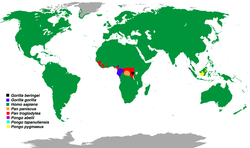
Hominoidea is a superfamily of primates. Members of this superfamily are called hominoids or apes, and include gorillas, chimpanzees, orangutans, gibbons, bonobos, and humans. Hominoidea is one of the six major groups in the order Primates. The majority are found in forests in Southeastern Asia and Equatorial Africa, with the exception of humans, which have spread worldwide to every biome. They range in size from some gibbon species in the genus Nomascus , at 40 cm (16 in), to the eastern gorilla, at 196 cm (77 in), not including limbs. Hominoids primarily eat fruit, leaves, flowers, and insects, though humans are omnivorous. Most hominoids do not have population estimates, but the ones that do range from 10 mature individuals to 47,000, in addition to over 8 billion humans. Nearly every species is categorized as endangered or critically endangered; aside from humans, the only exception is the eastern hoolock gibbon, classified as vulnerable.
Contents
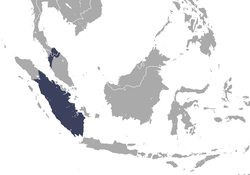
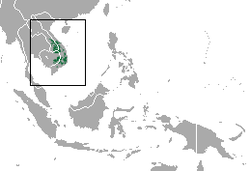
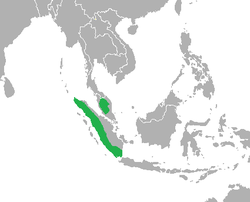
The twenty-eight extant species of Hominoidea are divided into two families: Hominidae, containing five gorilla, chimpanzee, and human species divided into three genera in the subfamily Homininae, and three orangutan species in a single genus in the subfamily Ponginae; and Hylobatidae, containing twenty gibbon species divided into four genera. Dozens of extinct prehistoric hominoid species have been discovered, though due to ongoing research and discoveries the exact number and categorization is not fixed. [1]