
Aluminium is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has a great affinity towards oxygen, and forms a protective layer of oxide on the surface when exposed to air. Aluminium visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, non-magnetic and ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al; this isotope is very common, making aluminium the twelfth most common element in the Universe. The radioactivity of 26Al is used in radiodating.

The halogens are a group in the periodic table consisting of five chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At). The artificially created element 117, tennessine (Ts), may also be a halogen. In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is known as group 17.

Fluorite (also called fluorspar) is the mineral form of calcium fluoride, CaF2. It belongs to the halide minerals. It crystallizes in isometric cubic habit, although octahedral and more complex isometric forms are not uncommon.
The Hall–Héroult process is the major industrial process for smelting aluminium. It involves dissolving aluminium oxide (alumina) in molten cryolite, and electrolysing the molten salt bath, typically in a purpose-built cell. The Hall–Héroult process applied at industrial scale happens at 940–980 °C and produces 99.5–99.8% pure aluminium. Recycled aluminum requires no electrolysis, thus it does not end up in this process. This process contributes to climate change through the emission of carbon dioxide in the electrolytic reaction and consumption of large amounts of electrical energy.
Potassium carbonate is the inorganic compound with the formula K2CO3. It is a white salt, which is soluble in water. It is deliquescent, often appearing as a damp or wet solid. Potassium carbonate is mainly used in the production of soap and glass.

In metallurgy, a flux is a chemical cleaning agent, flowing agent, or purifying agent. Fluxes may have more than one function at a time. They are used in both extractive metallurgy and metal joining.

Potassium fluoride is the chemical compound with the formula KF. After hydrogen fluoride, KF is the primary source of the fluoride ion for applications in manufacturing and in chemistry. It is an alkali halide and occurs naturally as the rare mineral carobbiite. Solutions of KF will etch glass due to the formation of soluble fluorosilicates, although HF is more effective.
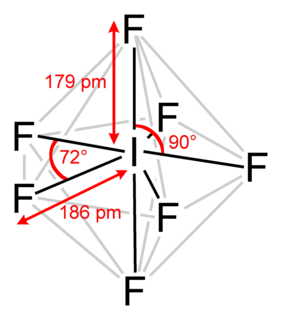
Iodine heptafluoride, also known as iodine(VII) fluoride or iodine fluoride, is an interhalogen compound with the chemical formula IF7. It has an unusual pentagonal bipyramidal structure, as predicted by VSEPR theory. The molecule can undergo a pseudorotational rearrangement called the Bartell mechanism, which is like the Berry mechanism but for a heptacoordinated system. It forms colourless crystals, which melt at 4.5 °C: the liquid range is extremely narrow, with the boiling point at 4.77 °C. The dense vapor has a mouldy, acrid odour. The molecule has D5h symmetry.

Monocalcium phosphate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca(H2PO4)2 ("AMCP" or "CMP-A" for anhydrous monocalcium phosphate). It is commonly found as the monohydrate ("MCP" or "MCP-M"), Ca(H2PO4)2·H2O. Both salts are colourless solids. They are used mainly as superphosphate fertilizers and are also popular leavening agents.

Cobalt(III) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula CoF
3. Hydrates are also known. The anhydrous compound is a hygroscopic brown solid. It is used to synthesize organofluorine compounds.

The Danishefsky Taxol total synthesis in organic chemistry is an important third Taxol synthesis published by the group of Samuel Danishefsky in 1996 two years after the first two efforts described in the Holton Taxol total synthesis and the Nicolaou Taxol total synthesis. Combined they provide a good insight in the application of organic chemistry in total synthesis.

Hydrogen fluoride is a chemical compound with the chemical formula HF. This colorless gas or liquid is the principal industrial source of fluorine, often as an aqueous solution called hydrofluoric acid. It is an important feedstock in the preparation of many important compounds including pharmaceuticals and polymers, e.g. polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). HF is widely used in the petrochemical industry as a component of superacids. Hydrogen fluoride boils at near room temperature, much higher than other hydrogen halides.

Hexafluorosilicic acid is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula H
2SiF
6 also written as (H
3O)
2[SiF
6]. It is a colorless liquid mostly encountered as diluted aqueous solution, from there, the second chemical notation also proposed. Hexafluorosilicic acid has a distinctive sour taste and pungent smell. It is produced naturally on a large scale in volcanoes. It is manufactured as a coproduct in the production of phosphate fertilizers. The resulting hexafluorosilicic acid is almost exclusively consumed as a precursor to aluminum trifluoride and synthetic cryolite, which are used in aluminium processing. Salts derived from hexafluorosilicic acid are called hexafluorosilicates.

Aluminium fluoride refers to inorganic compounds with the formula AlF3·xH2O. They are all colorless solids. Anhydrous AlF3 is used in the production of aluminium metal. Several occur as minerals.
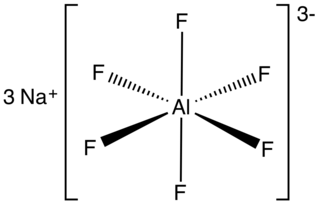
Sodium aluminium hexafluoride is an inorganic compound with formula Na3AlF6. This white solid, discovered in 1799 by Peder Christian Abildgaard (1740–1801), occurs naturally as the mineral cryolite and is used extensively in the industrial production of aluminium metal. The compound is the sodium (Na+) salt of the hexafluoroaluminate (AlF63−) ion.
A monofluoride is a chemical compound with one fluoride per formula unit. For a binary compound, this is the formula XF.
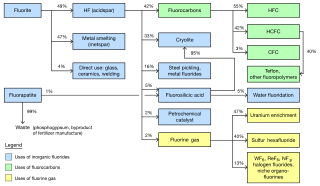
The global market for chemicals from fluorine was about US$16 billion per year as of 2006. The industry was predicted to reach 2.6 million metric tons per year by 2015. The largest market is the United States. Western Europe is the second largest. Asia Pacific is the fastest growing region of production. China in particular has experienced significant growth as a fluorochemical market and is becoming a producer of them as well. Fluorite mining was estimated in 2003 to be a $550 million industry, extracting 4.5 million tons per year.
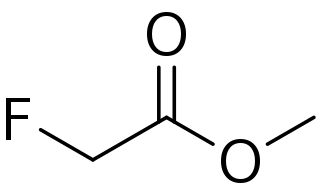
Methyl fluoroacetate (MFA) is an extremely toxic methyl ester of fluoroacetic acid. It is a colorless, odorless liquid at room temperature. It is used as a laboratory chemical and as a rodenticide. Because of its extreme toxicity, MFA was studied for potential use as chemical weapon. The general population is not likely to be exposed to methyl fluoroacetate. People who use MFA for work, however, can breathe in or have direct skin contact with the substance.
Potassium fluorosilicate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula K2[SiF6].

















