [21] | VU
900  [20] [20]
|
|---|
| Black-tailed jackrabbit  | L. californicus
Gray, 1837
- L. c. californicus
- L. c. deserticola
- L. c. insularis
- L. c. magdalenae
- L. c. melanotis
- L. c. texianus
| Western and central North America
 | Size: 47–63 cm (19–25 in) long, plus 5–12 cm (2–5 in) tail [22]
Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, grassland, and desert [23]
Diet: Grass and herbs, as well as twigs and bark [22] | LC
Unknown  [23] [23]
|
|---|
| Broom hare  | L. castroviejoi
Arribas, 1977 | Northern Spain
 | Size: 41–59 cm (16–23 in) long [24]
Habitat: Forest and shrubland [25]
Diet: Grass, herbs, field crops, twigs, buds, and bark [25] | VU
Unknown  [25] [25]
|
|---|
| Burmese hare  | L. peguensis
Blyth, 1855
- L. p. peguensis
- L. p. vassali
| Southeastern Asia
 | Size: 40–59 cm (16–23 in) long, plus 5–9 cm (2–4 in) tail [26]
Habitat: Forest, savanna, shrubland, and grassland [27]
Diet: Grass, bark and twigs [27] | LC
Unknown  [27] [27]
|
|---|
| Cape hare  | L. capensis
Linnaeus, 1758
- L. c. aegyptius
- L. c. aquilo
- L. c. arabicus
- L. c. atlanticus
- L. c. capensis
- L. c. carpi
- L. c. granti
- L. c. hawkeri
- L. c. isabellinus
- L. c. schlumbergeri
- L. c. sinaiticus
- L. c. whitakeri
| Africa and western Asia
 | Size: 52–60 cm (20–24 in) long [28]
Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and desert [29]
Diet: Grass, shrubs, and herbs [29] | LC
Unknown  [29] [29]
|
|---|
| Chinese hare  | L. sinensis
Gray, 1832
- L. s. formosus
- L. s. sinensis
- L. s. yuenshanensis
| Southeastern China and Taiwan
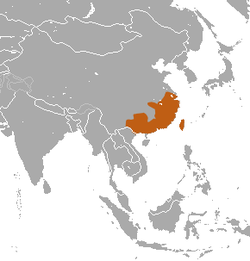 | Size: 36–42 cm (14–17 in) long, plus 17 cm (7 in) tail [30]
Habitat: Shrubland and grassland [31]
Diet: Leafy plants, green shoots, and twigs [31] | LC
Unknown  [31] [31]
|
|---|
| Corsican hare  | L. corsicanus
Winton, 1898 | Southern Italy
 | Size: 55–61 cm (22–24 in) long [32]
Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and coastal marine [33]
Diet: Grass, as well as mint, sedges, rushes, peas, and flowers [32] | VU
Unknown  [33] [33]
|
|---|
| Desert hare  | L. tibetanus
Waterhouse, 1841
- L. t. centrasiaticus
- L. t. craspedotis
- L. t. pamirensis
- L. t. stoliczkanus
- L. t. tibetanus
| Northwestern China
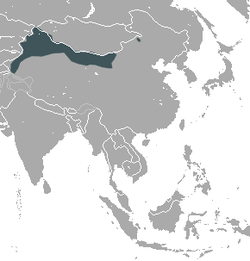 | Size: 40–76 cm (16–30 in) long [34]
Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and desert [35]
Diet: Variety of plants as well as seeds, berries, roots, and twigs [34] | LC
Unknown  [35] [35]
|
|---|
| Ethiopian hare | L. fagani
Thomas, 1903 | Ethiopia
 | Size: 42–50 cm (17–20 in) long, plus 7–11 cm (3–4 in) tail [36]
Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, and grassland [37]
Diet: Unknown plants [37] | LC
Unknown  [37] [37]
|
|---|
| Ethiopian highland hare  | L. starcki
Petter, 1963 | Central Ethiopia
 | Size: 46–60 cm (18–24 in) long, plus 7–12 cm (3–5 in) tail [38]
