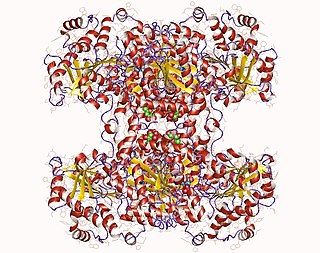
Glycogen synthase is a key enzyme in glycogenesis, the conversion of glucose into glycogen. It is a glycosyltransferase that catalyses the reaction of UDP-glucose and n to yield UDP and n+1.

Uridine diphosphate glucose is a nucleotide sugar. It is involved in glycosyltransferase reactions in metabolism.
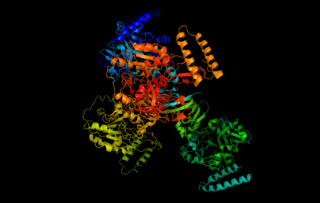
UTP—glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase also known as glucose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase is an enzyme involved in carbohydrate metabolism. It synthesizes UDP-glucose from glucose-1-phosphate and UTP; i.e.,
Glucose-1,6-bisphosphate synthase is a type of enzyme called a phosphotransferase and is involved in mammalian starch and sucrose metabolism. It catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to glucose-1-phosphate, yielding 3-phosphoglycerate and glucose-1,6-bisphosphate.
In enzymology, an UDP-glucuronate 4-epimerase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme [glycogen-synthase-D] phosphatase ({EC 3.1.3.42) catalyzes the reaction
In enzymology, a 1,4-beta-D-xylan synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2-coumarate O-beta-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an alpha,alpha-trehalose-phosphate synthase (UDP-forming) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an arylamine glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a cellulose synthase (GDP-forming) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a cyanohydrin beta-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a linamarin synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a NDP-glucose—starch glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-hydroxythioamide S-beta-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a phenol beta-glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a procollagen glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a scopoletin glucosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a starch synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Sucrose-phosphate synthase (SPS) is a plant enzyme involved in sucrose biosynthesis. Specifically, this enzyme catalyzes the transfer of a hexosyl group from uridine diphosphate glucose (UDP-glucose) to D-fructose 6-phosphate to form UDP and D-sucrose-6-phosphate. This reversible step acts as the key regulatory control point in sucrose biosynthesis, and is an excellent example of various key enzyme regulation strategies such as allosteric control and reversible phosphorylation.





