 | |
| Geographical range | Lower Dnieper and the Pontic steppe in Ukraine |
|---|---|
| Period | Copper Age |
| Dates | ca. 4400–3800 BC |
| Preceded by | Sredny Stog culture |
| Followed by | Yamnaya culture |
| Part of a series on |
| Indo-European topics |
|---|
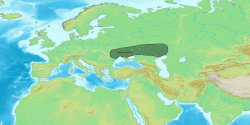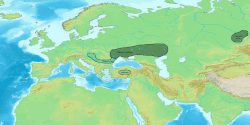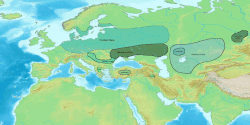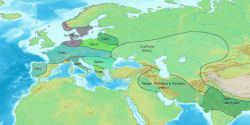 |
The Novodanilovka (Novodanylivka in Ukrainian) group, also called the Novodanilovka culture, was a Copper Age culture which flourished along the lower Dnieper and the steppes of Ukraine from c. 4400 BC to 3800 BC.
The Novodanilovka group is primarily defined by its small cemeteries and individual burials. These burials are characterized as flexed supine burials with orientation to east or northeast. The burials are similar to those of the Sredny Stog culture, but the burials are more elaborate with chambers of stone coverings. They are also distinguished by rich grave goods of flint, copper and stone weapons, and copper bracelets. It has been suggested that this is a reflection of an aristocratic element of the Sredny Stog culture, rather than a separate cultural group.
In the Kurgan hypothesis, the Novodanilovka group is often presented as the archetypical warlike patriarchal society of the early Indo-Europeans.