Habitat: Shrubland and grassland [39]
Diet: Grass as well as shrubs [39] | LC
Unknown  [39] [39]
|
|---|
| European hare  | L. europaeus
Pallas, 1778
- L. e. caspicus
- L. e. connori
- L. e. creticus
- L. e. cyprius
- L. e. cyrensis
- L. e. europaeus
- L. e. hybridus
- L. e. judeae
- L. e. karpathorum
- L. e. medius
- L. e. occidentalis
- L. e. parnassius
- L. e. ponticus
- L. e. rhodius
- L. e. syriacus
- L. e. transsylvanicus
| Europe, western Asia, northeastern North America, southern South America, eastern Oceana (introduced in light red)
 | Size: 60–75 cm (24–30 in) long, plus 7–11 cm (3–4 in) tail [40]
Habitat: Shrubland and grassland [41]
Diet: Grass, herbs, field crops, twigs, buds, and bark [40] | LC
Unknown  [41] [41]
|
|---|
| Granada hare  | L. granatensis
Rosenhauer, 1856
| Iberian Peninsula (introduced in pink)
 | Size: 44–48 cm (17–19 in) long, plus 9–12 cm (4–5 in) tail [42]
Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland [43]
Diet: Buds, twigs, bark, and crops [44] | LC
Unknown  [43] [43]
|
|---|
| Hainan hare  | L. hainanus
Swinhoe, 1870 | Hainan Island, China
 | Size: 35–40 cm (14–16 in) long, plus 4–7 cm (2–3 in) tail [45]
Habitat: Shrubland and grassland [46]
Diet: Plants [47] | EN
Unknown  [46] [46]
|
|---|
| Indian hare  | L. nigricollis
F. Cuvier, 1823
- L. n. aryabertensis
- L. n. dayanus
- L. n. nigricollis
- L. n. ruficaudatus
- L. n. sadiya
- L. n. simcoxi
- L. n. singhala
| Indian subcontinent
 | Size: 40–70 cm (16–28 in) long [48]
Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, inland wetlands, and desert [49]
Diet: Grass and flowering plants [48] | LC
Unknown  [49] [49]
|
|---|
| Japanese hare  | L. brachyurus
Temminck, 1845
- L. b. angustidens
- L. b. brachyurus
- L. b. lyoni
- L. b. okiensis
| Japan
 | Size: 45–54 cm (18–21 in) long, plus 2–5 cm (1–2 in) tail [50]
Habitat: Forest, shrubland, and grassland [51]
Diet: Grass, buds, seedlings, and shrubs [52] | LC
Unknown  [51] [51]
|
|---|
| Korean hare  | L. coreanus
Thomas, 1892 | Korea
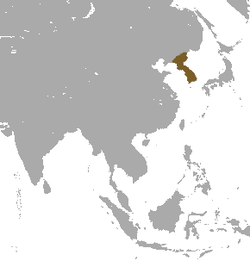 | Size: 45–54 cm (18–21 in) long, plus 2–5 cm (1–2 in) tail [53]
Habitat: Shrubland and grassland [54]
Diet: Grass, shrubs, and bark [53] | LC
Unknown  [54] [54]
|
|---|
| Manchurian hare  | L. mandshuricus
Radde, 1861 | Eastern Asia
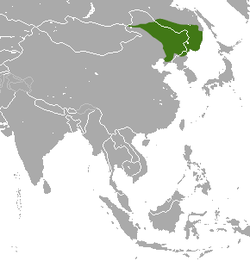 | Size: 41–54 cm (16–21 in) long, plus 5–8 cm (2–3 in) tail [55]
Habitat: Forest [56]
Diet: Bark and twigs, as well as shrubs, herbs, and fruit [57] | LC
Unknown  [56] [56]
|
|---|
| Mountain hare  | L. timidus
Linnaeus, 1758
- L. t. ainu
- L. t. begitschevi
- L. t. gichiganus
- L. t. hibernicus
- L. t. kamtschaticus
- L. t. kolymensis
- L. t. kozhevnikovi
- L. t. lugubris
- L. t. mordeni
- L. t. orii
- L. t. scoticus
- L. t. sibiricorum
- L. t. timidus
- L. t. transbaicalicus
- L. t. varronis
| Europe and northern Asia
 | Size: 50–55 cm (20–22 in) long, plus 5–7 cm (2–3 in) tail [58]
