The thalamus is a large mass of gray matter in the dorsal part of the diencephalon of the brain with several functions such as relaying of sensory signals, including motor signals to the cerebral cortex, and the regulation of consciousness, sleep, and alertness.

The internal capsule is a white matter structure situated in the inferomedial part of each cerebral hemisphere of the brain. It carries information past the basal ganglia, separating the caudate nucleus and the thalamus from the putamen and the globus pallidus. The internal capsule contains both ascending and descending axons, going to and coming from the cerebral cortex. It also separates the caudate nucleus and the putamen in the dorsal striatum, a brain region involved in motor and reward pathways.

The dorsal column–medial lemniscus pathway (DCML) is a sensory pathway of the central nervous system that conveys sensations of fine touch, vibration, two-point discrimination, and proprioception (position) from the skin and joints. It transmits information from the body to the primary somatosensory cortex in the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe of the brain. The pathway receives information from sensory receptors throughout the body, and carries this in nerve tracts in the white matter of the dorsal columns of the spinal cord, to the medulla where it is continued in the medial lemniscus, on to the thalamus and relayed from there through the internal capsule and transmitted to the somatosensory cortex. The name dorsal-column medial lemniscus comes from the two structures that carry the sensory information: the dorsal columns of the spinal cord, and the medial lemniscus in the brainstem.
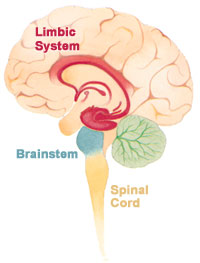
The Papez circuit, or medial limbic circuit, is a neural circuit for the control of emotional expression. In 1937, James Papez proposed that the circuit connecting the hypothalamus to the limbic lobe was the basis for emotional experiences. Paul D. MacLean reconceptualized Papez's proposal and coined the term limbic system. MacLean redefined the circuit as the "visceral brain" which consisted of the limbic lobe and its major connections in the forebrain – hypothalamus, amygdala, and septum. Over time, the concept of a forebrain circuit for the control of emotional expression has been modified to include the prefrontal cortex.

The septal nuclei are a set of structures that lie below the rostrum of the corpus callosum, anterior to the lamina terminalis. The septal nuclei are composed of medium-size neurons which are classified into medial, lateral, and posterior groups. The septal nuclei receive reciprocal connections from the olfactory bulb, hippocampus, amygdala, hypothalamus, midbrain, habenula, cingulate gyrus, and thalamus.

The ventral spinothalamic fasciculus situated in the marginal part of the anterior funiculus and intermingled more or less with the vestibulo-spinal fasciculus, is derived from cells in the posterior column or intermediate gray matter of the opposite side. Aβ fibres carry sensory information pertaining to crude touch from the skin. After entering the spinal cord the first order neurons synapse, and the second order neurons decussate via the anterior commissure. These second order neurons ascend synapsing in the VPL of the thalamus. It should also be noted incoming first order neurons can ascend or descend via the Lissauer tract.
The amygdalofugal pathway is one of the three major efferent pathways of the amygdala, meaning that it is one of the three principal pathways by which fibers leave the amygdala. It leads from the basolateral nucleus and central nucleus of the amygdala. The amygdala is a limbic structure in the medial temporal lobe of the brain. The other main efferent pathways from the amygdala are the stria terminalis and anterior commissure.
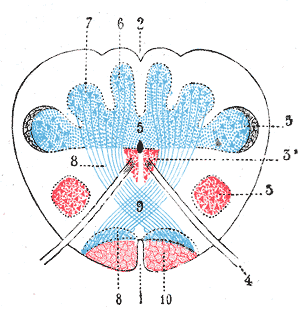
In neuroanatomy, the dorsal column nuclei are a pair of nuclei in the dorsal columns in the brainstem. The name refers collectively to the cuneate nucleus and gracile nucleus, which are present at the junction between the spinal cord and the medulla oblongata. Both nuclei contain second-order neurons of the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway, which carries fine touch and proprioceptive information from the body to the brain. Each nucleus has an associated nerve tract, the gracile fasciculus and the cuneate fasciculus.
The isothalamus is a division used by some researchers in describing the thalamus.

The stria medullaris is a part of the epithalamus. It is a fiber bundle containing afferent fibers from the septal nuclei, lateral preoptico-hypothalamic region, and anterior thalamic nuclei to the habenula. It forms a horizontal ridge on the medial surface of the thalamus, and is found on the border between dorsal and medial surfaces of thalamus. Superior and lateral to habenular trigone.

The anterior nuclei of thalamus are a collection of nuclei at the rostral end of the dorsal thalamus. They comprise the anteromedial, anterodorsal, and anteroventral nuclei.

The intralaminar nuclei are collections of neurons in the thalamus that are generally divided in two groups as follows:

The thalamic fasciculus is a component of the subthalamus. It is synonymous with field H1 of Forel. Nerve fibres form a tract containing cerebellothalamic (crossed) and pallidothalamic (uncrossed) fibres, that is insinuated between the thalamus and the zona incerta.

The pallidothalamic tracts are a part of the basal ganglia. They provide connectivity between the internal globus pallidus (GPi) and the thalamus, primarily the ventral anterior nucleus and the ventral lateral nucleus.
The fields of Forel are areas in a deep part of the brain known as the diencephalon. They are below the thalamus and consist of three defined, white matter areas of the subthalamus. These three regions are also named "H fields":
The dorsal tegmental nucleus (DTN), also known as dorsal tegmental nucleus of Gudden (DTg), is a group of neurons located in the brain stem, which are involved in spatial navigation and orientation.
The public domain consists of all the creative works to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable.

Gray's Anatomy is an English language textbook of human anatomy originally written by Henry Gray and illustrated by Henry Vandyke Carter. Earlier editions were called Anatomy: Descriptive and Surgical, Anatomy of the Human Body and Gray's Anatomy: Descriptive and Applied, but the book's name is commonly shortened to, and later editions are titled, Gray's Anatomy. The book is widely regarded as an extremely influential work on the subject, and has continued to be revised and republished from its initial publication in 1858 to the present day. The latest edition of the book, the 41st, was published in September 2015.