
Video is an electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting, and display of moving visual media. Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) systems which, in turn, were replaced by flat panel displays of several types.
The Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE), founded in 1916 as the Society of Motion Picture Engineers or SMPE, is a global professional association of engineers, technologists, and executives working in the media and entertainment industry. As an internationally recognized standards organization, SMPTE has published more than 800 technical standards and related documents for broadcast, filmmaking, digital cinema, audio recording, information technology (IT), and medical imaging.
Ericsson Television, formerly Tandberg Television, is a company providing MPEG-4 AVC, MPEG-2 and HEVC encoding decoding and control solutions, plus stream processing, packaging, network adaption and related products, for Contribution & Distribution (C+D), IPTV, Cable, DTT, Satellite DTH and OTT.
Broadcast engineering is the field of electrical engineering, and now to some extent computer engineering and information technology, which deals with radio and television broadcasting. Audio engineering and RF engineering are also essential parts of broadcast engineering, being their own subsets of electrical engineering.
The Grand Alliance (GA) was a consortium created in 1993 at the behest of the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) to develop the American digital television and HDTV specification, with the aim of pooling the best work from different companies. It consisted of AT&T Corporation, General Instrument Corporation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Philips Consumer Electronics, David Sarnoff Research Center, Thomson Consumer Electronics, and Zenith Electronics Corporation. The Grand Alliance DTV system is the basis for the ATSC standard.
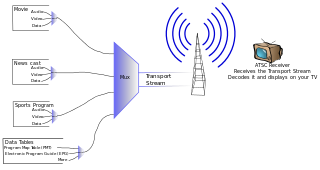
The Program and System Information Protocol (PSIP) is the MPEG and privately defined program-specific information originally defined by General Instrument for the DigiCipher 2 system and later extended for the ATSC digital television system for carrying metadata about each channel in the broadcast MPEG transport stream of a television station and for publishing information about television programs so that viewers can select what to watch by title and description. Its FM radio equivalent is Radio Data System (RDS).
Broadcast Television Systems (BTS) was a joint venture between Robert Bosch GmbH's Fernseh Division and Philips Broadcast in Breda, Netherlands, formed in 1986.
Faroudja Labs was a San Francisco based IP and research company founded by Yves Faroudja. Faroudja Labs should not be confused with Faroudja Enterprises, Yves Faroudja's latest venture.
High-definition television describes a television system providing a substantially higher image resolution than the previous generation of technologies. The term has been used since 1936, in more recent times it refers to the generation following standard-definition television (SDTV), often abbreviated to HDTV or HD-TV. It is the current de facto standard video format used in most broadcasts: terrestrial broadcast television, cable television, satellite television and Blu-ray Discs.

The Philo T. Farnsworth Award is a non-competitive award presented by the Academy of Television Arts & Sciences (ATAS) as part of the Primetime Engineering Emmy Awards to "an agency, company or institution whose contributions over time have significantly impacted television technology and engineering". Named for Philo Farnsworth, the inventor of the first fully working all-electronic television system and receiver, the winner is selected by a jury of television engineers from ATAS's Engineering Emmy Awards Committee, who consider "all engineering developments which have proven their efficacy during the awards year and determines which, if any, merit recognition with an Engineering Emmy statuette". The accolade was first awarded in 2003 as a result of about a year of lobbying to ATAS by Farnsworth's wife Pam Farnsworth and Hawaii-based Skinner Entertainment management and production firm owner Georja Skinner.
The 57th Technology & Engineering Emmy Awards was held on 29 September 2005. The National Television Academy announced the winners at Bristol-Myers Squibb in Princeton, New Jersey.

4K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. Digital television and digital cinematography commonly use several different 4K resolutions. In television and consumer media, 3840 × 2160 is the dominant 4K standard, whereas the movie projection industry uses 4096 × 2160.
Chris Cookson was the President of Sony Pictures Technologies, a division of Sony Pictures Entertainment, and Chief Officer, Sony 3D Technology Center, Sony Corporation of America. As President of Sony Pictures Technologies, Cookson oversaw the development and implementation of the studio’s technology policy and processes. He also served as Sony Pictures’ chief liaison with other Sony Corporation businesses in the area of technology. Cookson holds more than 50 U.S. patents, including several involving DVDs, and has been leading the effort to maintain high standards of quality on theatrical digital post-production technologies.
The 58th Technology & Engineering Emmy Awards was held on January 8, 2007. The National Television Academy announced the winners at The Venetian Hotel in Las Vegas. DIRECTV's Eddy Hartenstein received the Lifetime Achievement Award for his role in the company's becoming a global provider of digital television.
Joseph Antony Flaherty, Jr. was the Senior Vice President for Technology at CBS. He is the inventor and co-inventor of many television technologies including the miniature color camera, and off-line videotape editing, and co-inventor to Raymond D. Schneider of Electronic news-gathering. Flaherty was Chairman of the Planning Subcommittee of the U.S. Federal Communications Commission's (FCC) Advisory Committee on Advanced Television Service that developed the ATSC HDTV standard.
Richard (Dick) Green is Director of Liberty Global Corporation, Shaw Communications Inc., and currently serves as chairman of the Space Sciences Institute and the University of Colorado Boulder's ATLAS Institute in Boulder, Colorado. He previously served as president and CEO of not-for-profit research and development consortium CableLabs.
Harmonic Inc. is an American technology company that develops and markets video routing, server, and storage products for companies that produce, process, and distribute video content for television and the Internet.
The 60th Technology & Engineering Emmy Awards was held on January 8, 2009 at the 2009 International Consumer Electronics Show in Las Vegas. CEO of Verizon Communications, Ivan Seidenberg received the Lifetime Achievement Award
The 59th Technology & Engineering Emmy Awards was held on January 8, 2008 at the 2008 International Consumer Electronics Show in Las Vegas.
A Primetime Emmy Engineering Award is an award given most years by the Television Academy, also known as the Academy of Television Arts & Sciences (ATAS). It is a Primetime Emmy Award given specifically for Outstanding Achievement in Engineering Development. According to the Television Academy, the Primetime Emmy Engineering Award is presented to an individual, company or organization for engineering developments so significant an improvement on existing methods or so innovative in nature that they materially affect the transmission, recording or reception of television. The award, which is Television's highest engineering honor, is determined by a jury of highly qualified, experienced engineers in the Television industry.