Habitat: Forest, shrubland, grassland, and inland wetlands [59]
Diet: Seeds, berries, roots, twigs, and other plants [58] | LC
Unknown  [59] [59]
|
|---|
| Scrub hare  | L. saxatilis
F. Cuvier, 1823
- L. s. saxatilis
- L. s. subrufus
| Southern Africa
 | Size: 45–65 cm (18–26 in) long [60]
Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, grassland, and desert [61]
Diet: Grass [61] | LC
Unknown  [61] [61]
|
|---|
| Snowshoe hare  | L. americanus
Erxleben, 1777
- L. a. americanus
- L. a. bairdii
- L. a. cascadensis
- L. a. dalli
- L. a. struthopus
- L. a. virginianus
| Northern North America
 | Size: 38–51 cm (15–20 in) long, plus 4–6 cm (1.6–2.4 in) tail [62]
Habitat: Forest and shrubland [63]
Diet: Grass, forbs, sedges, and ferns [63] | LC
Unknown  [63] [63]
|
|---|
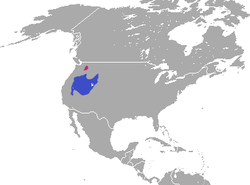
| Tehuantepec jackrabbit  | L. flavigularis
Wagner, 1844 | Small region of southern Mexico
 | Size: 56–61 cm (22–24 in) long [64]
Habitat: Savanna, shrubland, grassland, and coastal marine [65]
Diet: Grass, as well as other plants [64] | EN
300  [65] [65]
|
|---|
| Tolai hare  | L. tolai
Pallas, 1778
- L. t. aurigineus
- L. t. buchariensis
- L. t. cheybani
- L. t. cinnamomeus
- L. t. filchneri
- L. t. lehmanni
- L. t. swinhoei
- L. t. tolai
| Central and eastern Asia
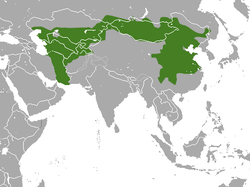 | Size: 40–59 cm (16–23 in) long, plus 7–11 cm (3–4 in) tail [66]
Habitat: Grassland and rocky areas [67]
Diet: Roots, grass, and herbs [67] | LC
Unknown  [67] [67]
|
|---|
| White-sided jackrabbit  | L. callotis
Wagler, 1830
- L. c. callotis
- L. c. gaillardi
| Southern North America
 | Size: 43–60 cm (17–24 in) long, plus 4–10 cm (2–4 in) tail [68]
Habitat: Shrubland and grassland [69]
Diet: Grass and sedges [68] | VU
Unknown  [69] [69]
|
|---|
| White-tailed jackrabbit  | L. townsendii
Bachman, 1839
- L. t. campanius
- L. t. townsendii
| Central and northern North America
 | Size: 53–60 cm (21–24 in) long [70]
Habitat: Shrubland and grassland [71]
Diet: Grass and forbs, as well as shrubs [71] | LC
Unknown  [71] [71]
|
|---|
| Woolly hare  | L. oiostolus
Hodgson, 1840
- L. o. hypsibius
- L. o. oiostolus
- L. o. pallipes
- L. o. przewalskii
| Central Asia
 | Size: 40–50 cm (16–20 in) long, plus 9 cm (4 in) tail [72]
Habitat: Shrubland, grassland, and desert [73]
Diet: Grass and leaves, as well as fruit and crops [72] | LC
Unknown  [73] [73]
|
|---|
| Yarkand hare  | L. yarkandensis
Günther, 1875 | Western China
 | Size: 28–43 cm (11–17 in) long, plus 5–9 cm (2–4 in) tail [74]
Habitat: Forest and shrubland [75]
Diet: Grass and crops [75] | NT
Unknown  [75] [75]
|
|---|
| Yunnan hare  | L. comus
Allen, 1927 | Southern China
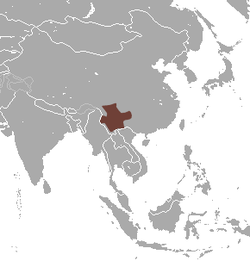 | Size: 28–43 cm (11–17 in) long, plus 5–9 cm (2–4 in) tail [76]
Habitat: Grassland [77]
Diet: Forbs and shrubs [78] | LC
Unknown  [77] [77]
|
|---|