
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it flows generally south for 2,340 miles (3,770 km) to the Mississippi River Delta in the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains all or parts of 32 U.S. states and two Canadian provinces between the Rocky and Appalachian mountains. The main stem is entirely within the United States; the total drainage basin is 1,151,000 sq mi (2,980,000 km2), of which only about one percent is in Canada. The Mississippi ranks as the thirteenth-largest river by discharge in the world. The river either borders or passes through the states of Minnesota, Wisconsin, Iowa, Illinois, Missouri, Kentucky, Tennessee, Arkansas, Mississippi, and Louisiana.

The Rhine is one of the major European rivers. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein, Swiss-Austrian, Swiss-German borders. After that the Rhine defines much of the Franco-German border, after which it flows in a mostly northerly direction through the German Rhineland. Finally in Germany the Rhine turns into a predominantly westerly direction and flows into the Netherlands where it eventually empties into the North Sea.

The Yarra River or historically, the Yarra Yarra River, is a perennial river in south-central Victoria, Australia.

The Humber River is a river in Southern Ontario, Canada. It is in the Great Lakes Basin, is a tributary of Lake Ontario and is one of two major rivers on either side of the city of Toronto, the other being the Don River to the east. It was designated a Canadian Heritage River on September 24, 1999.

The Duchy of Pomerania was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (Griffins). The country had existed in the Middle Ages, in years 1121–1160, 1264–1295, 1478–1531 and 1625–1637.

The Feather River is the principal tributary of the Sacramento River, in the Sacramento Valley of Northern California. The river's main stem is about 73 miles (117 km) long. Its length to its most distant headwater tributary is just over 210 miles (340 km). The main stem Feather River begins in Lake Oroville, where its four long tributary forks join—the South Fork, Middle Fork, North Fork, and West Branch Feather Rivers. These and other tributaries drain part of the northern Sierra Nevada, and the extreme southern Cascades, as well as a small portion of the Sacramento Valley. The total drainage basin is about 6,200 square miles (16,000 km2), with approximately 3,604 square miles (9,330 km2) above Lake Oroville.

The Murg is an 80.2-kilometre-long river and a right tributary of the Rhine in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It flows through the Northern Black Forest into the Upper Rhine Plain, crossing the counties of Freudenstadt and Rastatt.

The Berg River is a river located just north of Cape Town in the Western Cape Province of South Africa. It is approximately 294 km (183 mi) long with a catchment area of 7,715 km² (2979 mi²) and debouches into the Atlantic Ocean. About 65% of the Berg River area is under agriculture. The major towns in the Berg River area are Velddrif and Laaiplek near the coast, Piketberg, Hopefield, Moorreesburg and Darling further inland.

The River Crane, a tributary of the River Thames, runs 8.5 miles (13.6 km) in West London, England. It forms the lower course of Yeading Brook. It adjoins or passes through three London boroughs: Hillingdon, Hounslow and Richmond upon Thames, in the historic county of Middlesex. The drainage basin is heavily urbanised but many of the Hayes to Whitton flood-meadows have been conserved, forming a narrow, green vale, opening out to what remains of Hounslow Heath in the centre – a near-continuous belt of semi-natural habitat.

The Murr is a river in Baden-Württemberg, Germany, right tributary of the Neckar. The river gave its name to a small town on its banks, Murr, and to the Rems-Murr-Kreis district, which was also named after the river Rems, which runs roughly parallel to the south of the Murr.

Ueckermünde is a seaport town in northeast Germany, located in the district of Vorpommern-Greifswald, Western Pomerania, near Germany's border with Poland's Police County.

The Wiese is a river, 57.8 kilometres long, and a right-hand tributary of the Rhine in southwest Germany and northwest Switzerland.

The Ammer is a small river in Baden-Württemberg, Germany, a tributary of the Neckar.

The Stryi River starts in the Carpathian mountains in western Ukraine. It snakes through the mountains running for 231 km. After 193 km it passes Stryi. The river continues for another 32 km before joining the Dniester near Khodoriv.

The Oder is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows 742 kilometres (461 mi) through western Poland, later forming 187 kilometres (116 mi) of the border between Poland and Germany as part of the Oder–Neisse line. The river ultimately flows into the Szczecin Lagoon north of Szczecin and then into three branches that empty into the Bay of Pomerania of the Baltic Sea.

The River Foulness is a river in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England. Its name is derived from Old English fūle[n] ēa, meaning “dirty water”. Maintenance responsibilities for the river transferred from the Environment Agency to the Market Weighton Drainage Board on 1 October 2011. Market Weighton Drainage Board subsequently amalgamated with the Lower Ouse Internal Drainage Board on 1 April 2012 to create the Ouse and Humber Drainage Board. The river discharges into the Humber Estuary via Market Weighton Canal. Water levels within the river, its tributaries and the canal are managed and controlled by the Environment Agency. The river lies in an area known as the Humberhead Levels.
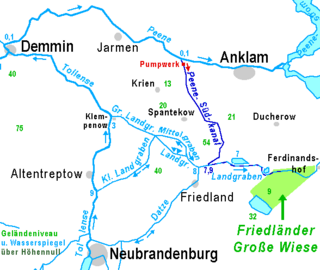
Landgraben is a river of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It forms a pseudobifurcation: its water west of Friedland flows towards the Großer Landgraben and the Tollense, and its water east of Friedland flows towards the Zarow, which flows into the Szczecin Lagoon. Its main tributary is the northflowing bifurcation of the Datze River, almost in the middle of its bed. The meaning of Landgraben is something like "Border Canal". For several centuries it was part of the border between Mecklenburg and Pomerania. The Landgraben drains one of the broad glacial valleys of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. In these valleys, there is no strict discrimination between natural and artificial courses of water.
Beginning in the 12th century, on the initiative of monasteries, as well as the local nobility, German settlers began migrating to Pomerania in a process later termed the Ostsiedlung. The local nobles and rulers encouraged the settlement in order to strengthen and consolidate their position and to develop and intensify land use, while the settlers were attracted by the privileges that were granted to them.

The Palatine Watershed forms the main drainage divide in the Palatinate between the Upper Rhine and the Middle Rhine, the two successive sections of the river Rhine that flow through the German state of Rhineland-Palatinate.

Nayar River is a perennial, non-glacial river in the North Indian state of Uttarakhand. The river system is one of the largest non-glacial perennial rivers in the state, second only to Ramganga (West) and flows entirely in the district of Pauri Garhwal. The two main branches of the river, Nayar East and Nayar West along with Ramganga river, rise in the dense forests and high meadows of Dudhatoli and merge to form Nayar roughly one kilometre ahead of Satpuli. Satpuli is a town on the left bank of Nayar East river.




















