Related Research Articles
The Louisiana School for the Deaf is a state school for deaf and hard-of-hearing students in Louisiana, located in Baton Rouge, the state capital. It was established in 1852 as a joint school for blind students. In 1860, its first purpose-built facility was completed and admired as an elegant monument to philanthropy. The schools were divided in 1898, and in 1908, Louisiana School for the Deaf was renamed.

The Florida School for the Deaf and the Blind (FSDB) is a state-supported boarding school for deaf and blind children established in 1885, in St. Augustine, Florida, United States.

The West Virginia Schools for the Deaf and the Blind (WVSDB) were established by an Act of the Legislature on March 3, 1870. The School for the Deaf and the School for the Blind offer comprehensive educational programs for hearing impaired and visually impaired students respectively. There is also a unit for deafblind and multihandicapped children. Students are eligible to enroll at the age of three, must be residents of the state of West Virginia and exhibit a hearing or visual loss sufficient to prevent normal progress in the usual public school setting. The West Virginia Schools for the Deaf and Blind are located on a campus in Romney in West Virginia's Eastern Panhandle. Locally, the schools are referred to simply as The state school.

Indiana School for the Deaf (ISD) is a fully accredited school for the deaf and hard of hearing, located in Indianapolis, Indiana, United States.

Minnesota State Academy for the Blind (MSAB) (formerly known as the Braille and Sight Saving School) is a public school in Faribault, Minnesota, United States. Its mission is the education and life education of blind, visually impaired, and deaf-blind learners from birth to age 21. The school has a residential option program and provides 24-hour programming including Braille, independent travel, assistive technologies, and individualized educational services. Students often have multiple disabilities and come from all regions of the state.

The California School for the Blind is a public educational institution for blind children, K-12, located in Fremont, California. Its campus is located next to the California School for the Deaf.

The Texas School for the Blind and Visually Impaired (TSBVI) is a Texas special public school, in the continuum of statewide placements for students who have a visual impairment. It is considered a statewide resource to parents of these children and professionals who serve them. Students, ages 6 through 21, who are blind, deaf-blind, or visually impaired, including those with additional disabilities, are eligible for consideration for services at TSBVI.

Oregon School for the Deaf (OSD) is a state-funded school in Salem, Oregon, United States. It serves deaf and hard of hearing students from kindergarten through high school, and up to 18 years of age.

The Oregon School for the Blind (OSB), was a state-run public school in Salem, Oregon, United States, serving blind and vision impaired students of kindergarten through high school grades through residential, day school, and part-time enrollment programs. Opened in 1873, the school was operated by the Oregon Department of Education. The school's closure in 2009 had been the culmination of several years of contentious debate that continued after the closure when lawsuits were filed concerning the sale of the campus.
The Tennessee Schools for the Deaf (TSD) is a state-operated residential and day school for deaf and hard-of-hearing students who reside in the state of Tennessee ranging from pre-kindergarten to grade 12 and also includes a Comprehensive Adult Program. The main campus is located in Knoxville, Tennessee within the historic Island Home Park neighborhood. There are two additional campuses serving elementary students in Nashville and Jackson.
West Campus is a neighborhood in central Austin, Texas west of Guadalupe Street and its namesake, the University of Texas at Austin. Due to its proximity to the university, West Campus is heavily populated by college students.

Texas School for the Deaf (TSD) is a state-operated primary and secondary school for deaf children in Austin, Texas. Opened in 1857 "in an old frame house, three log cabins, and a smokehouse", it is the oldest continually-operated public school in Texas. The school struggled under inadequate funding during the American Civil War, and its aftermath, with the students eating food that they grew themselves on the school farm. In 1951 the State Board of Education assumed oversight of the school.

Guadalupe College was a private Baptist college for African Americans in Seguin, Texas. It was established in 1884 and opened officially in 1887. Its founding was chiefly due to the efforts of William B. Ball, who later became its president. David Abner Jr. was president of Guadalupe College from 1891 to 1906, a 15-year tenure during which the college flourished and gained statewide recognition. At its height during his administration, the college had an enrollment of approximately 500 students.
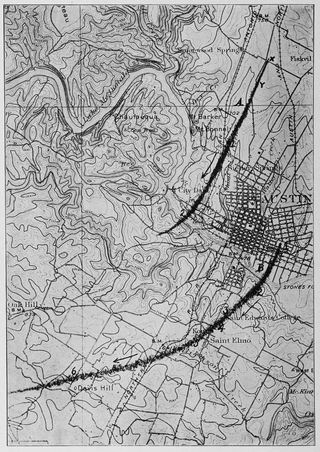
On the afternoon of May 4, 1922, two simultaneous tornadoes struck Austin, Texas, taking unusual southwesterly paths through the city and surrounding areas on both sides of the Colorado River. Meteorological details concerning the conditions that led to the event are sparse, though historical accounts described the morning and afternoon as sweltering; clouds began aggregating northeast of Austin by noon and had developed into thunderstorms over the city by around 4:00 p.m. The first tornado began in a rural area 6 mi (9.7 km) northwest of the Texas State Capitol and tracked across the Texas Deaf, Dumb, and Blind Institute for Colored Youth and Deep Eddy, injuring at least five people and causing around $25,000 in damage. The tornado was widely photographed and was estimated to have been an F2 tornado on the Fujita scale.

The South Carolina School for the Deaf and the Blind is a school in unincorporated Spartanburg County, South Carolina, United States, near Spartanburg and with a Spartanburg postal address. It was founded in 1849 by the Reverend Newton Pinckney Walker as a private school for students who were deaf. The School for the Blind was established in 1855, and the school became state funded in 1856.

The Little Campus is a historic district and part of the University of Texas at Austin campus in Austin, Texas. Originally built in 1856 as the Texas Asylum for the Blind, the complex was used for a variety of purposes through the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. It was acquired by the University of Texas after World War I and listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1974.

The Michigan School for the Blind (MSB) was a state-operated school for blind children in Michigan.
Tennessee School for the Blind is a K–12 school for blind children in Clover Bottom, Nashville, Tennessee. It is overseen by the Tennessee Department of Education.

Governor Morehead School (GMS), formerly North Carolina State School for the Blind and Deaf, is a K–12 public school for the blind in Raleigh, North Carolina. In the era of de jure educational segregation in the United States, it served blind people of all races and deaf black people.
Virginia School for the Deaf, Blind and Multi-Disabled at Hampton (VSDBM-H), also known as the Virginia School for the Deaf and the Blind-Hampton Campus (VSDB-Hampton) was a school for deaf and blind children in Hampton, Virginia. It was operated by the Commonwealth of Virginia.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Markham, James W. "TEXAS BLIND, DEAF, AND ORPHAN SCHOOL" (Archive). Handbook of Texas. Retrieved on May 12, 2015.
- ↑ Tabak, John. Significant Gestures: A History of American Sign Language. Greenwood Publishing Group, January 1, 2006. ISBN 0275989747, 9780275989743. p. 99.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Barnes, Michael (2016-09-15). "What's left of Austin's lost Blind, Deaf and Orphan School?". Austin American-Statesman . Retrieved 2021-06-19.
- 1 2 "Heritage Center" (Archive). Texas School for the Deaf. Retrieved on May 12, 2015.