
In chemistry, pyrophosphates are phosphorus oxyanions that contain two phosphorus atoms in a P–O–P linkage. A number of pyrophosphate salts exist, such as disodium pyrophosphate (Na2H2P2O7) and tetrasodium pyrophosphate (Na4P2O7), among others. Often pyrophosphates are called diphosphates. The parent pyrophosphates are derived from partial or complete neutralization of pyrophosphoric acid. The pyrophosphate bond is also sometimes referred to as a phosphoanhydride bond, a naming convention which emphasizes the loss of water that occurs when two phosphates form a new P–O–P bond, and which mirrors the nomenclature for anhydrides of carboxylic acids. Pyrophosphates are found in ATP and other nucleotide triphosphates, which are important in biochemistry. The term pyrophosphate is also the name of esters formed by the condensation of a phosphorylated biological compound with inorganic phosphate, as for dimethylallyl pyrophosphate. This bond is also referred to as a high-energy phosphate bond.
In enzymology, an ATP diphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.8) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a bis(5'-adenosyl)-triphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.29) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a bis(5'-nucleosyl)-tetraphosphatase (asymmetrical) (EC 3.6.1.17) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a dCTP diphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.12) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In Enzymology, a dUTP diphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.23) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a guanosine-5'-triphosphate,3'-diphosphate diphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.40) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a nucleoside-diphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a nucleoside-triphosphatase(NTPase) (EC 3.6.1.15) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Thiamine-triphosphatase is an enzyme involved in thiamine metabolism. It catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a triphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.25) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme polynucleotide 5′-phosphatase (RNA 5′-triphosphatase, RTPase, EC 3.1.3.33) is an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction
In enzymology, a dTDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-D-glucose transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a dTDP-4-amino-4,6-dideoxygalactose transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a galactose-1-phosphate thymidylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a glucose-1-phosphate thymidylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a thiamine-diphosphate kinase is an enzyme involved in thiamine metabolism. It catalyzes the chemical reaction
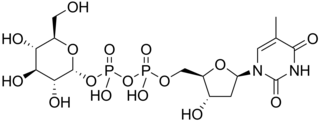
Thymidine diphosphate glucose is a nucleotide-linked sugar consisting of deoxythymidine diphosphate linked to glucose. It is the starting compound for the syntheses of many deoxysugars.
Thymidylate kinase catalyzes the phosphorylation of thymidine 5'-monophosphate (dTMP) to form thymidine 5'-diphosphate (dTDP) in the presence of ATP and magnesium:

5',3'-nucleotidase, mitochondrial, also known as 5'(3')-deoxyribonucleotidase, mitochondrial (mdN) or deoxy-5'-nucleotidase 2 (dNT-2), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NT5M gene. This gene encodes a 5' nucleotidase that localizes to the mitochondrial matrix. This enzyme dephosphorylates the 5'- and 2'(3')-phosphates of uracil and thymine deoxyribonucleotides. The gene is located within the Smith–Magenis syndrome region on chromosome 17.







