
The rotary engine is an early type of internal combustion engine, usually designed with an odd number of cylinders per row in a radial configuration. The engine's crankshaft remained stationary in operation, while the entire crankcase and its attached cylinders rotated around it as a unit. Its main application was in aviation, although it also saw use in a few early motorcycles and automobiles.

A turboprop is a gas turbine engine that drives an aircraft propeller.

Aircraft engine controls provide a means for the pilot to control and monitor the operation of the aircraft's powerplant. This article describes controls used with a basic internal-combustion engine driving a propeller. Some optional or more advanced configurations are described at the end of the article. Jet turbine engines use different operating principles and have their own sets of controls and sensors.

A flight engineer (FE), also sometimes called an air engineer, is the member of an aircraft's flight crew who monitors and operates its complex aircraft systems. In the early era of aviation, the position was sometimes referred to as the "air mechanic". Flight engineers can still be found on some larger fixed-wing airplanes and helicopters. A similar crew position exists on some spacecraft. In most modern aircraft, their complex systems are both monitored and adjusted by electronic microprocessors and computers, resulting in the elimination of the flight engineer's position.

Thrust reversal, also called reverse thrust, is the temporary diversion of an aircraft engine's thrust for it to act against the forward travel of the aircraft, providing deceleration. Thrust reverser systems are featured on many jet aircraft to help slow down just after touch-down, reducing wear on the brakes and enabling shorter landing distances. Such devices affect the aircraft significantly and are considered important for safe operations by airlines. There have been accidents involving thrust reversal systems, including fatal ones.

A conventional fixed-wing aircraft flight control system (AFCS) consists of flight control surfaces, the respective cockpit controls, connecting linkages, and the necessary operating mechanisms to control an aircraft's direction in flight. Aircraft engine controls are also considered flight controls as they change speed.

In aeronautics, air brakes or speed brakes are a type of flight control surface used on an aircraft to increase the drag on the aircraft. When extended into the airstream, air brakes cause an increase in the drag on the aircraft. When not in use, they conform to the local streamlined profile of the aircraft in order to help minimize drag.

The Learjet 25 is an American ten-seat, twin-engine, high-speed business jet aircraft manufactured by Learjet. It is a stretched version of the Learjet 24.
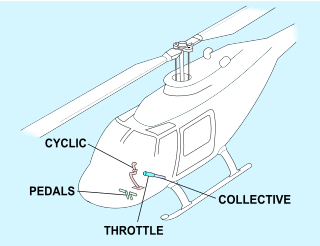
Helicopter flight controls are used to achieve and maintain controlled aerodynamic helicopter flight. Changes to the aircraft flight control system transmit mechanically to the rotor, producing aerodynamic effects on the rotor blades that make the helicopter move in a desired way. To tilt forward and back (pitch) or sideways (roll) requires that the controls alter the angle of attack of the main rotor blades cyclically during rotation, creating differing amounts of lift at different points in the cycle. To increase or decrease overall lift requires that the controls alter the angle of attack for all blades collectively by equal amounts at the same time, resulting in ascent, descent, acceleration and deceleration.

The Canadair CL-84 "Dynavert", designated by the Canadian Forces as the CX-131, was a V/STOL turbine tiltwing monoplane designed and manufactured by Canadair between 1964 and 1972. Only four of these experimental aircraft were built, with three entering flight testing. Two of the CL-84s crashed due to mechanical failures, with no fatalities in either accident. Despite the CL-84 being successful in the experimental and operational trials carried out between 1972 and 1974, none of the prospective customers placed any orders for the type.
Blade pitch or simply pitch refers to the angle of a blade in a fluid. The term has applications in aeronautics, shipping, and other fields.
A throttle is a mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by construction or obstruction.

TAM Transportes Aéreos Regionais Flight 402 was a scheduled domestic flight from Caxias do Sul, Brazil, to Recife International Airport in Recife, via São Paulo–Congonhas International Airport and Santos Dumont Airport in Rio de Janeiro. On 31 October 1996, at 8:27 (UTC-2), the starboard engine of the Fokker 100 operating the route reversed thrust while the aircraft was climbing away from the runway at Congonhas. The aircraft stalled and rolled beyond control to the right, then struck two buildings and crashed into several houses in a heavily populated area only 25 seconds after takeoff. All 95 people on board were killed, as well as another 4 on the ground. It is the fourth deadliest accident in Brazilian aviation history, the second at the time. It is also the deadliest aviation accident involving a Fokker 100.
A pressure carburetor is a type of fuel metering system manufactured by the Bendix Corporation for piston aircraft engines, starting in the 1940s. It is recognized as an early type of throttle-body fuel injection and was developed to prevent fuel starvation during inverted flight.

This article briefly describes the components and systems found in jet engines.

RwandAir Flight 205 was a Canadair CRJ100ER that crashed into the Terminal Building after an emergency landing at Kigali, Rwanda killing one passenger. The flight was operated by JetLink Express on behalf of RwandAir. In the aftermath of the accident, RwandAir suspended all operations with JetLink Express.

The Tecnam P2002 Sierra is a two-seat, low-wing, light aircraft designed and constructed by the Italian aircraft manufacturer Tecnam. Introduced during the early 2000s, the aircraft quickly became a staple of the company's product lineup, comprising 70 per cent of its available production capacity during some years.

On April 4, 1955, a United Air Lines Douglas DC-6 named Mainliner Idaho crashed shortly after taking off from Long Island MacArthur Airport, in Ronkonkoma, Islip, New York, United States.

Many variations of aircraft engine starting have been used since the Wright brothers made their first powered flight in 1903. The methods used have been designed for weight saving, simplicity of operation and reliability. Early piston engines were started by hand. Geared hand starting, electrical and cartridge-operated systems for larger engines were developed between the First and Second World Wars.

On 27 January 2001, an Antonov An-70 prototype crashed close to Omsk Tsentralny Airport, Russia during testing of the aircraft. All 33 passengers and crew on board the aircraft survived.


















