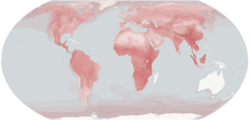
Carnivora is an order of placental mammals that have specialized in primarily eating flesh. Members of this order are called carnivorans, or colloquially carnivores, though the term more properly refers to any meat-eating organisms, and some carnivoran species are omnivores or herbivores. Carnivora is the fifth largest order of mammals and currently comprises 291 extant species, which are grouped into 131 genera. Carnivora can be divided into two suborders: the cat-like Feliformia and the dog-like Caniformia, which are differentiated largely based on the structure of their ear bones and cranial features. [1] The majority of feliform species are found in the Old World, though the cats have successfully diversified into the Americas. Members of the Caniformia group are found worldwide. Carnivorans live on every major landmass and in a variety of habitats, including polar regions, hyper-arid deserts, and the open seas. They come in a wide array of body plans in contrasting shapes and sizes, ranging from the 17 cm (7 in) least weasel to the 6 m (20 ft) and 3,700 kg (8,200 lb) male southern elephant seal. Some carnivorans, such as cats, dogs, and the ferret, have been domesticated, resulting in a worldwide distribution.
Contents
- Conventions
- Classification
- Carnivorans
- Suborder Caniformia
- Suborder Feliformia
- See also
- References
- Sources
The feliforms are further subdivided into seven families: Eupleridae, Felidae, Herpestidae, Hyaenidae, Nandiniidae, Prionodontinae, and Viverridae, and include the cats, the hyenas, the mongooses and the viverrids, among others. The caniforms are divided into nine families: Ailuridae, Canidae, Mephitidae, Mustelidae, Odobenidae, Otariidae, Phocidae, Procyonidae, and Ursidae, and include the dogs, bears, raccoons, weasels, and pinnipeds. The exact organization of the species is not fixed, with many recent proposals made based on molecular phylogenetic analysis, including smaller re-categorizations such as promoting the black mongoose subspecies of the slender mongoose to a full species or the 2011 discovery of the Vietnam ferret-badger, as well as larger changes such as formally recognizing the family Eupleridae as separate from Viverridae and Herpestidae in 2003. In addition to the extant species, six species have gone extinct since 1500 CE: the Falkland Islands wolf and South American fox in Canidae, the sea mink and Japanese otter in Mustelidae, the Japanese sea lion in Otariidae, and the Caribbean monk seal in Phocidae.